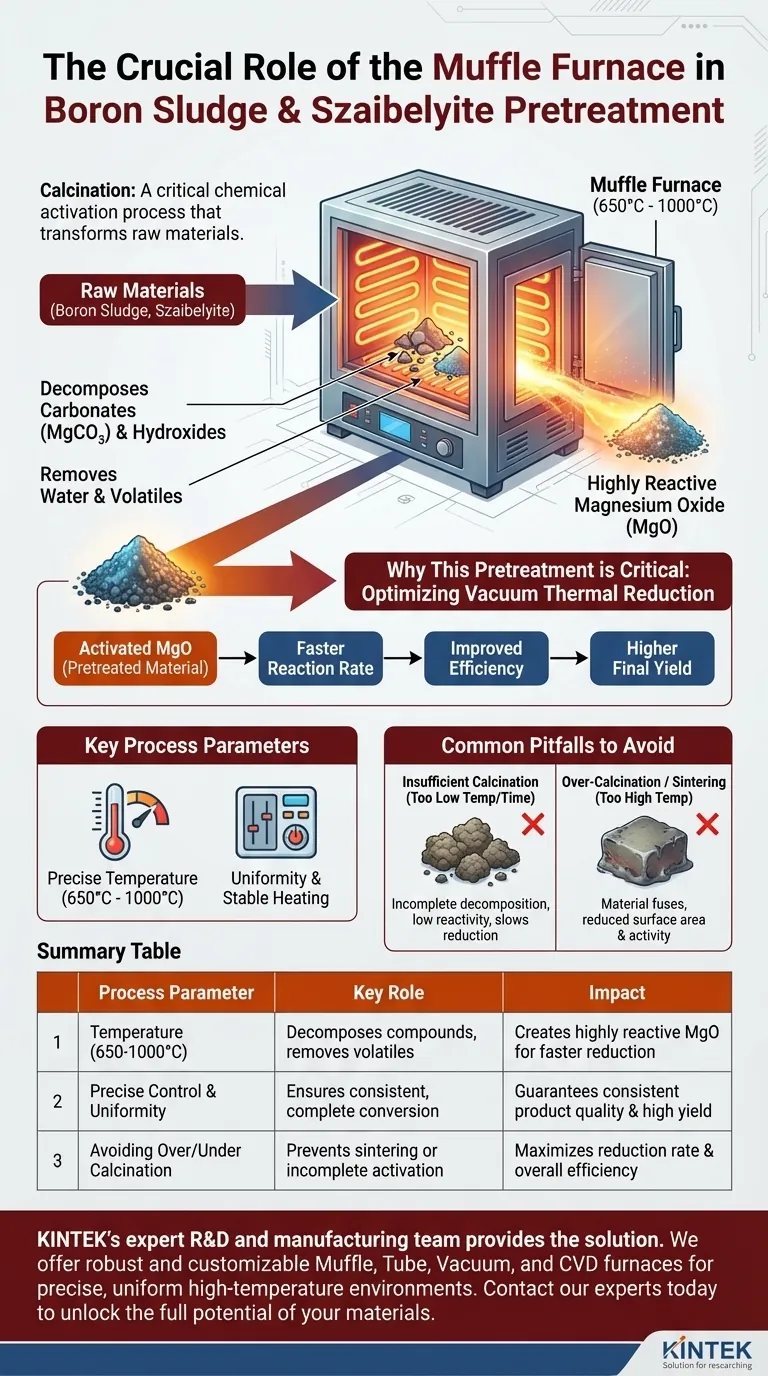
In the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite, the box-type resistance furnace, or muffle furnace, serves the critical role of calcination. This process uses a precisely controlled high-temperature environment (typically 650°C to 1000°C) to decompose carbonates and hydroxides, remove crystal water, and drive off volatile components from the raw materials. This fundamentally transforms the materials to prepare them for the next stage of processing.
The furnace is not simply a heater; it is a chemical reactor. Its primary purpose is to produce a highly reactive magnesium oxide, which is the key to improving the speed and overall efficiency of the subsequent vacuum thermal reduction process.

The Core Function: Calcination for Chemical Activation
The entire goal of placing boron sludge and szaibelyite into a muffle furnace is to activate the materials through a process called calcination. This isn't just about purification; it's about fundamentally changing the chemical properties of the feedstock.
Decomposing Unwanted Compounds
The raw materials contain stable compounds like magnesium carbonate (MgCO₃) and various hydroxides. The high heat inside the furnace provides the energy needed to break these chemical bonds, breaking them down into simpler, more useful forms.
Removing Water and Volatiles
During heating, any bound crystal water and other volatile impurities are vaporized and removed from the material. This purification step is essential for preventing unwanted side reactions in later stages.
Creating High-Activity Magnesium Oxide
This is the most important outcome. The decomposition of the carbonates and hydroxides produces magnesium oxide (MgO). The controlled conditions of the calcination process ensure this MgO has a high degree of chemical activity, meaning it will react more readily in subsequent steps.
Why This Pretreatment is Critical
The calcination step does not exist in isolation. It is performed specifically to optimize the next, more complex stage of the process: vacuum thermal reduction. Without proper pretreatment, the entire extraction becomes far less efficient.
Preparing for Vacuum Thermal Reduction
The ultimate goal is to use a reduction agent to extract valuable elements. The pretreated, activated material serves as the ideal input for this vacuum thermal reduction stage.
Improving Reduction Rate and Efficiency
The high chemical activity of the magnesium oxide produced during calcination is the key. This activated MgO reacts much faster and more completely during reduction, significantly improving the overall efficiency of the process.
Ensuring a Higher Final Yield
A more efficient reduction process directly translates to a higher yield of the final desired product. By properly preparing the materials, you maximize the output from the same amount of raw feedstock.
Understanding the Key Process Parameters
Simply heating the material is not enough. The success of calcination depends entirely on the precise control offered by the muffle furnace.
The Critical Role of Temperature
The temperature range of 650°C to 1000°C is not arbitrary. It is carefully selected to be high enough to ensure complete decomposition of carbonates and hydroxides.
The Importance of Precise Control
A muffle furnace provides a highly uniform and stable heating environment. This prevents localized overheating or under-heating, ensuring that the entire batch of material is converted evenly into the desired high-activity state.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes in the calcination stage can undermine the entire process, demonstrating why a specialized furnace is necessary.
Insufficient Calcination
If the temperature is too low or the heating time is too short, the decomposition will be incomplete. This leaves impurities and results in a less active MgO, which will significantly slow down and reduce the efficiency of the thermal reduction stage.
Over-Calcination or Sintering
If the temperature is too high, the newly formed magnesium oxide particles can begin to fuse together, a process known as sintering. This drastically reduces the material's surface area and its chemical activity, defeating the purpose of the pretreatment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Optimizing the calcination step is about balancing decomposition with activation. Your goal determines your focus.
- If your primary focus is maximizing material reactivity: Your goal is to find the highest possible temperature that achieves full decomposition without initiating sintering.
- If your primary focus is overall process efficiency: Recognize that proper calcination is a direct investment in a faster, more effective, and higher-yield vacuum reduction stage.
- If your primary focus is product consistency: Leverage the precise temperature control of the muffle furnace to guarantee that every batch of material is pretreated to the exact same standard.
Ultimately, mastering the calcination step is fundamental to unlocking the full potential of your raw materials.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Key Role in Pretreatment | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (650°C - 1000°C) | Decomposes carbonates/hydroxides; removes volatiles. | Creates highly reactive MgO for faster reduction. |
| Precise Control & Uniformity | Ensures complete, even decomposition batch after batch. | Guarantees consistent product quality and high final yield. |
| Avoiding Over/Under Calcination | Prevents sintering or incomplete activation. | Maximizes reduction rate and overall process efficiency. |
Ready to optimize your boron sludge and szaibelyite pretreatment process?
A precisely controlled calcination step is not just heating—it's a critical chemical activation that directly determines the success and efficiency of your entire vacuum thermal reduction operation. Choosing the right furnace is choosing higher yields and faster processes.
KINTEK's expert R&D and manufacturing team provides the solution. We offer a range of robust and customizable Muffle, Tube, Vacuum, and CVD furnaces designed to deliver the precise, uniform high-temperature environment your lab requires for consistent, high-quality results.
Let's discuss how a KINTEK furnace can become the cornerstone of your efficiency. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and unlock the full potential of your materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals



















