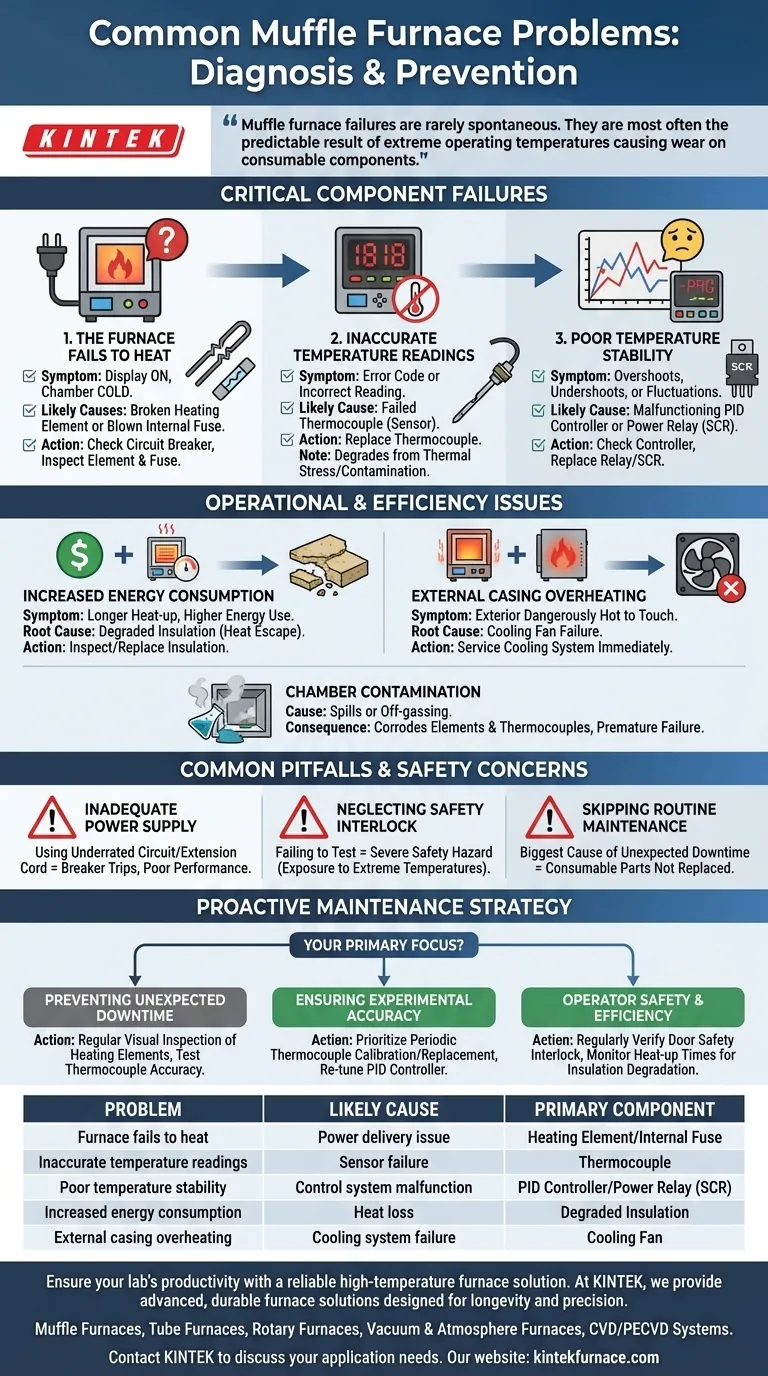
In practice, the most common problems with muffle furnaces are a failure to heat, inaccurate temperature readings, and unstable temperature control. These issues typically point to the failure of one of three key components: the heating element itself, the thermocouple that measures the temperature, or the controller that regulates the power.
Muffle furnace failures are rarely spontaneous. They are most often the predictable result of extreme operating temperatures causing wear on consumable components like heating elements and thermocouples, or issues within the electrical control system. Understanding this allows you to move from reactive repair to proactive maintenance.

Diagnosing Critical Component Failures
Problems with a muffle furnace almost always trace back to a specific component failing under the stress of high-heat cycles. Identifying the symptom is the first step to locating the faulty part.
The Furnace Fails to Heat
This is the most straightforward failure. If the furnace display is on but the chamber remains cold, the issue lies in the power delivery system.
First, check external factors. Ensure the furnace has not tripped its dedicated circuit breaker.
If the power supply is stable, the problem is likely a broken heating element or a blown internal fuse. Elements are consumable parts that degrade and eventually break after many high-temperature cycles.
Inaccurate or Impossible Temperature Readings
If the controller displays an error code (like "1818" on some models) or a temperature that is clearly wrong, the thermocouple has likely failed.
The thermocouple is the furnace's sensor, extending into the heating chamber to measure temperature. Due to constant thermal stress and potential contamination from samples, these sensors can degrade, break, or lose accuracy over time.
Poor Temperature Stability
When the furnace temperature overshoots the setpoint, undershoots it, or fluctuates wildly, the problem lies with the control system.
This could be a failing PID controller, the device that automatically manages power. More commonly, it is a malfunction in the power-switching component it governs, such as a relay or SCR. These components can wear out and fail to regulate power precisely.
Understanding Operational and Efficiency Issues
Beyond outright component failure, muffle furnaces can develop problems that degrade performance, waste energy, and create safety risks.
Increased Energy Consumption
If you notice the furnace is taking longer to heat up or using significantly more energy, the root cause is almost always degraded insulation.
The high-purity fibrous alumina insulation within the furnace walls can become brittle and less effective over time, allowing more heat to escape. This forces the furnace to work harder and longer to maintain its temperature.
External Casing Overheating
The furnace's exterior should remain safe to touch, a function managed by its double-walled construction and a cooling fan.
If the fan fails, heat will build up between the inner and outer walls, making the exterior dangerously hot. This indicates an immediate need to service the cooling system.
Contamination of the Chamber
Spills or aggressive off-gassing from samples (e.g., during ashing) can leave residues inside the chamber.
This contamination can directly attack and corrode both the heating elements and the thermocouple, leading to premature failure and inaccurate readings.
Common Pitfalls and Safety Concerns
Many furnace problems are introduced by incorrect setup, use, or a lack of basic upkeep. Avoiding these common mistakes is critical for reliability and safety.
Using an Inadequate Power Supply
A muffle furnace is a high-demand device. Plugging it into a circuit with other equipment or using an underrated extension cord will frequently trip the breaker and can starve the furnace of the power it needs to operate correctly.
Neglecting the Safety Interlock
Most furnaces feature a safety interlock that automatically cuts power to the heating elements when the door is opened. This switch can fail or become misaligned.
Failing to periodically test this feature creates a severe safety hazard, exposing the operator to the chamber's extreme internal temperatures.
Skipping Routine Maintenance
The single biggest cause of unexpected downtime is the lack of a regular maintenance schedule. Heating elements, thermocouples, and door seals are not permanent; they are consumable parts that require inspection and eventual replacement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to furnace maintenance should align with your operational priorities. A proactive strategy is always more effective than a reactive one.
- If your primary focus is preventing unexpected downtime: Implement a regular maintenance schedule to visually inspect heating elements for wear and test thermocouple accuracy.
- If your primary focus is ensuring experimental accuracy: Prioritize periodic thermocouple calibration or replacement and consider re-tuning the PID controller if you observe temperature instability.
- If your primary focus is operator safety and efficiency: Regularly verify the door safety interlock and monitor heat-up times to detect insulation degradation before it becomes a major energy drain.
By understanding these common failure points, you can ensure your muffle furnace remains a reliable, accurate, and safe tool for your work.
Summary Table:
| Problem | Likely Cause | Primary Component |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace fails to heat | Power delivery issue | Heating Element / Internal Fuse |
| Inaccurate temperature readings | Sensor failure | Thermocouple |
| Poor temperature stability | Control system malfunction | PID Controller / Power Relay (SCR) |
| Increased energy consumption | Heat loss | Degraded Insulation |
| External casing overheating | Cooling system failure | Cooling Fan |
Ensure your lab's productivity and experimental accuracy with a reliable high-temperature furnace solution.
At KINTEK, we understand that unexpected equipment failure disrupts critical workflows. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced, durable furnace solutions designed for longevity and precision.
Our product line includes:
- Muffle Furnaces
- Tube Furnaces
- Rotary Furnaces
- Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces
- CVD/PECVD Systems
Complemented by our strong deep customization capability, we can precisely tailor a furnace to meet your unique experimental requirements and operational environment, helping you minimize downtime and maintain consistent results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application needs and discover how our robust furnace solutions can enhance your lab's efficiency and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















