In essence, the safety and usability of a modern tube furnace are defined by three core principles: robust thermal containment, precise process control, and atmospheric integrity. These systems are engineered with features that protect the operator from extreme heat while providing the highly controlled, repeatable environment necessary for advanced material processing.
The critical insight is that safety and usability in a tube furnace are not separate goals; they are intertwined. Features that provide greater control over the process, such as programmable temperature zones and automated gas flow, inherently reduce the risk of human error and equipment failure, leading to safer and more reliable outcomes.
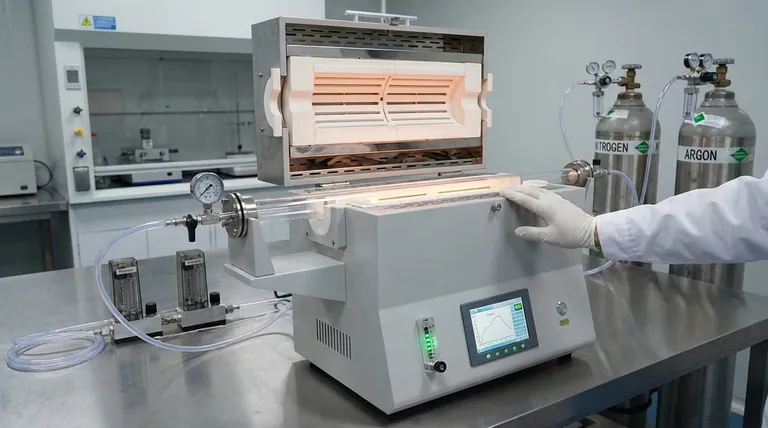

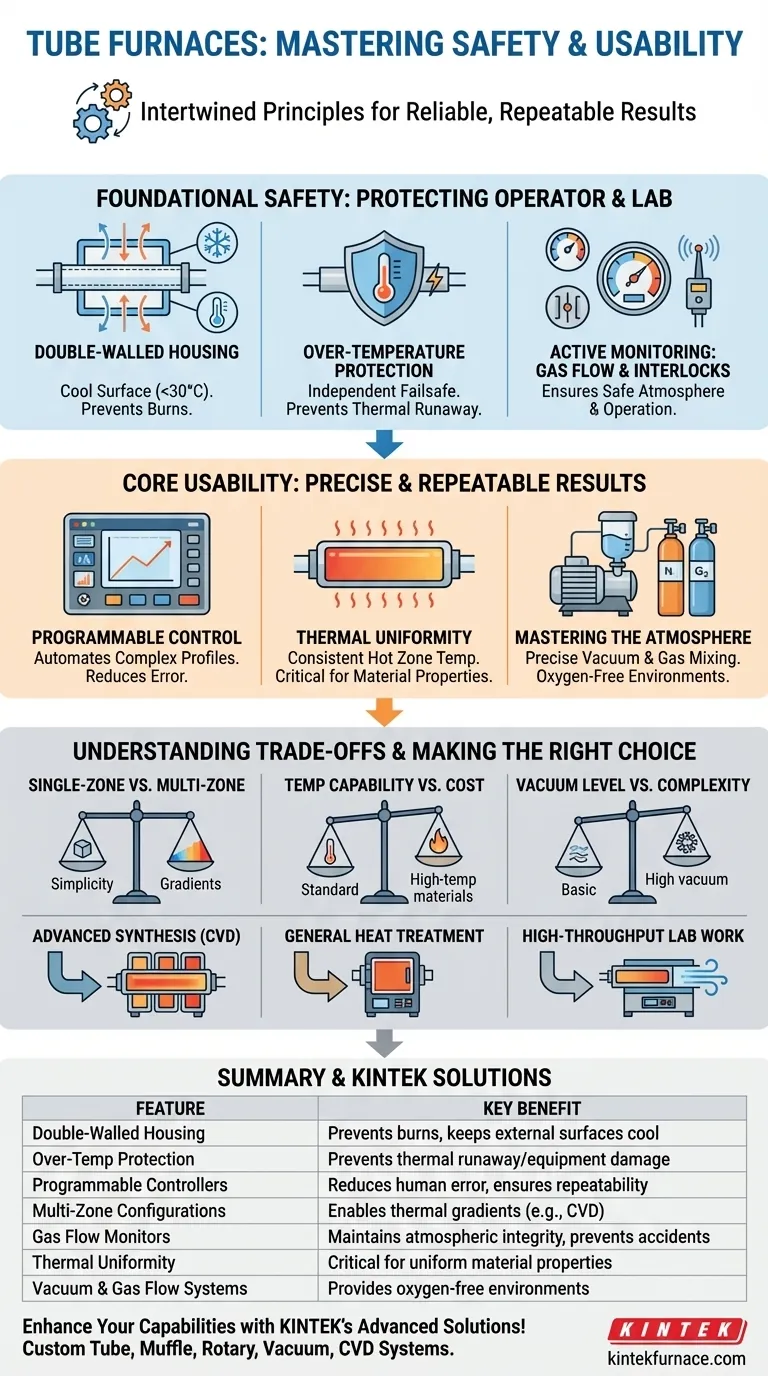
Foundational Safety: Protecting the Operator and the Lab
The primary safety objective of a tube furnace is to contain extreme heat, ensuring the laboratory and its personnel are protected from temperatures that can exceed 1700°C.
Thermal Containment with Double-Walled Housing
Nearly all modern tube furnaces use a double-walled housing design. This creates an air gap between the internal heating chamber and the external casing.
This simple but effective feature allows for active or passive air cooling, keeping the outer surface temperature remarkably low—often around 30°C—even when the internal temperature is at 800°C or higher. This dramatically reduces the risk of accidental burns.
Automated Failsafes: Over-Temperature Protection
Over-temperature protection is a critical, non-negotiable safety feature. It is an independent control circuit that automatically shuts off power to the heating elements if the furnace exceeds a user-defined maximum temperature.
This failsafe protects not only the sample and the furnace itself from catastrophic failure but also prevents a thermal runaway event in the lab.
Active Monitoring: Gas Flow and System Interlocks
For processes requiring specific atmospheres, gas flow monitors ensure the correct gases are being delivered at the correct rates. This can prevent the accidental introduction of oxygen to a sensitive or flammable process.
Safety interlocks are also common, preventing the system from operating under unsafe conditions, such as a misaligned component or a critical sensor failure.
Core Usability: Achieving Precise and Repeatable Results
Usability in a tube furnace is measured by its ability to execute a process with precision and repeatability. This is achieved through sophisticated control over temperature and atmosphere.
The Power of Programmable Control
Modern furnaces use programmable digital controllers that allow users to define complex heating and cooling profiles. This automates the process, reducing manual oversight and human error.
For longer furnaces, multi-zone configurations with up to three independent controllers are available. This enables the user to create precise temperature gradients along the length of the tube, which is essential for specialized processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
A key performance metric is thermal uniformity, or the consistency of temperature across the central "hot zone." High-quality insulation and well-designed heating elements ensure that the entire sample experiences the same thermal conditions.
This uniformity is critical for applications like annealing, where even small temperature deviations can lead to inconsistent material properties.
Mastering the Atmosphere
Many processes require an oxygen-free environment. Tube furnaces achieve this through integrated vacuum and gas flow systems. A vacuum pump first removes ambient air from the sealed process tube.
Afterward, a precise flow of an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is introduced. Features like sealed end caps and gas mixing systems give the user complete control over the exact composition of the atmosphere inside the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While rich in features, tube furnaces require careful selection based on specific needs. Understanding the trade-offs between different configurations is key to making a cost-effective decision.
Single-Zone vs. Multi-Zone Furnaces
A single-zone furnace is simpler, less expensive, and perfectly adequate for basic heat treatments requiring a uniform hot zone.
A multi-zone furnace offers superior temperature uniformity and the ability to create thermal gradients, but at a higher cost and complexity. It is necessary for sensitive deposition processes but may be overkill for simple annealing.
Temperature Capability vs. Cost
The maximum operating temperature is dictated by the material of the heating elements. Furnaces operating up to 1200°C often use more affordable elements.
Reaching temperatures of 1700°C or 1800°C requires advanced, expensive materials for the elements and insulation, significantly increasing the furnace's cost.
Vacuum Level vs. System Complexity
Achieving a basic vacuum to purge air is relatively simple. However, reaching a high vacuum (e.g., 10⁻⁵ torr) requires a more complex and costly multi-stage pumping system, which may not be necessary for all atmosphere-controlled applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a tube furnace involves matching its features to your primary experimental or production goal.
- If your primary focus is advanced material synthesis (like CVD): Prioritize a multi-zone furnace with precise gas mixing capabilities and software for data logging.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment or annealing: A robust single-zone furnace with reliable over-temperature protection is likely the most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput lab work: Features like a sliding design for rapid cooling and programmable controls will significantly improve your efficiency.
Ultimately, a thorough understanding of these safety and usability features empowers you to select an instrument that is not only safe but perfectly suited to your technical objectives.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Double-Walled Housing | Creates an air gap for cooling | Prevents burns, keeps external surfaces cool |
| Over-Temperature Protection | Independent circuit shuts off power | Prevents thermal runaway and equipment damage |
| Programmable Digital Controllers | Allows complex heating/cooling profiles | Reduces human error, ensures repeatability |
| Multi-Zone Configurations | Independent temperature control along tube | Enables thermal gradients for processes like CVD |
| Gas Flow Monitors | Ensures correct gas delivery rates | Maintains atmospheric integrity, prevents accidents |
| Thermal Uniformity | Consistent temperature in hot zone | Critical for uniform material properties |
| Vacuum and Gas Flow Systems | Removes air, introduces inert gases | Provides oxygen-free environments for sensitive processes |
Enhance your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced tube furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnaces, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for safety, usability, and performance. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your material processing and drive innovation in your work!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















