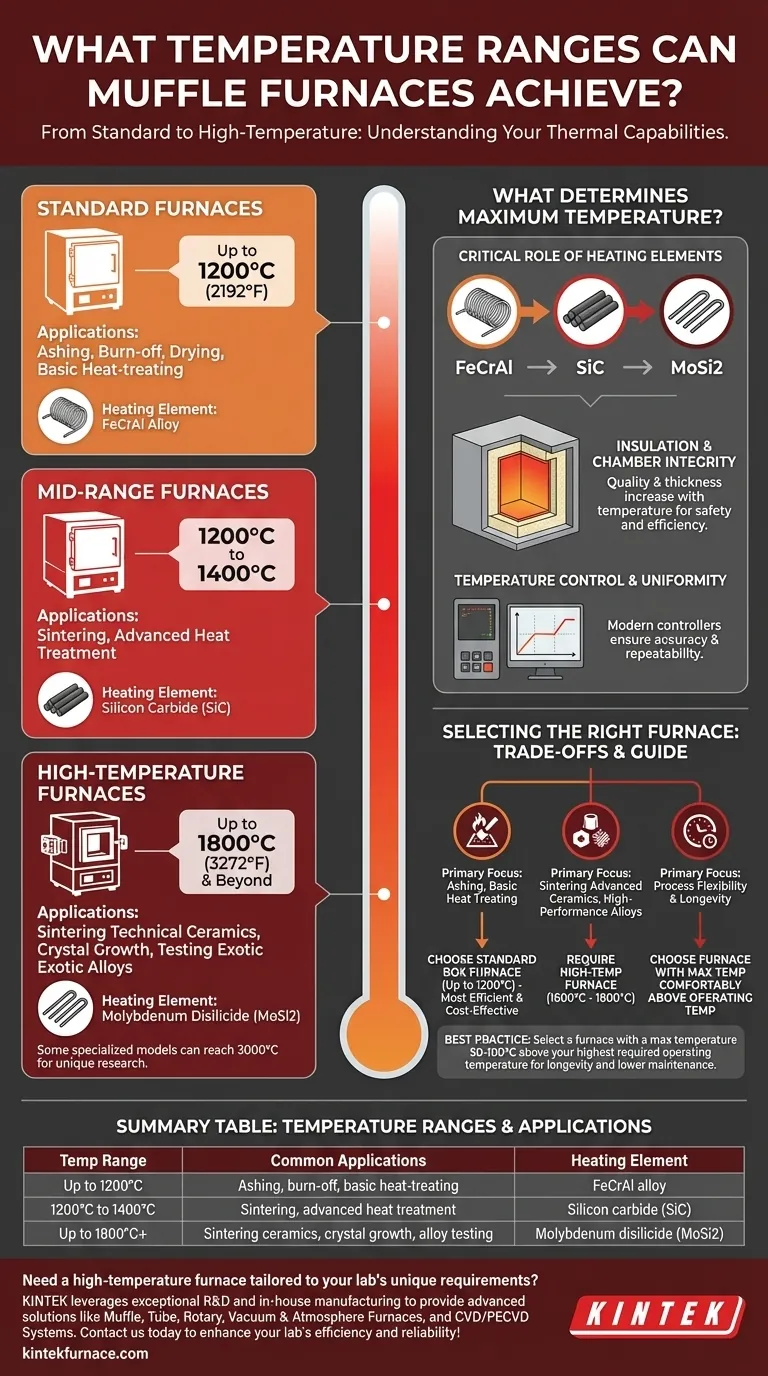
In practice, muffle furnaces operate across a wide thermal spectrum, but they are most commonly categorized by their maximum achievable temperature. Standard laboratory models typically operate up to 1200°C (2192°F), while high-temperature versions designed for advanced materials can reliably reach 1800°C (3272°F).
A furnace's temperature range is not a single specification but a direct reflection of its underlying technology. The choice between a standard or high-temperature model depends entirely on the heating elements and insulation used, which must be matched to your specific application's thermal demands.

Deconstructing the Temperature Range: From Standard to High-Temp Models
The term "muffle furnace" describes a category of equipment, not a single device. The primary differentiator is the maximum operating temperature, which sorts them into distinct classes based on their construction and intended use.
Standard Furnaces (Up to 1200°C)
These are the most common muffle furnaces found in general laboratory and light industrial settings. They are often called box furnaces.
Their temperature range makes them ideal for routine applications such as ashing, burn-off, drying, and basic heat-treating of metals.
Mid-Range Furnaces (1200°C to 1400°C)
Occupying a space between standard and high-temperature models, these furnaces provide a higher thermal capacity for more demanding processes.
They are often used for applications that require temperatures slightly beyond the limit of common box furnaces, such as certain types of sintering or advanced heat treatment cycles.
High-Temperature Furnaces (Up to 1800°C and Beyond)
These specialized furnaces are engineered for advanced materials science, ceramics research, and high-performance metallurgy.
Reaching 1600°C to 1800°C is common for this class, enabling processes like sintering technical ceramics, growing crystals, and testing exotic alloys. Highly specialized models can even exceed this, reaching up to 3000°C for unique research applications.
What Determines a Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
A furnace's temperature rating is not an arbitrary number; it is dictated by the physical limits of its core components.
The Critical Role of Heating Elements
The heating element is the heart of the furnace. The material used for the element directly determines the maximum stable temperature.
- Standard Furnaces (up to ~1200°C): Typically use iron-chrome-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloy wire elements.
- Mid-Range Furnaces (up to ~1400°C): Often rely on silicon carbide (SiC) rods.
- High-Temperature Furnaces (up to 1800°C+): Require molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements to operate reliably at extreme temperatures.
Insulation and Chamber Integrity
The furnace chamber must be lined with refractory insulation that can withstand the intense heat generated by the elements.
As temperatures increase, the required quality and thickness of this insulation also increase dramatically, impacting the furnace's size, weight, and cost.
Temperature Control and Uniformity
Achieving a high temperature is only half the battle. A quality furnace must also maintain that temperature with high precision and uniformity throughout the chamber.
Modern furnaces use programmable controllers to manage heating and cooling rates, ensuring the process is both repeatable and accurate.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance needs with practical limitations. A higher temperature capability introduces significant trade-offs.
Operating vs. Maximum Temperature
It is a critical best practice to select a furnace with a maximum temperature slightly above your highest required operating temperature, typically by 50-100°C.
Continuously running a furnace at its absolute maximum rating significantly shortens the lifespan of the heating elements and increases maintenance costs. This small buffer ensures longevity and operational flexibility.
Rise Time and Power Consumption
Higher maximum temperatures demand more power. Consequently, high-temperature furnaces have higher energy consumption and may have a slower rise time (the time it takes to reach the setpoint).
Cost and Complexity
The relationship between temperature and cost is exponential. The specialized heating elements (MoSi2) and advanced refractory materials needed for 1800°C furnaces make them substantially more expensive than standard 1200°C models.
How to Select the Right Furnace for Your Application
Use your core process requirement as the primary guide for selecting the correct furnace class.
- If your primary focus is ashing, burn-off, or basic heat treating: A standard box furnace operating up to 1200°C is the most efficient and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is sintering advanced ceramics or testing high-performance alloys: You will require a high-temperature furnace rated for at least 1600°C to 1800°C.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility and equipment longevity: Always choose a furnace with a maximum temperature rating comfortably above your highest anticipated working temperature.
By matching the furnace's engineering to your specific thermal requirements, you ensure both process success and long-term equipment reliability.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Common Applications | Heating Element |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Ashing, burn-off, basic heat-treating | FeCrAl alloy |
| 1200°C to 1400°C | Sintering, advanced heat treatment | Silicon carbide (SiC) |
| Up to 1800°C+ | Sintering ceramics, crystal growth, alloy testing | Molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's unique requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your experimental needs, whether for standard processes or advanced materials. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and reliability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















