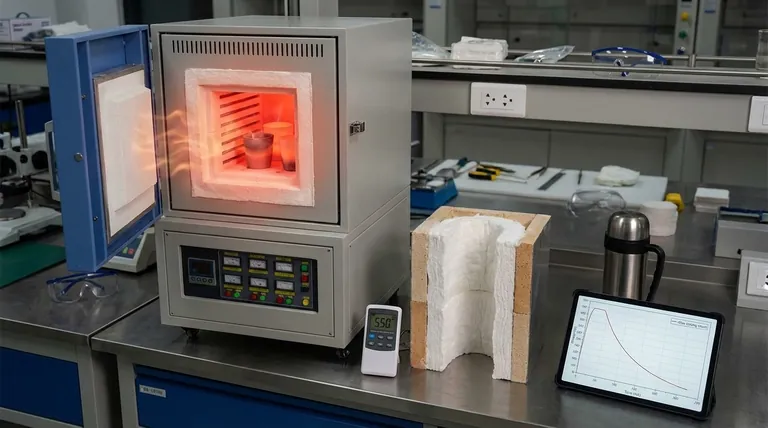
The slow cooling of a muffle furnace is not a defect, but a direct consequence of its fundamental design. The very materials that make it incredibly efficient at reaching and holding high temperatures are the same ones that prevent that heat from escaping quickly. Your furnace cools slowly because it is working exactly as intended.
The core issue is a trade-off between heating efficiency and cooling speed. A muffle furnace is built with dense, low-conductivity insulation to retain heat effectively, which inherently makes it slow to dissipate that same heat.
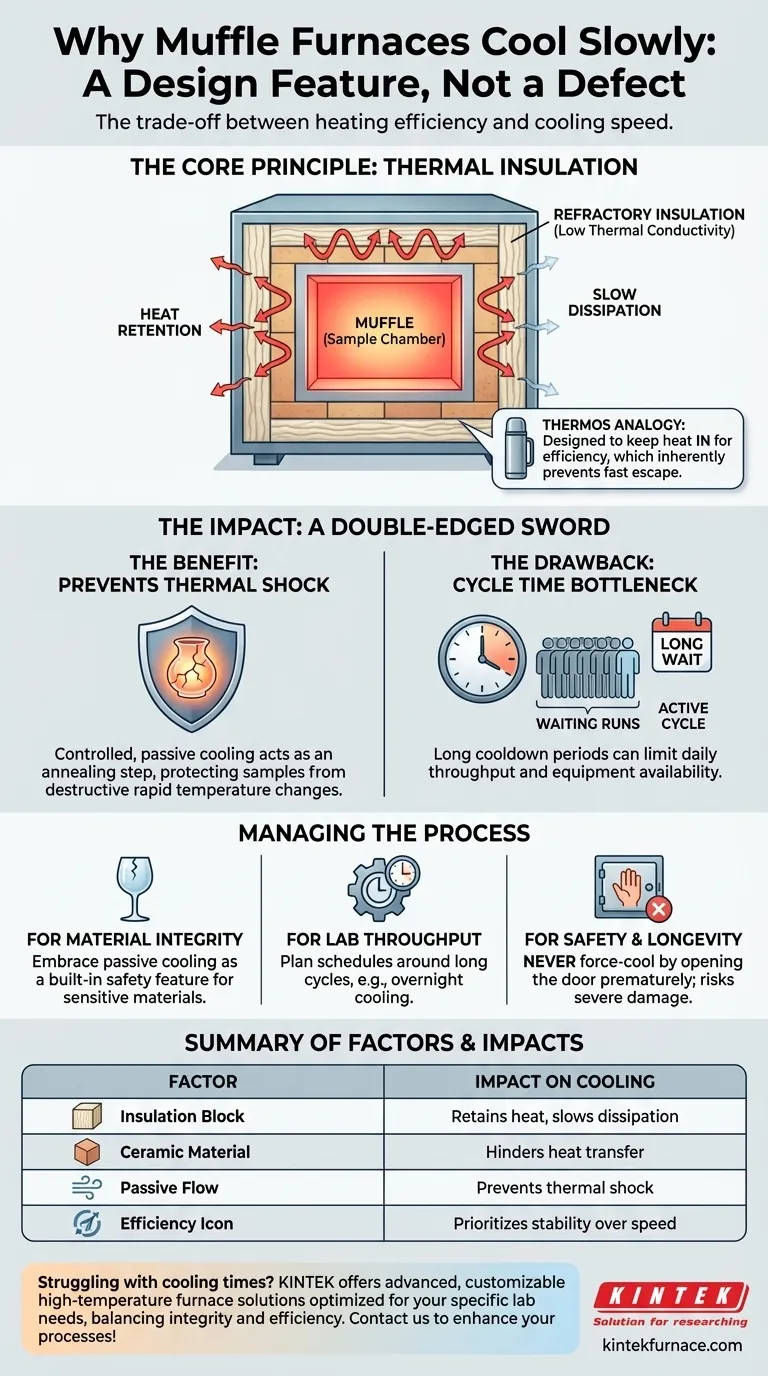
The Core Principle: Thermal Insulation
A muffle furnace is engineered for one primary purpose: to create a stable, uniform, and extremely hot environment. This is achieved through aggressive thermal insulation.
What is the "Muffle"?
The term "muffle" refers to the inner chamber that contains the sample. This chamber isolates the workload from the direct radiation of the heating elements, ensuring more uniform heat and preventing contamination.
To be effective, this chamber must be sealed and heavily insulated from the outside world.
The Role of Refractory Materials
The walls of the furnace are constructed from refractory materials, such as ceramic fiber blocks and firebricks. These materials are chosen for their extremely low thermal conductivity.
This means they are very poor at transferring heat. When heating, this property keeps the intense energy inside the furnace. During cooling, it means there is no efficient pathway for that stored heat to escape.
A Simple Analogy: The Thermos
Think of a muffle furnace like a high-end thermos. You fill it with hot coffee because you trust it to keep the heat in for hours.
You would never expect that same thermos to cool your coffee down quickly. The furnace's insulation works on the exact same principle, only at much higher temperatures.
The Impact on Your Process
This slow cooling rate is a double-edged sword, acting as both a critical feature and a potential bottleneck.
The Benefit: Preventing Thermal Shock
For many materials, especially ceramics, glass, and certain metal alloys, cooling down too quickly is destructive. Rapid temperature change creates internal stresses that can cause cracking and complete failure.
The furnace's naturally slow cooling rate, known as passive cooling, can act as a controlled annealing step. It protects your samples from the damaging effects of thermal shock.
The Drawback: Cycle Time and Throughput
The obvious downside is the impact on your workflow. A cooling cycle can take many hours, during which the furnace is unusable for another run.
In a busy lab or production environment, this long cooldown period can become a significant bottleneck, limiting the number of cycles you can complete in a day.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The slow cooling is not a problem to be solved, but a trade-off to be managed. Understanding this is key to using the equipment effectively.
Efficiency vs. Speed
A furnace that cools quickly would, by definition, be poorly insulated. It would consume vastly more energy to reach and maintain its target temperature, and it might struggle to achieve higher temperature ranges at all.
The design of a standard muffle furnace prioritizes thermal efficiency and temperature stability above all else. Rapid cooling is a secondary concern.
The Dangers of "Helping" it Cool
It can be tempting to speed up the process by opening the door slightly once the temperature drops to a few hundred degrees. This should be avoided.
Opening the door introduces a rush of cool air that can cause severe thermal shock to both your sample and the furnace's internal ceramic lining, potentially causing costly damage to the equipment itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Managing the cooling cycle depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is material integrity: Embrace the slow, passive cooling rate. View it as a built-in safety feature that protects your valuable samples from thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is lab throughput: Plan your schedule around the long cooling cycle. Start a run at the end of the day and allow it to cool overnight to maximize equipment uptime.
- If your primary focus is safety and equipment longevity: Never force-cool the furnace by opening the door prematurely. Always allow the cycle to complete naturally as specified by the manufacturer.
By understanding this core design principle, you can turn a potential frustration into a predictable and manageable part of your process.

Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cooling Speed |
|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High insulation retains heat, slowing dissipation |
| Refractory Materials | Low conductivity materials hinder heat transfer |
| Passive Cooling | Natural cooling prevents thermal shock to samples |
| Design Priority | Emphasizes efficiency and stability over speed |
Struggling with slow furnace cooling affecting your lab's throughput? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems with deep customization to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Our designs optimize for both material integrity and operational efficiency, ensuring reliable performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory processes with our innovative furnace technologies!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















