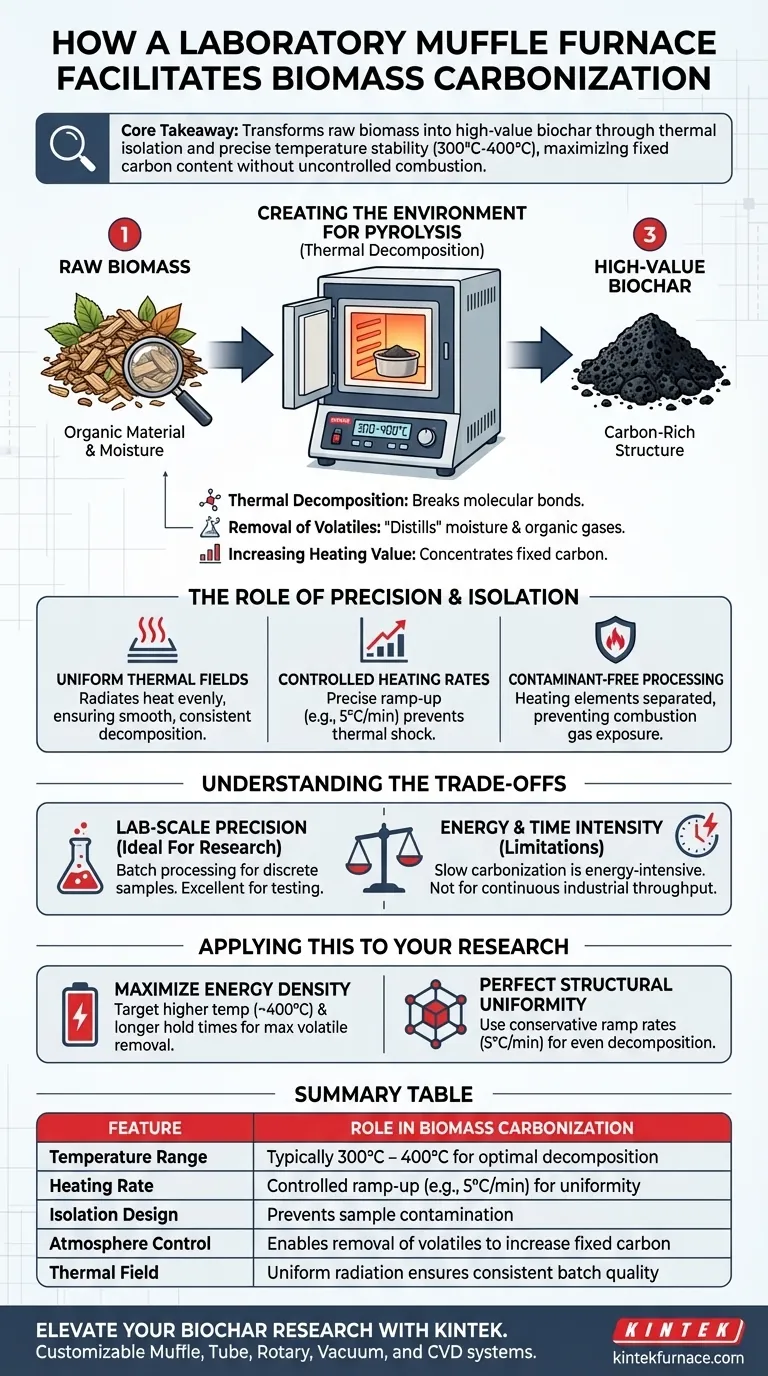
A laboratory muffle furnace facilitates biomass carbonization by creating a strictly controlled, high-temperature environment essential for thermal decomposition. By maintaining precise temperatures—typically between 300°C and 400°C—the furnace breaks molecular bonds within raw biomass, drives off moisture, and evaporates organic volatiles to produce carbon-rich biochar.
Core Takeaway To transform raw biomass into high-value biochar, you must apply heat without uncontrolled combustion. A muffle furnace provides the thermal isolation and precise temperature stability required to maximize fixed carbon content and heating value while ensuring a uniform resulting structure.

Creating the Environment for Pyrolysis
To understand how the furnace aids carbonization, you must look at the specific physical changes it forces the biomass to undergo.
Thermal Decomposition
The primary function of the furnace is to initiate thermal decomposition. By heating dried biomass to a specific range (300°C to 400°C), the furnace provides the energy required to shatter the chemical bonds holding the organic material together.
Removal of Volatiles
As the temperature rises, the furnace facilitates the evaporation of moisture and organic volatiles. This effectively "distills" the raw material, stripping away non-carbon elements and leaving behind a concentrated carbon structure.
Increasing Heating Value
The result of this strictly controlled heating is a significant shift in the material's properties. The process concentrates the fixed carbon content, which directly increases the overall heating value of the resulting biochar compared to the raw biomass.
The Role of Precision and Isolation
The "muffle" design is not merely a heating element; it is an isolation tool that ensures the quality of the carbonization.
Uniform Thermal Fields
A muffle furnace is designed to provide a uniform thermal field. Unlike direct flame heating, the muffle radiates heat evenly from the walls into the insulated chamber, ensuring that the biomass decomposes smoothly and results in a structurally uniform carbon precursor.
Controlled Heating Rates
Successful carbonization often relies on a slow, stable heating rate, such as 5°C per minute. The digital control systems in these furnaces allow you to regulate this ramp-up precisely, preventing thermal shock or uneven carbonization that can occur with rapid temperature spikes.
Contaminant-Free Processing
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is that the heating elements are separated from the sample chamber. This ensures the biomass is not exposed to combustion gases or direct contact with electrical elements, providing a clean environment where the chemistry is driven solely by heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While a muffle furnace is ideal for laboratory-scale precision, there are inherent limitations you should recognize.
Batch Processing Limitations
These furnaces are typically designed for batch processing, meaning they handle discrete, often small, sample sizes. They are excellent for research and testing but do not offer the continuous throughput required for industrial-scale production.
Energy and Time Intensity
Achieving the precise "slow carbonization" necessary for high fixed carbon content is energy-intensive. The requirement to maintain stable temperatures over extended periods means the process cannot be rushed without sacrificing the structural integrity or caloric value of the biochar.
Applying This to Your Research
To get the most out of your muffle furnace for carbonization, align your settings with your specific experimental goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy density: Prioritize the upper end of the temperature range (near 400°C) and longer hold times to ensure maximum removal of volatiles and the highest possible fixed carbon content.
- If your primary focus is structural uniformity: Set a conservative heating ramp rate (e.g., 5°C/min) to ensure the decomposition happens evenly throughout the sample, preventing cracking or uneven porosity.
By leveraging the precise temperature control and isolation of a muffle furnace, you turn variable raw biomass into a consistent, high-energy carbon resource.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Biomass Carbonization |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Typically 300°C - 400°C for optimal decomposition |
| Heating Rate | Controlled ramp-up (e.g., 5°C/min) for structural uniformity |
| Isolation Design | Prevents sample contamination from heating elements/gases |
| Atmosphere Control | Enables removal of volatiles to increase fixed carbon content |
| Thermal Field | Uniform radiation ensures consistent batch quality |
Elevate Your Biochar Research with KINTEK
Precise carbonization requires absolute control over thermal fields and heating rates. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all of which are fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory needs.
Whether you are maximizing fixed carbon content or perfecting structural porosity, our high-temperature furnaces provide the stability and isolation necessary for world-class results. Contact us today to find the perfect thermal solution for your research!
Visual Guide
References
- Mersi Suriani Sinaga, Dadi Oslar Sitinjak. Quality Analysis of Biobriquettes Combination Ratio of Oil palm Frond and Water Hyacinth Waste with Durian Seed Flour Adhesive. DOI: 10.9767/jcerp.20407
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do electrical muffle furnaces work? Unlock Precision Heating for Your Lab
- What is a box type resistance furnace and what is it used for? Discover Precision Heating Solutions
- What are the common heating elements used in muffle furnaces and their corresponding temperature ranges? Choose the Right Element for Your Lab
- How does a muffle furnace support controlled atmosphere operations? Ensure Purity and Precision in Your Lab
- What makes muffle furnaces particularly useful for sensitive materials? Ensure Precision, Purity & Protection
- Why is a commercial high-temperature furnace required for TL material pretreatment? Ensure Accurate Dosimetry
- What role does a laboratory muffle furnace play in the industrial analysis of plastic waste? Optimizing Pyrolysis Yield
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature box resistance furnace in HA synthesis? Optimize Your Calcination.



















