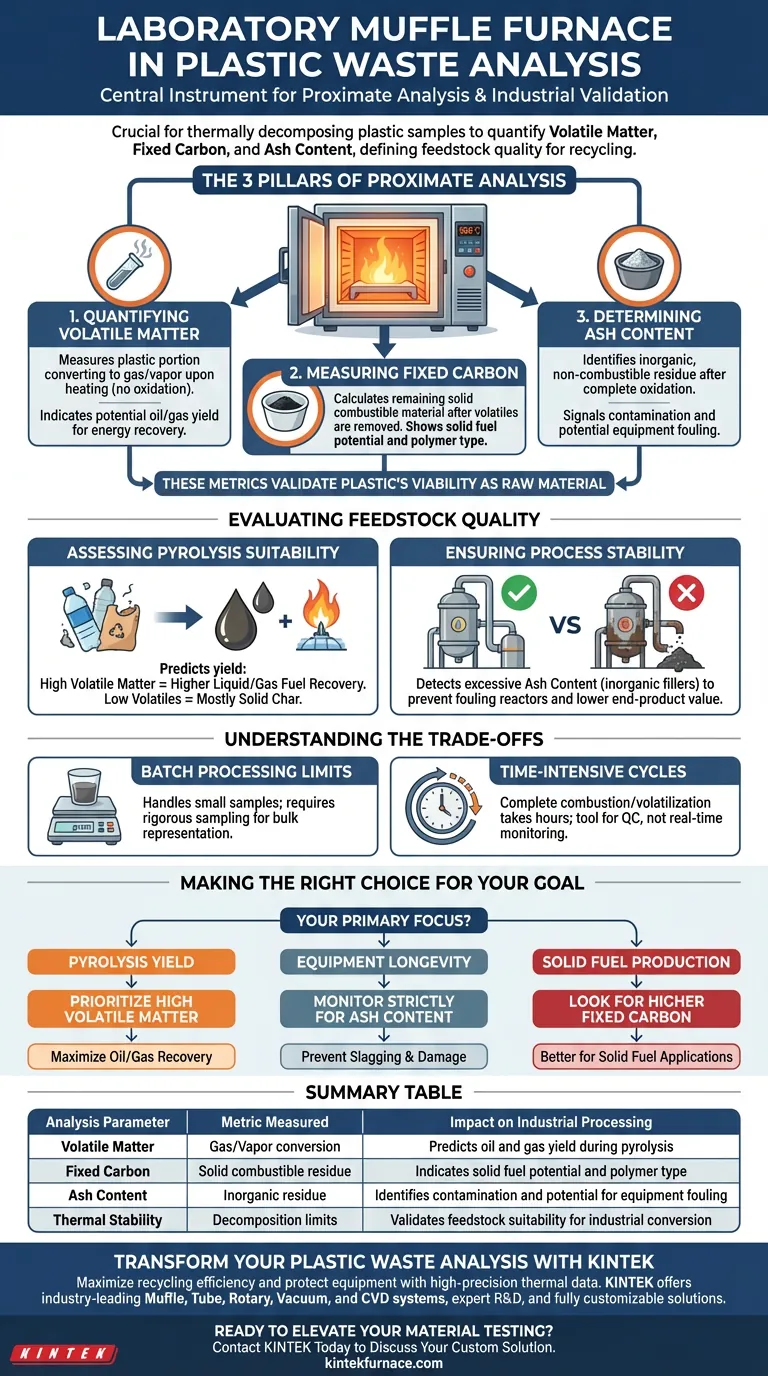
A laboratory muffle furnace serves as the central instrument for the proximate analysis of plastic waste. It provides a precisely controlled, high-temperature environment necessary to thermally decompose samples, allowing chemists to quantify volatile matter, fixed carbon, and ash content. This data is the definitive metric for assessing the quality and potential of plastic waste when used as a feedstock for recycling processes like pyrolysis.
The muffle furnace isolates the chemical composition of plastic waste through controlled thermal degradation, providing the essential data needed to predict yield and purity before the material enters industrial conversion systems.
The Pillars of Industrial Analysis
To understand the value of plastic waste, you must understand its composition. The muffle furnace facilitates this by subjecting samples to constant, extreme heat to measure three critical indicators.
Quantifying Volatile Matter
Volatile matter represents the portion of the plastic that converts into gas or vapor when heated. By heating the sample in a muffle furnace (often in a covered crucible to prevent oxidation), analysts can determine how much of the material will effectively turn into oil or gas during industrial processing. High volatile content typically indicates a better yield for energy recovery.
Measuring Fixed Carbon
After the volatiles are driven off, the remaining solid combustible material is known as fixed carbon. The muffle furnace allows for the precise calculation of this metric by continuing the heating process. This indicates the solid fuel potential of the waste and helps characterize the type of plastic polymer present.
Determining Ash Content
Ash content refers to the inorganic, non-combustible residue left behind after complete oxidation. In the muffle furnace, the organic components are fully combusted, leaving only minerals and fillers. High ash content often signals contamination or the presence of additives, which can negatively impact the efficiency of downstream recycling machinery.
Evaluating Feedstock Quality
The primary "Deep Need" for using a muffle furnace is not just to generate data, but to validate the plastic's viability as a raw material.
Assessing Pyrolysis Suitability
Pyrolysis involves heating plastic in the absence of oxygen to create fuel. The muffle furnace simulates the thermal degradation limits of the material. By analyzing the ratio of volatiles to fixed carbon, operators can predict whether a specific batch of plastic waste will produce high-quality pyrolysis oil or mostly solid char.
Ensuring Process Stability
Inconsistent feedstock is the enemy of industrial processing. The constant-temperature environment of the muffle furnace ensures that quality checks are reproducible. This allows facility operators to reject batches of waste that contain excessive inorganic fillers (ash) that could foul reactors or lower the caloric value of the end product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While muffle furnaces are indispensable for accuracy, they present specific operational constraints that must be managed.
Batch Processing Limits
Muffle furnaces are inherently batch-processing tools, typically handling small sample sizes (grams) at a time. This requires rigorous sampling methods to ensure the small amount tested in the furnace truly represents the bulk tons of plastic waste being processed.
Time-Intensive Cycles
The analysis is not instantaneous. Achieving complete combustion to determine ash content, or precise volatilization, can take hours depending on the protocol (similar to the 6-hour cycles used for waste glass or the high-temperature requirements for coal). This makes it a tool for quality control rather than real-time process monitoring.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The data derived from a muffle furnace should dictate your downstream processing decisions.
- If your primary focus is Pyrolysis Yield: Prioritize samples with high volatile matter, as this correlates directly to the amount of liquid or gas fuel you can recover.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: Monitor ash content strictly; high values indicate abrasive inorganic fillers that can cause slagging and damage industrial reactors.
- If your primary focus is Solid Fuel Production: Look for higher fixed carbon values, which suggest the waste is better suited for solid fuel applications rather than liquid conversion.
By leveraging the muffle furnace for precise component isolation, you transform raw waste into a predictable, manageable industrial asset.
Summary Table:
| Analysis Parameter | Metric Measured | Impact on Industrial Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Volatile Matter | Gas/Vapor conversion | Predicts oil and gas yield during pyrolysis |
| Fixed Carbon | Solid combustible residue | Indicates solid fuel potential and polymer type |
| Ash Content | Inorganic residue | Identifies contamination and potential for equipment fouling |
| Thermal Stability | Decomposition limits | Validates feedstock suitability for industrial conversion |
Transform Your Plastic Waste Analysis with KINTEK
Maximize your recycling efficiency and protect your industrial equipment with high-precision thermal data. KINTEK provides industry-leading solutions including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all backed by expert R&D and fully customizable to your specific laboratory needs.
Whether you are assessing pyrolysis suitability or ensuring process stability, our high-temperature furnaces deliver the reliability you require.
Ready to elevate your material testing? Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Yong Li, Fengfu Yin. Synergistic Effects Between Mixed Plastics and Their Impact on Pyrolysis Behavior and Pyrolysis Products. DOI: 10.3390/molecules29246059
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What were the results of annealing silicon-based material in the muffle furnace? Achieve Enhanced Conductivity for Semiconductors
- Why is precise temperature control important in a muffle furnace? Ensure Reliable Results in Heat Treatment
- What role does a high-temperature muffle furnace play in the component analysis of Moringa oleifera seeds?
- Why is a high-temp muffle furnace required for graphene catalyst calcination? Achieve Precise Phase Transformation
- How does advanced technology in muffle furnaces improve their performance in pharmaceutical applications? Boost Precision and Purity in Pharma Labs
- What temperature ranges can muffle furnaces achieve? Find the Perfect Heat for Your Lab Needs
- What substances should never be introduced into a muffle furnace? Protect Your Equipment from Damage
- How are high-temperature muffle furnaces and AAS utilized in lipstick heavy metal detection for consumer safety?



















