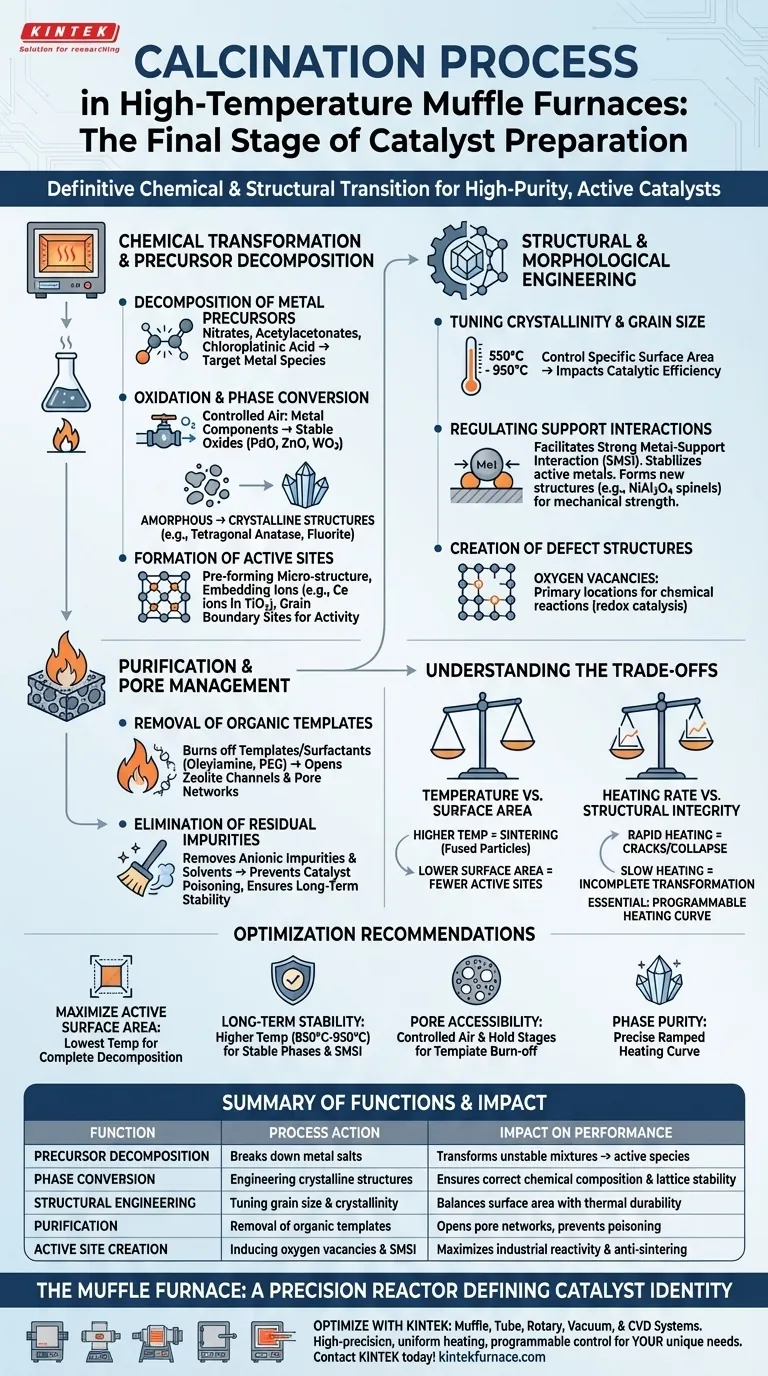
Calcination in an industrial high-temperature muffle furnace serves as the definitive chemical and structural transition stage in catalyst preparation. This process utilizes precise thermal energy to decompose metal precursors, remove organic impurities, and engineer the final crystalline phase of the material. By controlling the oxidation environment, the furnace transforms unstable chemical mixtures into high-purity, active, and physically stable catalytic structures.
The core function of calcination is the thermal transformation of precursors into their final active states, ensuring the catalyst possesses the correct chemical composition, crystal structure, and surface morphology required for industrial reactivity.

Chemical Transformation and Precursor Decomposition
Decomposition of Metal Precursors
The furnace provides the heat necessary to break down metal salts and complexes adsorbed on the catalyst support. Common ligands like nitrates, acetylacetonates, and chloroplatinic acid are thermally decomposed during this stage. This leaves behind the target metal species in a state ready for further reaction or final use.
Oxidation and Phase Conversion
In a controlled air environment, metal components are converted into stable oxide states such as palladium oxide (PdO), zinc oxide (ZnO), or tungsten trioxide (WO3). The furnace allows for the transformation of amorphous precursor materials into specific crystalline structures, such as the tetragonal anatase structure in titanium dioxide or the fluorite structure in cerium oxide.
Formation of Active Sites
The calcination process is responsible for pre-forming the micro-structure of active sites. It can facilitate the embedding of ions into a lattice—such as cerium ions into a titanium dioxide lattice—or the formation of active sites at grain boundaries, which are essential for photocatalytic or chemical activity.
Structural and Morphological Engineering
Tuning Crystallinity and Grain Size
By adjusting the furnace temperature—often ranging from 550°C to 950°C—manufacturers can precisely control the crystallinity and grain size of the catalyst. This temperature tuning directly impacts the specific surface area, which is a primary driver of catalytic efficiency.
Regulating Support Interactions
High-temperature treatment facilitates Strong Metal-Support Interaction (SMSI), which stabilizes active metals on a support. In some cases, calcination induces solid-phase reactions that form new structures like NiAl2O4 spinels, which significantly improve the catalyst’s mechanical strength and anti-sintering properties.
Creation of Defect Structures
Thermal processing in the muffle furnace can be used to intentionally create oxygen vacancies. These defects often serve as the primary locations for chemical reactions, particularly in oxidation-reduction (redox) catalysis.
Purification and Pore Management
Removal of Organic Templates and Surfactants
Many catalysts are synthesized using organic "templates" or surfactants like oleylamine or PEG to control shape and size. Calcination "burns off" these organic materials, effectively opening zeolite channels or pore networks that would otherwise be blocked.
Elimination of Residual Impurities
The furnace environment ensures the complete removal of residual anionic impurities and solvents. This high-purity result is critical for preventing catalyst poisoning and ensuring the long-term stability of the final oxide powder.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature vs. Surface Area
While higher temperatures are often required to achieve a stable crystalline phase, they also promote sintering. Excessive heat causes small particles to fuse together, which drastically reduces the available surface area and, consequently, the number of available active sites.
Heating Rate vs. Structural Integrity
Using a programmable heating curve is essential; if the temperature ramps too quickly, the rapid escape of decomposing gases can cause physical cracks or structural collapse in the catalyst support. Conversely, a heating process that is too slow may result in incomplete phase transformation or unintended grain growth.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Recommendations for Optimization
Successful calcination requires balancing thermal energy with the delicate physical structure of the catalyst.
- If your primary focus is maximizing active surface area: Prioritize the lowest possible calcination temperature that still achieves complete precursor decomposition to prevent sintering.
- If your primary focus is long-term thermal stability: Utilize higher temperatures (e.g., 850°C–950°C) to facilitate the formation of stable crystalline phases and strong metal-support interactions.
- If your primary focus is pore accessibility in zeolites: Ensure a controlled air flow and specific hold stages to completely oxidize organic template agents without collapsing the pore framework.
- If your primary focus is phase purity: Use a programmable muffle furnace to follow a precise ramped heating curve, ensuring the entire bulk of the material reaches the target transition temperature.
The muffle furnace is not merely a heater but a precision reactor that defines the final identity and performance of the industrial catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Calcination Function | Process Action | Impact on Catalyst Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor Decomposition | Breaks down metal salts (nitrates, etc.) | Transforms unstable mixtures into active metal/oxide species |
| Phase Conversion | Engineering crystalline structures (e.g., Anatase) | Ensures the correct chemical composition and lattice stability |
| Structural Engineering | Tuning grain size and crystallinity | Balances specific surface area with thermal durability |
| Purification | Removal of organic templates/surfactants | Opens pore networks and prevents catalyst poisoning |
| Active Site Creation | Inducing oxygen vacancies and SMSI | Maximizes industrial reactivity and anti-sintering properties |
Optimize Your Catalyst Production with KINTEK
Precise calcination is the difference between a high-performance catalyst and a failed batch. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all customizable for your unique lab and industrial needs.
Whether you are engineering specific grain sizes or maximizing active surface area, our high-temperature furnaces provide the uniform heating and programmable control required for perfection.
Ready to upgrade your laboratory’s capabilities? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- C. Romero, R.M. Navarro. Methanol Synthesis from CO2 over ZnO-Pd/TiO2 Catalysts: Effect of Pd Precursors on the Formation of ZnPd-ZnO Active Sites. DOI: 10.3390/catal15010055
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why might the cooling process be slower in a muffle furnace? Discover the Design Trade-Offs for Better Results
- Why is a box furnace required for the calcination of hydroxide precursors? Master P2-Type Oxide Synthesis
- What is the role of precise temperature gradient control in a high-temperature box furnace? Master Mo6S8 Synthesis
- What is the function of an industrial muffle furnace in converting microalgae into cobalt oxide nanomaterials?
- How are Box Furnaces typically loaded? Manual Methods for Flexible Batch Processing
- What is the role of a laboratory muffle furnace in ilmenite pretreatment? Optimize Thermal Activation at 950 °C
- Why is controlled and consistent heating important in a muffle furnace? Ensure Reliable Results in Your Lab
- What is the purpose of long-duration calcination in a high-temperature box resistance furnace for catalyst precursors? Explained



















