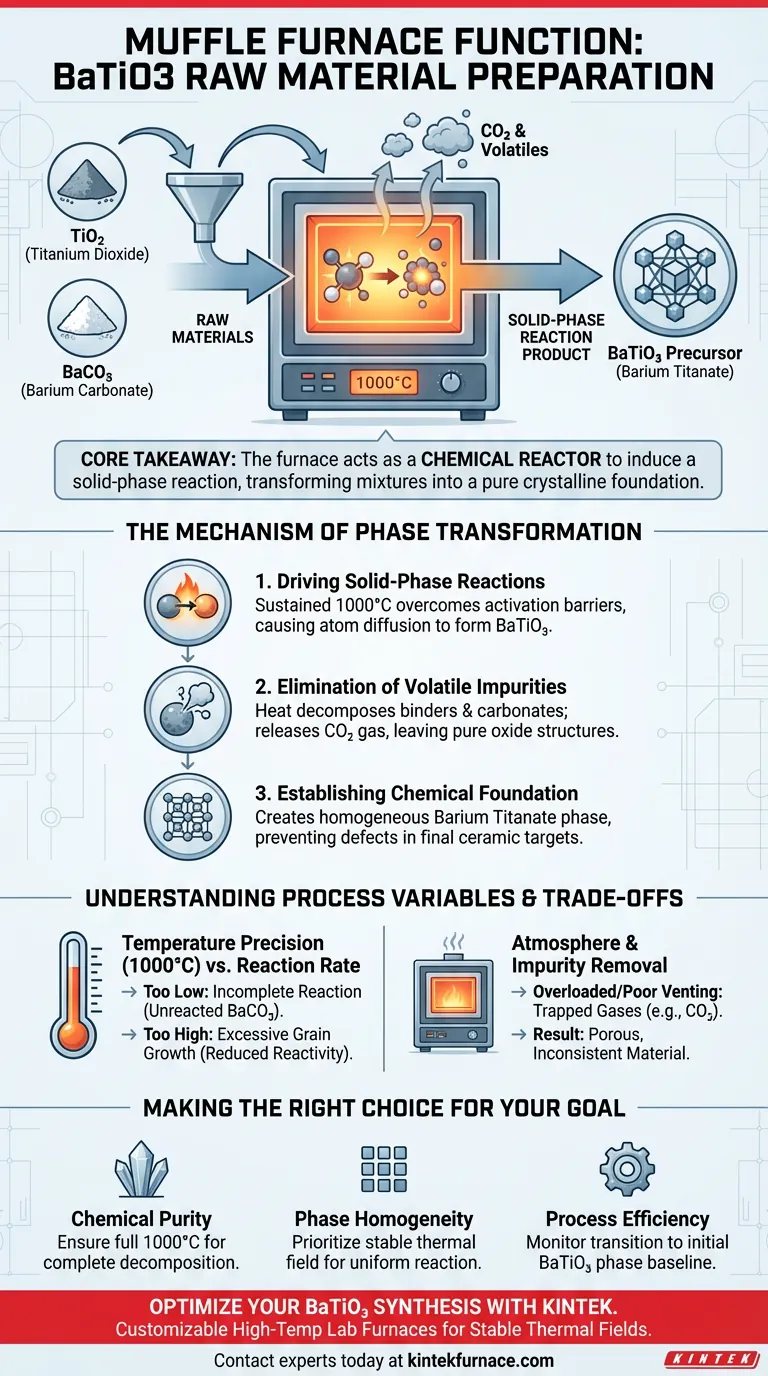
The primary function of a muffle furnace during the preparation of BaTiO3 (Barium Titanate) raw materials is to execute high-temperature pre-calcination. Specifically, the furnace maintains a stable environment at 1000°C to drive a solid-phase reaction between Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) and Barium Carbonate (BaCO3) powders. This heat treatment is essential for eliminating volatile impurities and synthesizing the initial Barium Titanate phase before the material is molded into targets.
Core Takeaway: The muffle furnace acts as a chemical reactor, not just a heater. Its role is to thermally induce a solid-phase reaction that transforms raw chemical mixtures into a pure, crystalline Barium Titanate foundation suitable for high-performance ceramic targets.
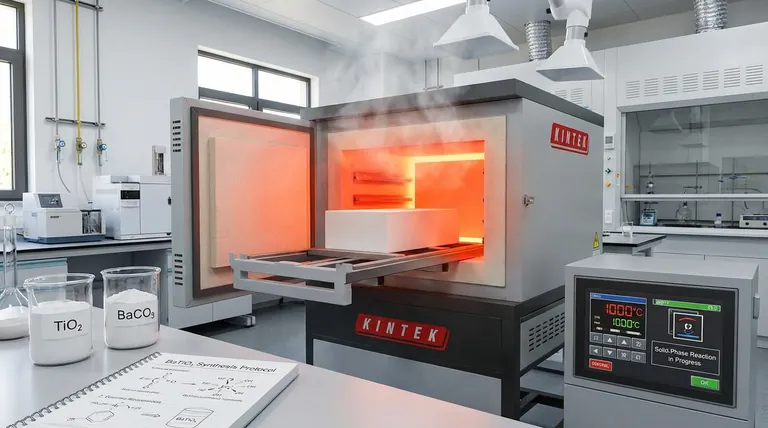

The Mechanism of Phase Transformation
The preparation of ceramic raw materials is a chemical synthesis process that relies on precise thermal energy. The muffle furnace facilitates this through three distinct mechanisms.
Driving Solid-Phase Reactions
Raw materials like TiO2 and BaCO3 do not react spontaneously at room temperature. They require significant thermal energy to overcome activation barriers.
The muffle furnace provides a sustained temperature of 1000°C. At this energy level, the powder particles undergo a solid-phase reaction, where the atoms diffuse across particle boundaries to form a new compound: Barium Titanate.
Elimination of Volatile Impurities
Raw powders often contain organic binders, moisture, or carbonates that decompose upon heating.
During the calcination process, the furnace heat drives these volatile impurities out of the material. For example, the carbonate component of BaCO3 is released as carbon dioxide gas, leaving behind pure oxide structures necessary for the final ceramic.
Establishing the Chemical Foundation
The output of this furnace stage is not the final product, but the "chemical foundation."
By ensuring the powders are fully reacted into the Barium Titanate phase prior to molding, the furnace ensures that subsequent steps—like target molding and sintering—start with a chemically homogeneous material. This prevents structural defects in the final ceramic target.
Understanding Process Variables and Trade-offs
While the muffle furnace is a robust tool, the calcination process requires careful management of specific variables to avoid material degradation.
Temperature Precision vs. Reaction Rate
The primary reference specifies 1000°C as the target temperature.
If the temperature is too low, the solid-phase reaction will be incomplete, leaving unreacted Barium Carbonate in the mix. If the temperature is significantly uncontrolled or too high, you risk excessive grain growth, which can reduce the reactivity of the powder during later sintering stages.
Atmosphere and Impurity Removal
The furnace relies on a stable thermal field to drive off impurities.
However, if the furnace chamber is overloaded or lacks appropriate venting, volatile gases (like CO2) can become trapped within the powder bed. This leads to porous or chemically inconsistent raw materials, which will compromise the density of the final molded target.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The effectiveness of your raw material preparation hinges on how you utilize the muffle furnace's capabilities.
If your primary focus is Chemical Purity:
- Ensure the furnace reaches the full 1000°C threshold to guarantee the complete decomposition of carbonates and the removal of all volatile byproducts.
If your primary focus is Phase Homogeneity:
- Prioritize a stable thermal field (uniform temperature distribution) to ensure the solid-phase reaction occurs evenly throughout the entire batch of TiO2 and BaCO3.
If your primary focus is Process Efficiency:
- Monitor the transition of the material into the initial Barium Titanate phase, as this specific chemical structure is the requisite baseline for all subsequent molding and densification steps.
The muffle furnace is the critical bridge that transforms a simple physical mixture of powders into a chemically unified ceramic precursor.
Summary Table:
| Process Goal | Mechanism | Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Synthesis | Solid-phase reaction between TiO2 and BaCO3 | 1000°C Stable Thermal Energy |
| Impurity Removal | Decomposition of carbonates and volatile organic matter | Controlled Venting & High Temp |
| Pre-Calcination | Establishing initial Barium Titanate crystalline phase | Precise Temperature Control |
| Uniformity | Ensuring chemical homogeneity across raw powders | Stable Internal Thermal Field |
Optimize Your BaTiO3 Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is non-negotiable when synthesizing high-performance Barium Titanate. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to your specific temperature and atmosphere requirements. Our high-temp lab furnaces ensure a stable thermal field, allowing you to achieve complete solid-phase reactions and superior phase homogeneity every time.
Ready to elevate your material preparation? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your lab’s unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Fugang Qi, Yanwei Cao. The Effect of Sputtering Target Density on the Crystal and Electronic Structure of Epitaxial BaTiO3 Thin Films. DOI: 10.3390/cryst14040304
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is it important to check the power supply of a muffle furnace? Ensure Safety and Accurate Results
- What is a muffle furnace and what temperature range can it reach? Discover High-Temp Solutions
- What role does a muffle furnace play in material testing and analysis? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment for Accurate Results
- What functions does the calcination process in an industrial high-temperature muffle furnace perform? Catalyst Prep Guide
- What are the common problems with muffle furnaces? Troubleshoot heating, temperature, and control issues
- What are the temperature and chamber size options for vacuum muffle furnaces? Find Your Perfect Fit for High-Temp Processes
- How is the furnace door of a box type resistance furnace secured and operated? Ensure Safety and Efficiency in Your Lab
- What is the function of a high-temperature lift furnace in the sintering process of SSZ electrolyte pellets?



















