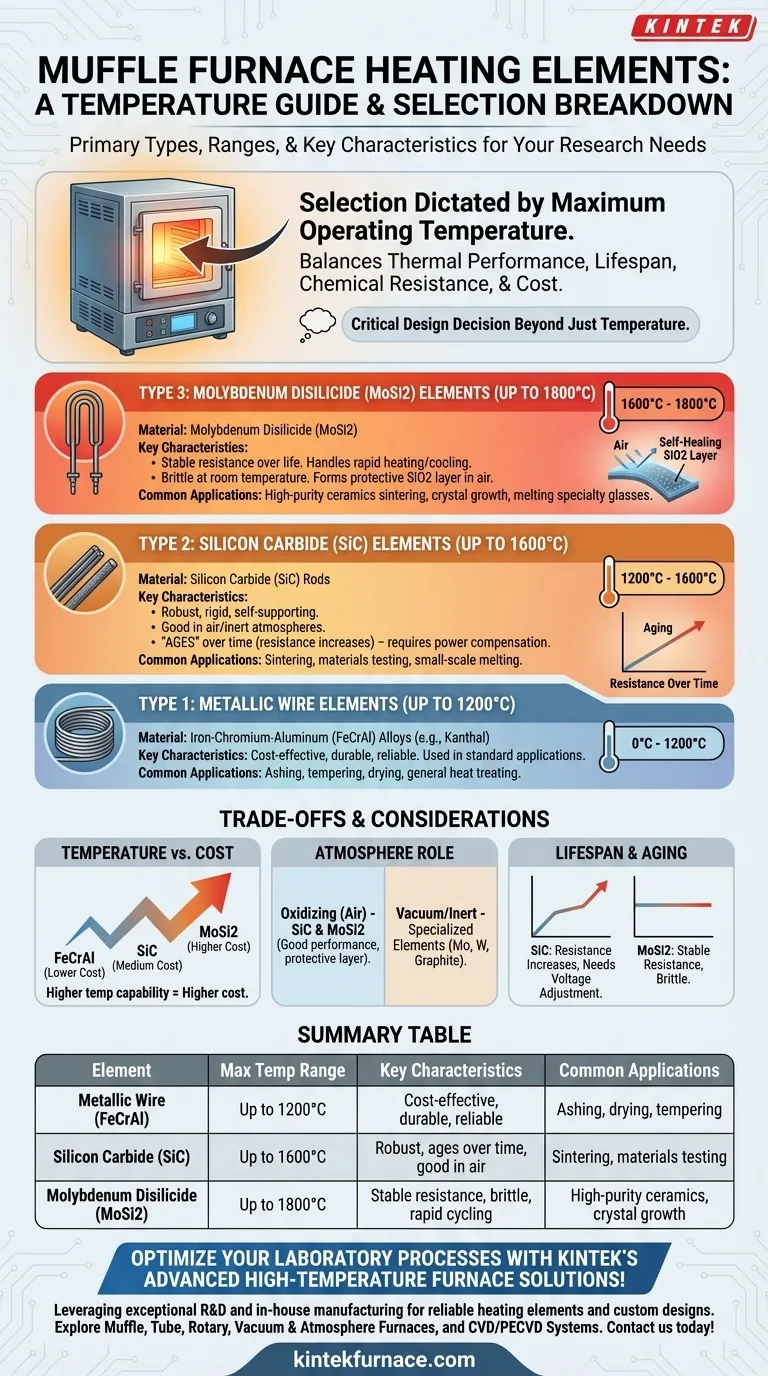
The selection of a heating element for a muffle furnace is dictated primarily by the required maximum operating temperature. The three most common types are metallic resistance wires for temperatures below 1200°C, silicon carbide (SiC) rods for temperatures up to 1600°C, and molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements for the highest temperature applications, reaching up to 1800°C.
Choosing a heating element is a critical design decision that goes beyond maximum temperature. The right choice balances thermal performance with element lifespan, resistance to chemical attack from the furnace atmosphere, and overall cost.

A Breakdown of Common Heating Elements
The vast majority of electric muffle furnaces rely on one of three types of resistance heating elements. Each is suited for a different operational temperature range and carries its own set of characteristics.
Type 1: Metallic Wire Elements (Up to 1200°C)
For lower-temperature applications, metallic resistance wires are the standard. These are most often iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloys, known widely by trade names like Kanthal.
They are cost-effective, durable, and highly reliable for processes such as ashing, tempering, drying, and general-purpose heat treating that do not exceed 1200°C.
Type 2: Silicon Carbide (SiC) Elements (Up to 1600°C)
When temperatures need to exceed 1200°C, silicon carbide (SiC) becomes the element of choice. These rigid, self-supporting rods are robust and can operate effectively in air or inert atmospheres.
SiC elements are used in a wide range of industrial and laboratory applications, including sintering, materials testing, and small-scale melting. They are the workhorse for the mid-to-high temperature range.
Type 3: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Elements (Up to 1800°C)
For the most demanding high-temperature work in an air atmosphere, molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements are required. These are used in advanced laboratory and production furnaces for sintering high-purity ceramics, growing crystals, and melting specialty glasses.
Their primary advantage is their stable resistance over their lifetime and their ability to handle very rapid heating and cooling cycles without damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a furnace is not as simple as picking the one with the highest temperature rating. The element's interaction with its environment and its long-term behavior are critical factors.
Temperature vs. Cost
The relationship is straightforward: higher temperature capability comes at a higher cost. MoSi2 elements are significantly more expensive than SiC elements, which are in turn more expensive than FeCrAl wire elements.
Over-specifying a furnace for a temperature you will never need results in unnecessary upfront and replacement costs.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere
Both SiC and MoSi2 are prized for their excellent performance in oxidizing atmospheres (i.e., normal air). At high temperatures, they form a protective, self-healing layer of glassy silicon dioxide (SiO2) that prevents the element from burning out.
This is in stark contrast to elements like pure molybdenum, tungsten, or graphite, which oxidize and are destroyed rapidly in air at high temperatures. These materials are reserved for specialized furnaces that operate under a vacuum or with an inert gas atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon).
Lifespan and "Aging"
Heating elements are consumable components with a finite lifespan. A key difference between element types is how they fail.
SiC elements "age" over time; their electrical resistance gradually increases with use. The furnace's power controller must be able to compensate by delivering a higher voltage to maintain the same power output.
MoSi2 elements, by contrast, maintain a relatively stable resistance throughout their service life. They are, however, very brittle at room temperature and must be handled with care to avoid mechanical shock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Consider your primary process requirements to determine the correct furnace technology for your needs.
- If your primary focus is general lab work below 1200°C (e.g., ashing, drying, pre-heating): A furnace with metallic wire elements (FeCrAl) offers the best balance of cost and performance.
- If you need to reach temperatures between 1200°C and 1600°C for processes like sintering or heat treating in air: Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are the industry standard, but be prepared for their gradual aging characteristic.
- If your application demands the highest temperatures in air (up to 1800°C) with rapid heating rates: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) elements are the superior choice, essential for advanced ceramics and materials science.
- If you are working in a vacuum or inert atmosphere at very high temperatures: You must look beyond standard muffle furnaces to specialized equipment using molybdenum, tungsten, or graphite elements.
Understanding these core differences ensures you select a furnace that is not just capable of reaching a temperature, but is truly optimized for your specific process.
Summary Table:
| Heating Element Type | Maximum Temperature Range | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallic Wire (FeCrAl) | Up to 1200°C | Cost-effective, durable, reliable | Ashing, drying, tempering |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | Robust, ages over time, good in air | Sintering, materials testing |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) | Up to 1800°C | Stable resistance, brittle, rapid cycling | High-purity ceramics, crystal growth |
Optimize your laboratory processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable heating elements and custom furnace designs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, tailored to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















