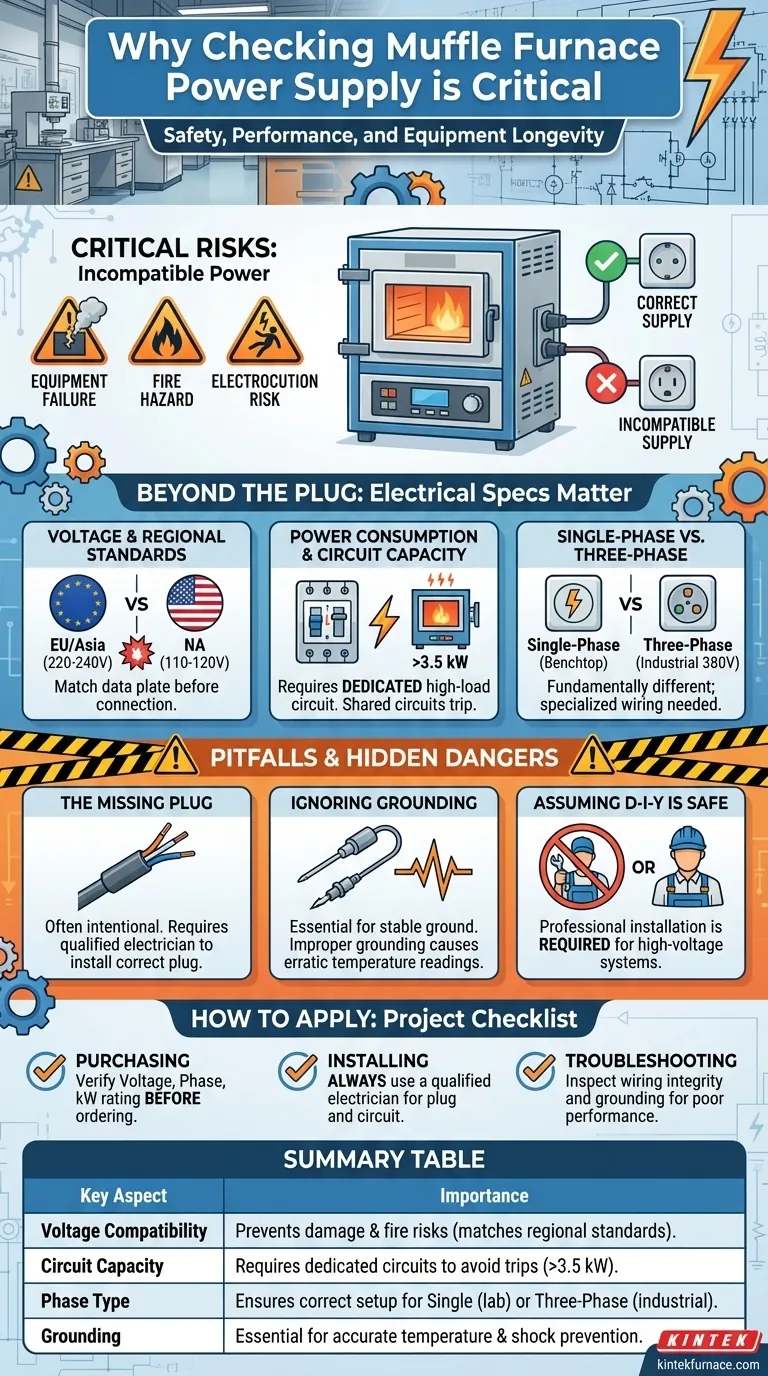
Verifying the power supply of a muffle furnace is a critical safety and operational mandate. These are high-consumption devices, and many models are engineered for specific regional electrical standards, such as 220-240V, which may not match your facility's outlets. Attempting to use a furnace with an incompatible power supply can result in immediate equipment failure, create a significant fire or electrocution hazard, and ruin your work.
Beyond simple plug-and-play convenience, a furnace's electrical setup is the foundation of its performance and safety. Ensuring the correct voltage, phase, and dedicated circuit capacity is not just about preventing damage—it is essential for stable temperature control and achieving accurate, repeatable results.

Beyond the Plug: Why Electrical Specs Matter
A muffle furnace is not a typical appliance. Its high power demand and sensitive control electronics require strict adherence to its specified electrical needs.
Voltage and Regional Standards
A furnace designed for European or Asian markets (typically 220-240V) will be instantly and irreparably damaged if connected to a standard North American 110-120V outlet, and vice versa. Always confirm the voltage rating on the furnace's data plate matches your local power supply before attempting to connect it.
Power Consumption (kW) and Circuit Capacity
Furnaces draw a significant amount of power, often 3.5 kW or more. This requires a dedicated electrical circuit with a breaker rated to handle the high load. Plugging a furnace into a circuit shared with other equipment will likely cause a trip, interrupting your process and potentially creating a safety issue.
Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase Power
Smaller benchtop furnaces typically use single-phase power (like that found in homes and standard labs). Larger, industrial-scale furnaces often require a three-phase 380V power supply. This is a fundamentally different type of electrical service that requires specialized wiring and installation.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Hidden Dangers
Mistakes in the electrical setup are common and costly. Understanding these pitfalls is the first step toward avoiding them.
The Fallacy of the Missing Plug
Many high-power furnaces are shipped with a power cable but no plug attached. This is done intentionally. It forces the user to have a qualified electrician install the correct, heavy-duty plug that matches the specific high-amperage receptacle required for the furnace.
Ignoring the Importance of Grounding
Proper grounding is essential for more than just shock prevention. The furnace's thermocouple, the sensor that measures temperature, relies on a stable ground reference. Improper grounding can introduce electrical "noise," leading to erratic and inaccurate temperature readings, ultimately compromising the validity of your results.
Assuming Professional Help is Optional
For any furnace requiring three-phase power or a non-standard connection, a professional electrician is not a recommendation; it is a requirement. Incorrectly wiring a high-voltage system is extremely dangerous and can lead to severe electric shock or fire.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Use these guidelines to ensure your furnace is set up for safe and effective operation from day one.
- If your primary focus is purchasing a new furnace: Verify the unit's voltage, phase, and kilowatt rating against your facility's available power before you place the order.
- If your primary focus is installing a new furnace: Always use a qualified electrician to install the correct plug and connect the unit to a dedicated, properly rated circuit.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting poor performance: Inspect the integrity of your wiring and confirm the unit is well-grounded, as unstable power is a common cause of inaccurate temperature control.
Proper electrical management is the bedrock of safe, reliable, and precise muffle furnace operation.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Importance |
|---|---|
| Voltage Compatibility | Prevents equipment damage and fire risks by matching regional standards (e.g., 220-240V vs. 110-120V). |
| Circuit Capacity | Requires dedicated circuits to handle high power loads (≥3.5 kW), avoiding breaker trips and interruptions. |
| Phase Type | Ensures correct setup for single-phase (standard labs) or three-phase (industrial) power needs. |
| Grounding | Essential for accurate temperature readings and shock prevention, stabilizing thermocouple performance. |
Ensure your lab's safety and precision with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all customizable to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today for expert guidance and reliable performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















