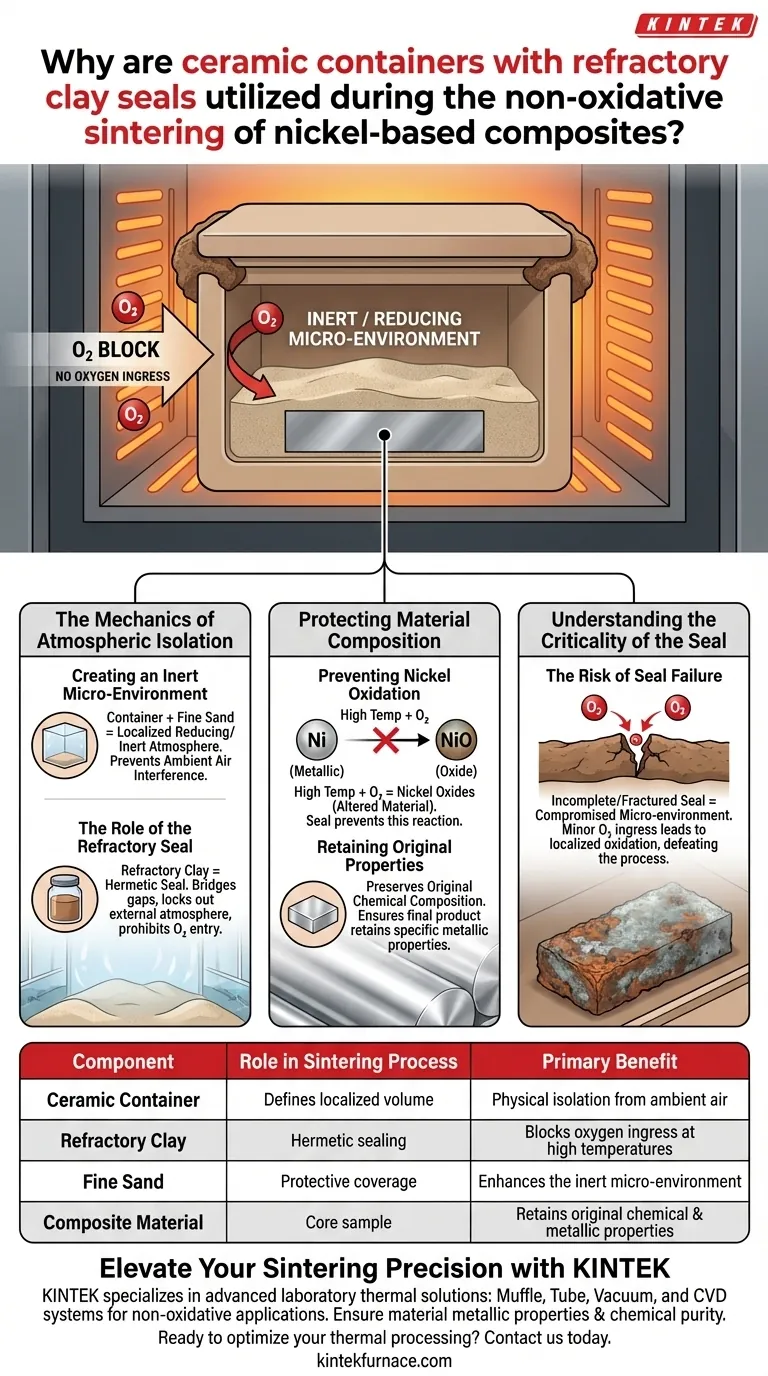
Ceramic containers sealed with refractory clay are critical tools for creating a protective micro-environment. This assembly, often used in conjunction with fine sand coverage, physically isolates the nickel-based composite from the surrounding air. By establishing this barrier, the setup prevents atmospheric oxygen from reaching the material during the high-temperature sintering process.
By excluding oxygen, this configuration maintains a localized reducing or inert atmosphere. This ensures the nickel remains in its metallic state and the composite retains its original chemical composition.

The Mechanics of Atmospheric Isolation
Creating an Inert Micro-Environment
The primary function of the ceramic container is to define a specific volume around the composite materials.
When combined with coverage materials like fine sand, the container fosters a localized atmosphere that is reducing or inert. This separation is essential for processes that must occur without the interference of ambient air.
The Role of the Refractory Seal
Refractory clay serves as the hermetic seal for this isolation system.
It bridges any gaps in the container assembly, effectively locking out the external atmosphere. This seal ensures that atmospheric oxygen is strictly prohibited from entering the sintering zone.
Protecting Material Composition
Preventing Nickel Oxidation
Metallic nickel is highly susceptible to oxidation when exposed to the high temperatures required for sintering.
If oxygen were allowed to contact the heated material, it would react with the nickel to form oxides. This reaction would fundamentally alter the material, stripping it of its metallic characteristics.
Retaining Original Properties
The ultimate goal of using this sealed configuration is to preserve the original chemical composition of the composite.
By successfully blocking oxidation, the process ensures that the final product retains the specific metallic properties intended by the design.
Understanding the Criticality of the Seal
The Risk of Seal Failure
The effectiveness of this entire process relies on the integrity of the refractory clay application.
If the seal is incomplete or fractures, the inert micro-environment will be compromised. Even minor oxygen ingress can lead to localized oxidation, defeating the purpose of the non-oxidative sintering process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the success of your sintering process, consider the following specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Ensure the refractory clay seal is continuous and robust to prevent any interaction with atmospheric oxygen.
- If your primary focus is Material Performance: Rely on this sealed container method to maintain the metallic nickel phase, which is essential for the composite's mechanical properties.
Effective isolation is the single most important factor in preserving the integrity of nickel-based composites at high temperatures.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Sintering Process | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Container | Defines localized volume | Physical isolation from ambient air |
| Refractory Clay | Hermetic sealing | Blocks oxygen ingress at high temperatures |
| Fine Sand | Protective coverage | Enhances the inert micro-environment |
| Composite Material | Core sample | Retains original chemical & metallic properties |
Elevate Your Sintering Precision with KINTEK
Preserving the integrity of nickel-based composites requires more than just high temperatures—it demands total atmospheric control. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory thermal solutions, offering expert-engineered Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for non-oxidative applications.
Whether you need customizable high-temp furnaces or R&D-backed manufacturing support, our team ensures your materials retain their metallic properties and chemical purity.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact us today to discover how KINTEK’s precision equipment can support your unique lab requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- Hermansyah Aziz, Ibrahim k. salman. Effect of Adding Nano Carbon on Density, Porosity, and Water Absorption of Nickel by Powder Metallurgy. DOI: 10.55810/2313-0083.1102
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary functions of multilayer fixtures within a lithium battery vacuum oven? Optimize Your Drying Process
- What are the mechanical and chemical advantages of alumina ceramic tubes? Discover Durability for High-Temp and Corrosive Environments
- Why are micrometer-scale micro-fiber filter candles used to treat condensed flue gases in pyrolysis systems?
- What critical functions do high-purity graphite molds perform? The Engine of SPS for High-Entropy Ceramics
- Why are alumina crucibles used for titanium alkoxide nitridation? Ensure High-Purity Synthesis Results
- What are the advantages of using an infrared thermograph over traditional thermocouples in Plasma Flash Sintering (PFS)?
- What creates the pumping action in a circulating water vacuum pump? Discover the Liquid Ring Mechanism
- What role does a molecular pump set play in an electric current-assisted TLP bonding system? Enhance Vacuum Purity



















