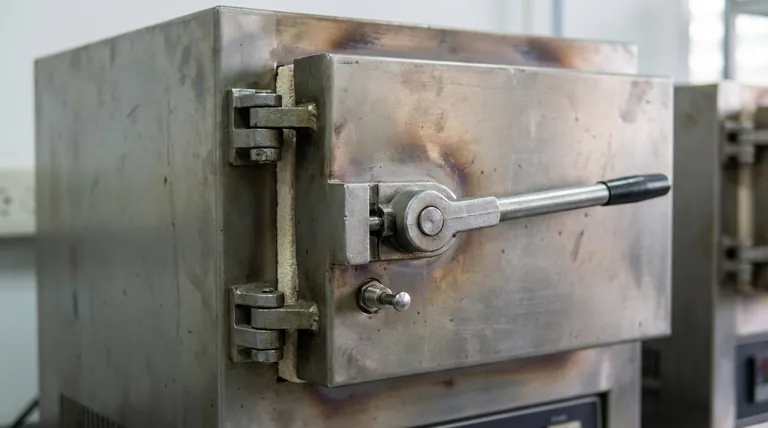
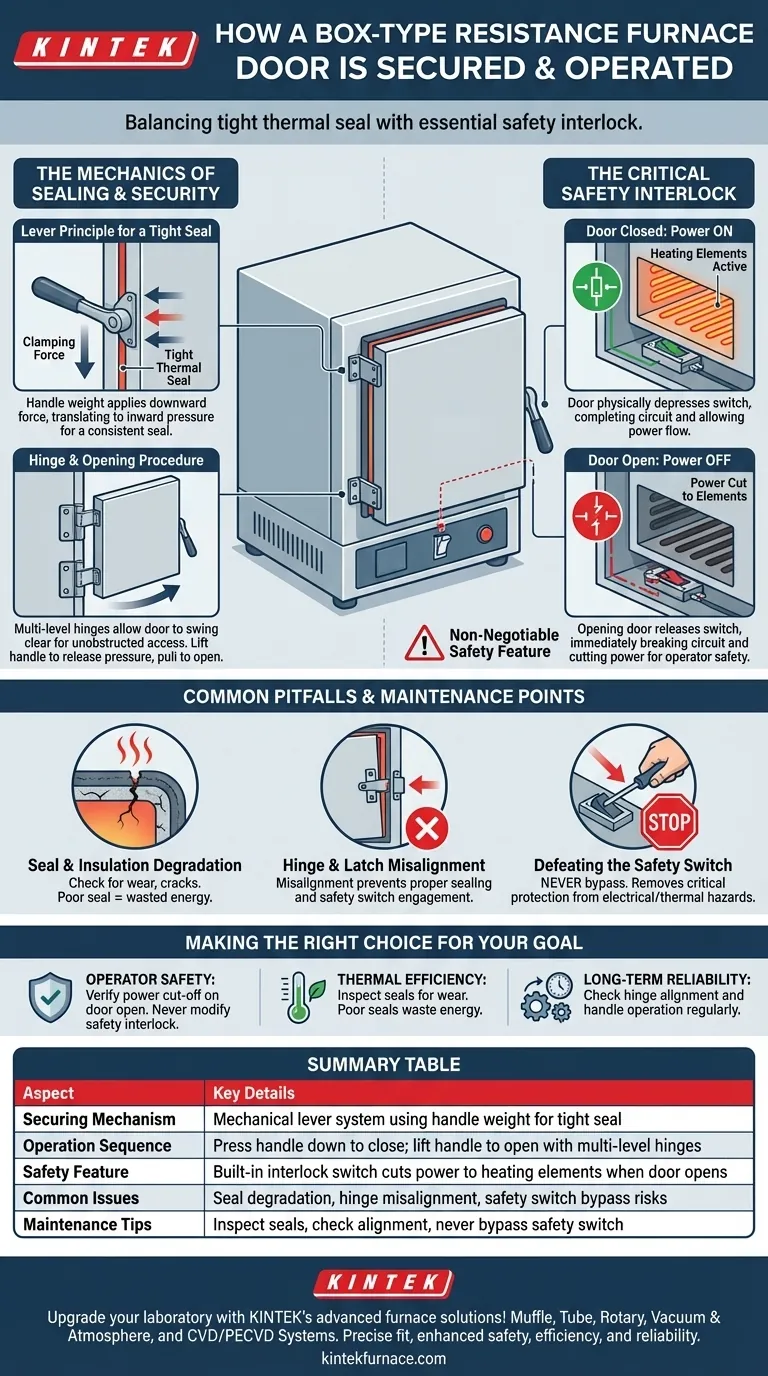
The door of a box-type resistance furnace is secured using a mechanical lever system and is operated in a specific sequence to ensure both a tight seal and operator safety. The handle's own weight provides the clamping force to press the door shut, while a built-in safety switch automatically cuts power to the heating elements the moment the door is opened.
The design of a furnace door is not just about access; it's an engineered system that balances the need for a tight thermal seal with an essential, non-negotiable safety interlock to protect the operator from electrical and thermal hazards.

The Mechanics of Sealing and Security
Understanding the door mechanism involves two key concepts: the physical sealing method and the integrated safety system.
The Lever Principle for a Tight Seal
The furnace door closure isn't a simple latch. It relies on the lever principle.
The weight of the handle itself is used to apply significant, consistent pressure against the furnace body. This ensures a tight seal that minimizes heat loss and maintains a stable internal temperature.
To close the door, you swing it shut and press the handle down, engaging the lock. The mechanism translates the downward force on the handle into inward pressure on the door.
The Hinge and Opening Procedure
The door is mounted on the furnace panel with multi-level hinges. This allows it to swing open and be placed to the side, providing unobstructed access to the furnace chamber.
To open the door, you must lift the handle lock upward to release the pressure. You then pull the hook or handle outward to swing the door fully open.
The Critical Safety Interlock
The most important feature of the furnace door is its role in the safety circuit. This is not an optional component.
How the Safety Switch Works
A safety interlock switch is positioned at the lower end of the furnace mouth. This is a simple, highly reliable mechanical switch.
When the furnace door is closed, it physically depresses this switch, completing the electrical circuit and allowing power to flow to the heating elements.
The moment the door begins to open, it releases the switch. This immediately breaks the circuit and cuts all power to the heating elements, regardless of the temperature controller's setting.
Why This Interlock is Non-Negotiable
This design prevents accidental exposure to two primary dangers: the intense radiant heat from active heating elements and the high voltage used to power them.
The automatic power cut-off is a fundamental safety feature that protects the operator during loading and unloading.
Common Pitfalls and Maintenance Points
While robust, the door system requires attention to function correctly and safely over its lifespan.
Seal and Insulation Degradation
The material that forms the seal around the door can become compressed or brittle over time, leading to heat leaks. This compromises thermal efficiency and can create hot spots on the furnace exterior.
Hinge and Latch Misalignment
Heavy use or accidental impact can cause the hinges or latching mechanism to become misaligned. A misaligned door will not seal properly and may fail to correctly engage the safety interlock switch.
Defeating the Safety Switch
Under no circumstances should an operator ever attempt to bypass or defeat the safety interlock. This removes the single most important safety feature of the furnace and creates an extremely hazardous condition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your operational priority dictates where you should focus your attention regarding the furnace door.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Always verify that the power indicator for the heating elements turns off when the door is opened. Never, under any circumstances, attempt to modify or bypass the safety interlock switch.
- If your primary focus is thermal efficiency: Periodically inspect the door seal for signs of wear, cracks, or compression. A poor seal directly translates to wasted energy and inconsistent heating.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Regularly check the door's hinge alignment and the smooth operation of the latching handle. A well-maintained mechanism prevents premature wear on all components.
By understanding these mechanical and safety principles, you ensure both the integrity of your process and the well-being of the operator.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Securing Mechanism | Mechanical lever system using handle weight for tight seal |
| Operation Sequence | Press handle down to close; lift handle to open with multi-level hinges |
| Safety Feature | Built-in interlock switch cuts power to heating elements when door opens |
| Common Issues | Seal degradation, hinge misalignment, safety switch bypass risks |
| Maintenance Tips | Inspect seals, check alignment, never bypass safety switch |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs, enhancing safety, efficiency, and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- What are the material requirements for furnace tubes? Optimize Performance and Safety in High-Temperature Labs
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control



















