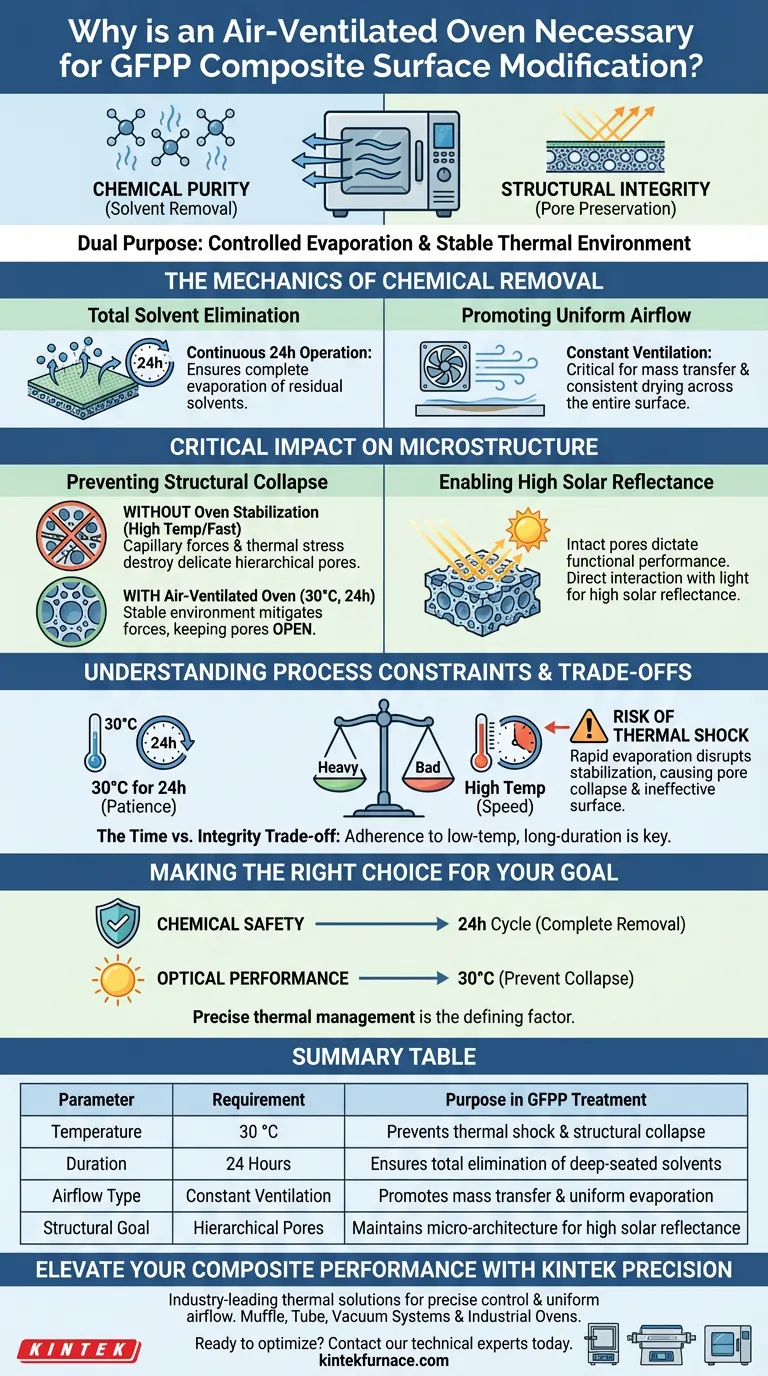
An industrial air-ventilated oven is indispensable for the post-treatment phase of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene (GFPP) composites because it guarantees both chemical purity and structural integrity. It serves a dual purpose: ensuring the absolute removal of residual solvents following surface modification and providing a stable thermal environment to preserve the material's microscopic architecture.
The air-ventilated oven provides a controlled evaporation process rather than simple drying. This stability is the key to locking in high solar reflectance properties by preventing the collapse of delicate hierarchical pore structures.

The Mechanics of Chemical Removal
Achieving Total Solvent Elimination
The primary logistical function of the oven is to drive out volatile chemicals used during the treatment phase.
By operating continuously for 24 hours, the oven ensures that residual solvents trapped deep within the composite sheets are completely evaporated.
Promoting Uniform Airflow
The "air-ventilated" aspect of the equipment is critical for mass transfer.
Constant airflow prevents the saturation of the air immediately surrounding the sample, allowing for consistent evaporation rates across the entire surface of the GFPP sheets.
Critical Impact on Microstructure
Preventing Structural Collapse
The most technically significant role of the oven is protecting the physical structure of the modified surface.
During evaporation, capillary forces and thermal stress can easily destroy the delicate hierarchical pore structures formed during treatment.
The oven provides a stable environment that mitigates these forces, ensuring the pores remain open and intact.
Enabling High Solar Reflectance
The preservation of these pore structures is not merely cosmetic; it dictates the functional performance of the material.
These hierarchical pores are the mechanism responsible for interacting with light.
By preventing pore collapse, the oven treatment directly enables the formation of high solar reflectance properties in the final composite.
Understanding Process Constraints and Trade-offs
The Time vs. Integrity Trade-off
Operators often face pressure to accelerate manufacturing timelines, but this process requires patience.
The reference protocol dictates a specific regimen: 30 °C for 24 hours.
Attempting to speed up this process by increasing the temperature is a common pitfall that yields immediate negative results.
The Risk of Thermal Shock
Introducing higher temperatures to reduce drying time disrupts the stabilization process.
Rapid evaporation or thermal shock will likely cause the pore structures to collapse, rendering the surface modification ineffective regarding solar reflectance.
Adhering to the low-temperature (30 °C), long-duration cycle is the only way to balance drying needs with structural preservation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your GFPP composites perform as intended, you must strictly adhere to the drying parameters.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Safety: Ensure the cycle runs the full 24 hours to guarantee the complete removal of all residual solvents from the sheets.
- If your primary focus is Optical Performance: Strictly maintain the temperature at 30 °C to prevent pore collapse and maximize solar reflectance.
Precise thermal management is not a formality; it is the defining factor in stabilizing the material's functional properties.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Requirement | Purpose in GFPP Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 30 °C | Prevents thermal shock and structural collapse of pores |
| Duration | 24 Hours | Ensures total elimination of deep-seated residual solvents |
| Airflow Type | Constant Ventilation | Promotes mass transfer and uniform evaporation rates |
| Structural Goal | Hierarchical Pores | Maintains micro-architecture for high solar reflectance |
Elevate Your Composite Performance with KINTEK Precision
Don't let improper thermal stabilization ruin your GFPP surface modification. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions backed by expert R&D and manufacturing. From customizable Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum systems to specialized industrial ovens, our equipment ensures the precise temperature control and uniform airflow needed to preserve delicate hierarchical structures.
Ready to optimize your material properties? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temp furnace or oven tailored to your unique lab and manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polypropylene Composites with High Solar Reflectance for Thermal Insulation Applications. DOI: 10.3390/polym17030274
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is the drying step using an industrial electric oven critical in catalyst preparation? Ensure Structural Integrity
- What role does a high-temperature sintering furnace play in lead-free piezoelectric ceramics? Optimizing Performance
- How does metallic magnesium facilitate deep purification of molten chloride salts at 800 °C? Achieve Ultra-High Purity
- Why are batch furnaces considered essential for certain applications? Achieve Precision and Flexibility in Heat Treatment
- What are the core technical advantages of an industrial microwave sintering system? Gain Speed and Material Integrity
- What is the primary purpose of high-temperature pyrolysis? Unlock Superior PFAS Removal with Enhanced Hydrophobicity
- Why is zone refining essential for alkali halide crystals? Achieve Pure Intrinsic Luminescence Data
- What role does the vitreous carbon foam framework play in PTTM? Unlock Biomimetic Dental Implant Precision



















