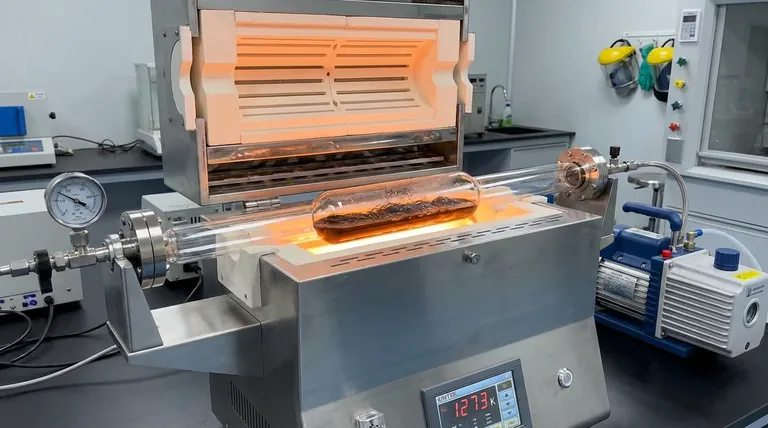
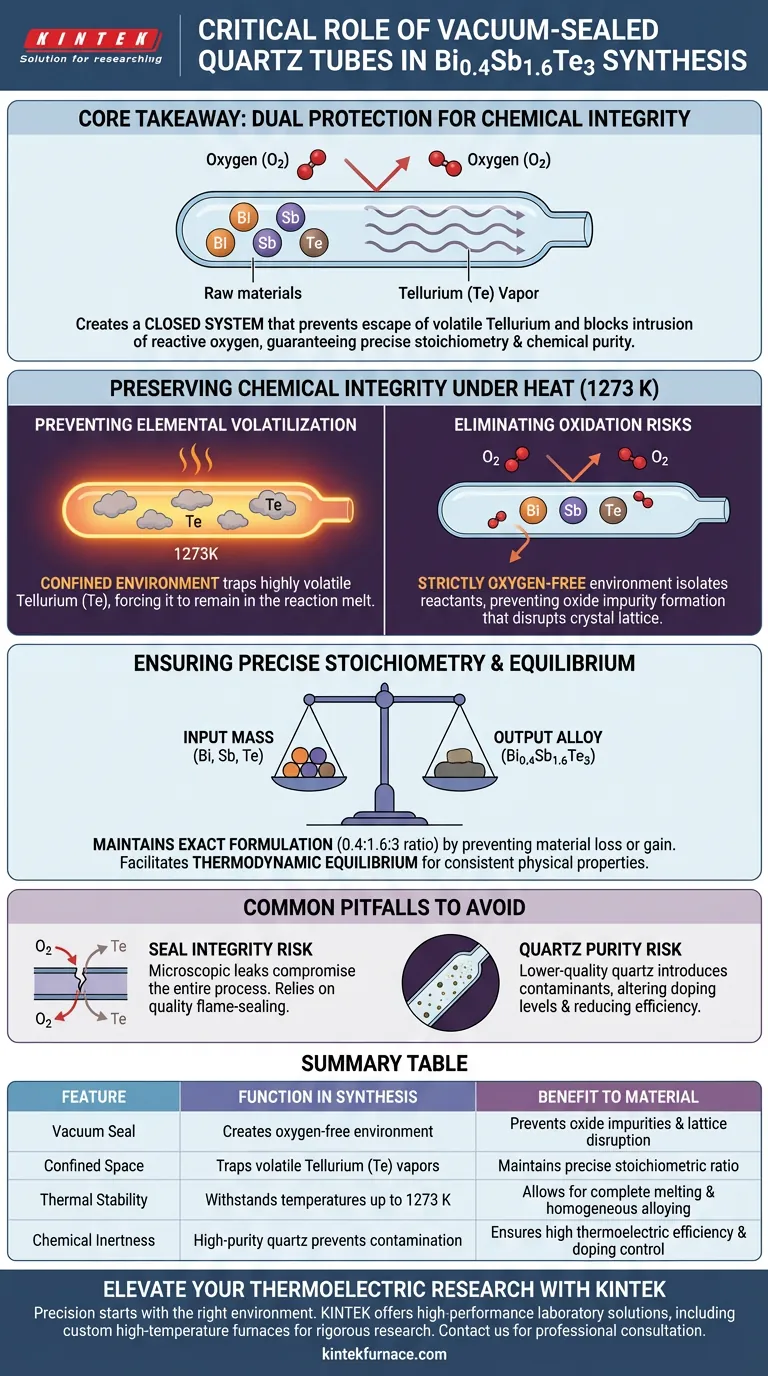
The vacuum-sealed quartz tube acts as the primary control barrier for maintaining chemical integrity during the high-temperature synthesis of Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3. By isolating the raw Bismuth (Bi), Antimony (Sb), and Tellurium (Te) in a strictly oxygen-free environment, the tube allows the materials to be melted at 1273 K without suffering from atmospheric contamination or mass loss.
Core Takeaway The critical function of the quartz tube is to create a closed system that simultaneously prevents the escape of volatile Tellurium and blocks the intrusion of reactive oxygen. This dual protection is the only way to guarantee the precise stoichiometric ratio and chemical purity required for the material to function effectively as a thermoelectric semiconductor.

Preserving Chemical Integrity Under Heat
Preventing Elemental Volatilization
The synthesis of $Bi_{0.4}Sb_{1.6}Te_3$ requires melting raw materials at extremely high temperatures, specifically around 1273 K.
At this thermal extreme, certain elements within the compound, particularly Tellurium (Te), become highly volatile and prone to vaporization.
The vacuum-sealed quartz tube creates a confined environment that traps these vapors. This prevents the Tellurium from escaping the system, forcing it to remain part of the reaction melt.
Eliminating Oxidation Risks
Bismuth, Antimony, and Tellurium are sensitive to air and can easily degrade if exposed to oxygen during heating.
The quartz tube provides a strictly oxygen-free environment, isolating the reactants from the outside atmosphere.
This isolation is critical to prevent the formation of oxide impurities, which would disrupt the crystal lattice and degrade the electronic performance of the final alloy.
Ensuring Precise Stoichiometry
Maintaining the Exact Formulation
Thermoelectric performance is dictated by the exact ratio of elements, known as stoichiometry.
If the volatile Tellurium were allowed to escape, or if oxygen were allowed to react with the Bismuth, the final ratio would drift away from the intended $Bi_{0.4}Sb_{1.6}Te_3$ formula.
The sealed environment ensures that the input mass matches the output mass, guaranteeing the resulting alloy has the correct chemical composition.
Establishing Thermodynamic Equilibrium
Beyond simple protection, the stable environment allows for long-duration processing.
The isolation provided by the quartz tube enables the material to undergo high-temperature annealing without degradation.
This facilitates the formation of a homogeneous alloy that represents the true thermodynamic equilibrium state of the material, which is essential for consistent physical properties.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of Seal Integrity
While the quartz tube is robust, the vacuum seal acts as a single point of failure.
Even a microscopic leak can introduce enough oxygen to oxidize the surface of the melt or allow Tellurium vapor to leak out.
Therefore, the effectiveness of this method is entirely dependent on the quality of the flame-sealing process and the initial vacuum pressure applied.
Quartz Purity and Inertness
Not all quartz tubes are created equal; the tube itself must be chemically inert relative to the melt.
High-purity fused quartz is required to ensure that impurities from the container do not infiltrate the reaction.
Lower-quality quartz could introduce contaminants that alter the doping levels of the semiconductor, negatively impacting its thermoelectric efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To achieve high-performance thermoelectric materials, you must treat the quartz tube as an active component of your synthesis protocol.
- If your primary focus is Compositional Accuracy: Prioritize a robust seal to prevent the volatilization of Tellurium, as even slight losses will alter the $Bi_{0.4}Sb_{1.6}Te_3$ ratio.
- If your primary focus is High Phase Purity: Ensure the initial vacuum environment is absolute (oxygen-free) to completely eliminate the risk of oxide formation during the 1273 K melt.
The quartz tube is not merely a container; it is the fundamental tool that stabilizes the physics of the reaction.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 Synthesis | Benefit to Material |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Seal | Creates an oxygen-free environment | Prevents oxide impurities and lattice disruption |
| Confined Space | Traps volatile Tellurium (Te) vapors | Maintains precise stoichiometric ratio (0.4:1.6:3) |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands temperatures up to 1273 K | Allows for complete melting and homogeneous alloying |
| Chemical Inertness | High-purity quartz prevents contamination | Ensures high thermoelectric efficiency and doping control |
Elevate Your Thermoelectric Research with KINTEK
Precision in material synthesis starts with the right environment. KINTEK provides high-performance laboratory solutions—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—specifically designed to meet the rigorous demands of thermoelectric research.
Whether you are synthesizing Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 or developing next-generation alloys, our expert R&D and manufacturing team offers customizable high-temperature furnaces to ensure absolute chemical integrity and process repeatability.
Ready to achieve superior phase purity?
Contact KINTEK Today for a Professional Consultation
Visual Guide
References
- Xian Yi Tan, Qingyu Yan. Synergistic Combination of Sb <sub>2</sub> Si <sub>2</sub> Te <sub>6</sub> Additives for Enhanced Average ZT and Single‐Leg Device Efficiency of Bi <sub>0.4</sub> Sb <sub>1.6</sub> Te <sub>3</sub> ‐based Composites. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202400870
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of high-purity alumina crucibles in NRBBO:Eu2+ sintering? Ensure Pure Phosphor Synthesis
- Why are high-purity alumina grinding balls used for Al2O3/TiC milling? Master Chemical Consistency
- What are the advantages of using high-purity alumina crucibles? Achieve Precise Cast Iron Phase Equilibrium Data
- What functions does a high-density graphite crucible perform? More Than a Container for Copper Refining
- What is the necessity of quartz vacuum sealing for BiCuSeO? Protect Phase Purity and Prevent Selenium Volatilization
- Why are alumina boats used for Bi2Se3 deposition? Ensure High-Purity Synthesis for Topological Insulators
- How do quartz crucibles and quartz cover plates protect the substrate? Optimize TiO2 Nanowire Growth
- How many taps does the water circulating vacuum pump have? Choose the Right Model for Your Lab



















