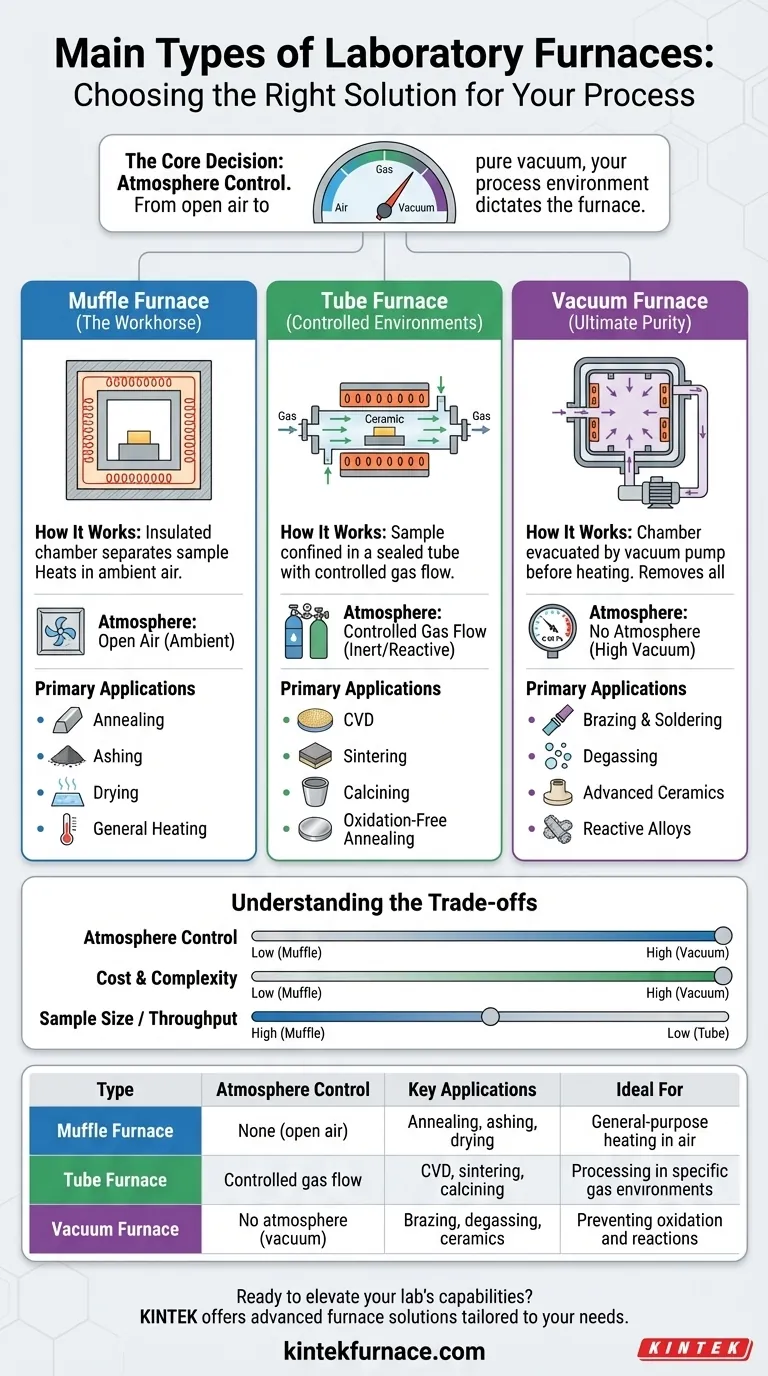
When selecting a laboratory furnace, the decision hinges on much more than just temperature. The primary types are muffle furnaces, tube furnaces, and vacuum furnaces. Each is fundamentally defined by its ability to control the atmosphere surrounding the sample, which is often the most critical variable in a high-temperature process.
The core decision in choosing a furnace is not simply about heat, but about atmosphere control. Your choice between a muffle, tube, or vacuum furnace depends entirely on whether your process can occur in open air, requires a specific gas, or must be free of any reactive gases like oxygen.

The Workhorse: Muffle Furnaces
What They Are
A muffle furnace is the most common type of laboratory furnace. It heats a sample in an insulated chamber, using heating elements to generate radiant heat.
Think of it as a highly precise, high-temperature oven. The term "muffle" refers to the insulated chamber that separates the sample from the direct heat of the elements, ensuring uniform temperature.
Primary Applications
Muffle furnaces are ideal for general-purpose heating processes where the sample can be exposed to ambient air. Common applications include annealing metals to improve ductility, ashing organic materials, drying, and general materials testing.
They are also used for applications like fusing glass, creating enamel coatings, and curing polymers where a standard air atmosphere is acceptable or desired.
For Controlled Environments: Tube Furnaces
How They Work
A tube furnace confines the sample within a cylindrical tube, typically made of ceramic, quartz, or a metal alloy. Heating elements surround this tube, heating the sample contained inside.
The key advantage is that the sealed tube allows you to purge the air and introduce a precisely controlled flow of inert or reactive gases. The atmosphere becomes a controlled variable in your experiment.
Primary Applications
Tube furnaces are essential for any process that cannot be exposed to oxygen or requires a specific gas environment. This includes chemical vapor deposition (CVD), sintering, calcining, and specific types of annealing where oxidation must be prevented.
Common Configurations
Tube furnaces come in several orientations. Horizontal furnaces are the most common for general use. Vertical furnaces are better for processes involving powders or melts where gravity is a factor, such as thermal decomposition or certain crystal growth methods.
For Ultimate Purity: Vacuum Furnaces
How They Work
A vacuum furnace is a highly specialized system that first removes the atmosphere from a sealed chamber using a vacuum pump. Once the desired vacuum level is reached, the heating cycle begins.
This process removes virtually all oxygen and other atmospheric gases, creating the purest possible environment for heating a material.
Primary Applications
Vacuum furnaces are used for the most sensitive applications where any atmospheric reaction would be catastrophic. This includes brazing and soldering of reactive metals, degassing components for ultra-high vacuum systems, and processing advanced ceramics and alloys that cannot tolerate any oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Atmosphere Control vs. Simplicity
A muffle furnace is the simplest to operate but offers zero atmosphere control. A tube furnace adds the complexity of gas handling systems but provides full control. A vacuum furnace offers the highest purity but requires complex vacuum pumps and controls.
Cost and Complexity
Cost directly correlates with atmosphere control. Muffle furnaces are the most affordable and straightforward. Tube furnaces represent a mid-range investment, while vacuum furnaces are the most complex and expensive due to their sophisticated pumping and sealing systems.
Sample Size and Throughput
Muffle furnaces often come in larger "box" or "cabinet" configurations, allowing for larger samples or batch processing. Tube furnaces, by their nature, restrict sample geometry and size to what can fit inside the process tube, limiting throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace begins with a clear understanding of your process requirements, particularly regarding the atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating in air: A muffle furnace is the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is processing samples in a specific gas environment: A tube furnace is the necessary tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is preventing any oxidation or atmospheric reaction: A vacuum furnace is the only choice to ensure absolute purity.
Choosing the right furnace is about matching the tool's capabilities to the non-negotiable requirements of your work.
Summary Table:
| Type | Atmosphere Control | Key Applications | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | None (open air) | Annealing, ashing, drying | General-purpose heating in air |
| Tube Furnace | Controlled gas flow | CVD, sintering, calcining | Processing in specific gas environments |
| Vacuum Furnace | No atmosphere (vacuum) | Brazing, degassing, ceramics | Preventing oxidation and reactions |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials science, chemistry, or engineering, we can help you achieve precise atmosphere control and superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research and development goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production



















