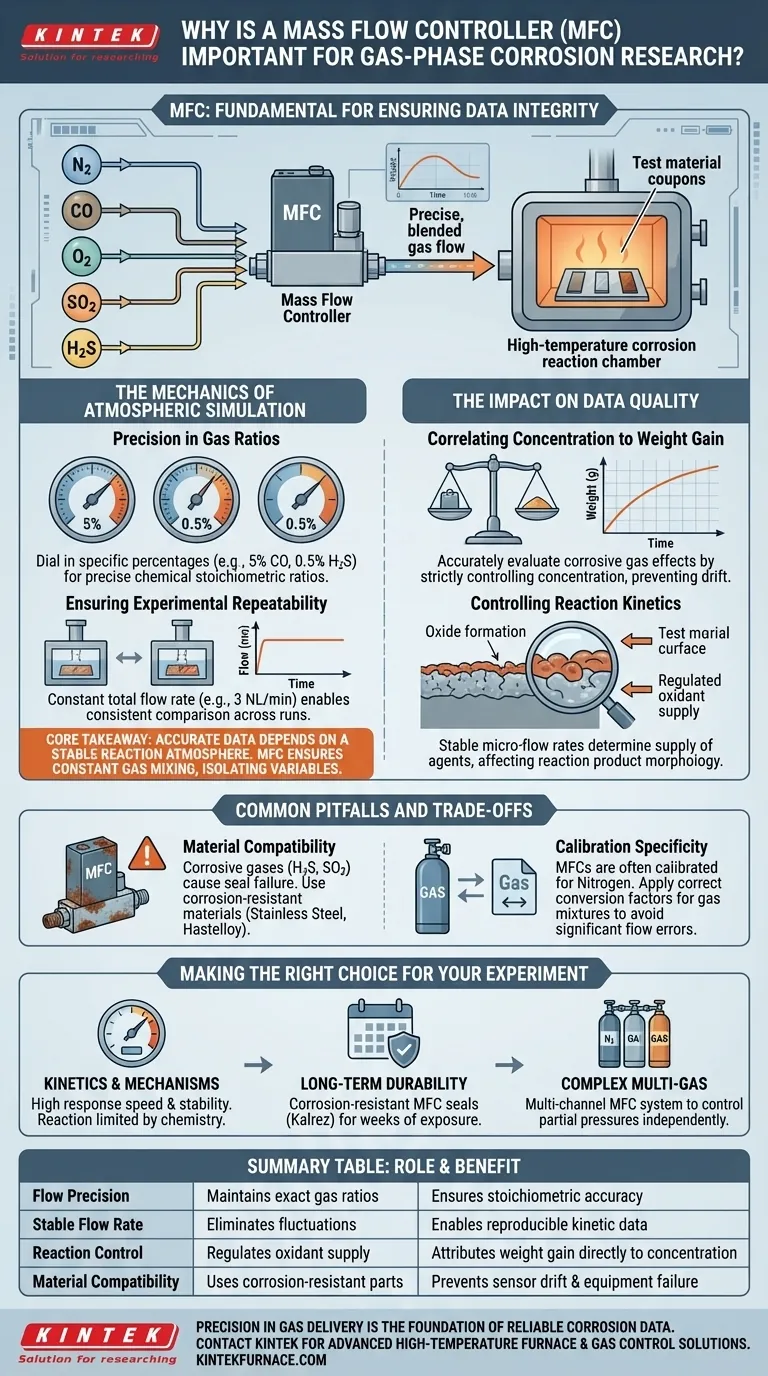
A Mass Flow Controller (MFC) is the fundamental instrument for ensuring data integrity in gas-phase corrosion research. It precisely regulates the flow rates of specific gas components—such as Nitrogen ($N_2$), Carbon Monoxide ($CO$), Oxygen ($O_2$), Sulfur Dioxide ($SO_2$), and Hydrogen Sulfide ($H_2S$)—to create a stable, reproducible simulation environment.
Core Takeaway In corrosion research, accurate data depends entirely on a stable reaction atmosphere. An MFC ensures that gas mixing ratios remain constant throughout the experiment, allowing you to isolate variables and attribute material degradation (weight gain) directly to specific gas concentrations rather than environmental fluctuations.

The Mechanics of Atmospheric Simulation
Precision in Gas Ratios
Laboratory simulations require exact mixtures to mimic real-world conditions, such as industrial flues or sour gas environments.
An MFC allows you to dial in specific percentages, for example, maintaining a mixture of exactly 5% $CO$ and 0.5% $H_2S$.
By controlling the input of each component individually, the MFC ensures the final atmosphere inside the reaction chamber adheres to precise chemical stoichiometric ratios.
Ensuring Experimental Repeatability
Corrosion is a kinetic process that evolves over time. If the gas flow fluctuates, the reaction rate changes, rendering the data noisy and unreliable.
MFCs deliver a constant total flow rate (e.g., 3 NL/min). This stability is critical for comparing results across different test runs or different material samples.
Without this regulation, it is impossible to determine if a change in corrosion rate is due to the material's properties or an accidental shift in gas supply.
The Impact on Data Quality
Correlating Concentration to Weight Gain
The primary metric in many corrosion studies is "corrosion weight gain"—the increase in mass as the material reacts with the atmosphere.
To accurately evaluate how a specific corrosive gas affects this weight gain, the concentration of that gas must be strictly controlled.
MFCs prevent "drift" in gas concentration. This ensures that the measured weight gain is a true reflection of the material's reactivity to the set parameters.
Controlling Reaction Kinetics
Just as in crystal growth or synthesis, the rate at which gas molecules are supplied to a surface influences the morphology of the reaction product.
In corrosion, the flow rate determines the supply of oxidants or sulfidizing agents to the metal surface.
Stable micro-flow rates provided by an MFC allow researchers to study the specific mechanisms of oxide or sulfide scale formation without the interference of flow-induced turbulence or starvation.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Material Compatibility
While MFCs control corrosive gases, they are also susceptible to them.
Using a standard MFC for highly corrosive gases like $H_2S$ or $SO_2$ can lead to seal failure or sensor drift within the controller itself. You must ensure the MFC wetted path is constructed from corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., stainless steel or Hastelloy).
Calibration Specificity
An MFC is typically calibrated for a specific gas (often Nitrogen).
When using gas mixtures or different corrosive agents, you must apply the correct conversion factors. Failing to account for the thermal properties of gases like $CO$ or $SO_2$ will result in significant flow rate errors, invalidating your stoichiometric calculations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
If your primary focus is Kinetics and Mechanisms:
- Prioritize an MFC with high response speed and stability to ensure the reaction rate is limited by the chemistry, not the gas supply.
If your primary focus is Long-term Durability Testing:
- Ensure your setup utilizes corrosion-resistant MFC seals (like Kalrez) to maintain accuracy over weeks of exposure to $H_2S$ or $SO_2$.
If your primary focus is Complex Multi-gas Atmospheres:
- Use a multi-channel MFC system to control the partial pressures of individual components ($N_2$, $O_2$, $CO$) independently for precise stoichiometric simulation.
Precision in input equals validity in output. In gas-phase corrosion, the Mass Flow Controller is the gatekeeper of that validity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Corrosion Research | Benefit for Researchers |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Precision | Maintains exact gas mixing ratios (e.g., H2S, CO, SO2) | Ensures chemical stoichiometric accuracy |
| Stable Flow Rate | Eliminates fluctuations in total gas volume | Enables reproducible kinetic data |
| Reaction Control | Regulates oxidant supply to material surfaces | Attributes weight gain directly to gas concentration |
| Material Compatibility | Uses corrosion-resistant wetted parts (Hastelloy/SS) | Prevents sensor drift and equipment failure |
Precision in gas delivery is the foundation of reliable corrosion data. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance lab solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable for your unique research needs. Ensure your atmospheric simulations are stable and reproducible with our advanced high-temperature furnace and gas control technologies. Contact us today to optimize your laboratory setup!
Visual Guide
References
- Yifan Ni, Chenghao Fan. Investigating Fireside Corrosion Behavior and Mechanism of Low-Alloy Water Wall Tube of Ultra-Supercritical Power Plant. DOI: 10.3390/ma18071666
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 304 316 Stainless Steel High Vacuum Ball Stop Valve for Vacuum Systems
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- Ultra High Vacuum CF Flange Stainless Steel Sapphire Glass Observation Sight Window
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does a laboratory blast drying oven perform? Optimize Pretreatment for Magnetic Particles
- Why are ceramic containers with refractory clay seals utilized during the non-oxidative sintering of nickel composites?
- What is the role of vacuum-sealed quartz tubes in Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry
- Why use alumina crucibles for NaNbO3:Pr3+ annealing? Ensure High Purity and Thermal Stability
- Why is a heat-resistant crucible indispensable for magnesium purification? Ensuring Purity and Efficiency in Vacuum Sublimation
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during the SPS of TiB2-SiC? Expert Material Densification Insights
- What are the main types of laboratory furnaces? Find Your Perfect High-Temperature Solution
- What is the technical purpose of double-sealing raw materials in vacuum quartz tubes? Expert Synthesis Guide



















