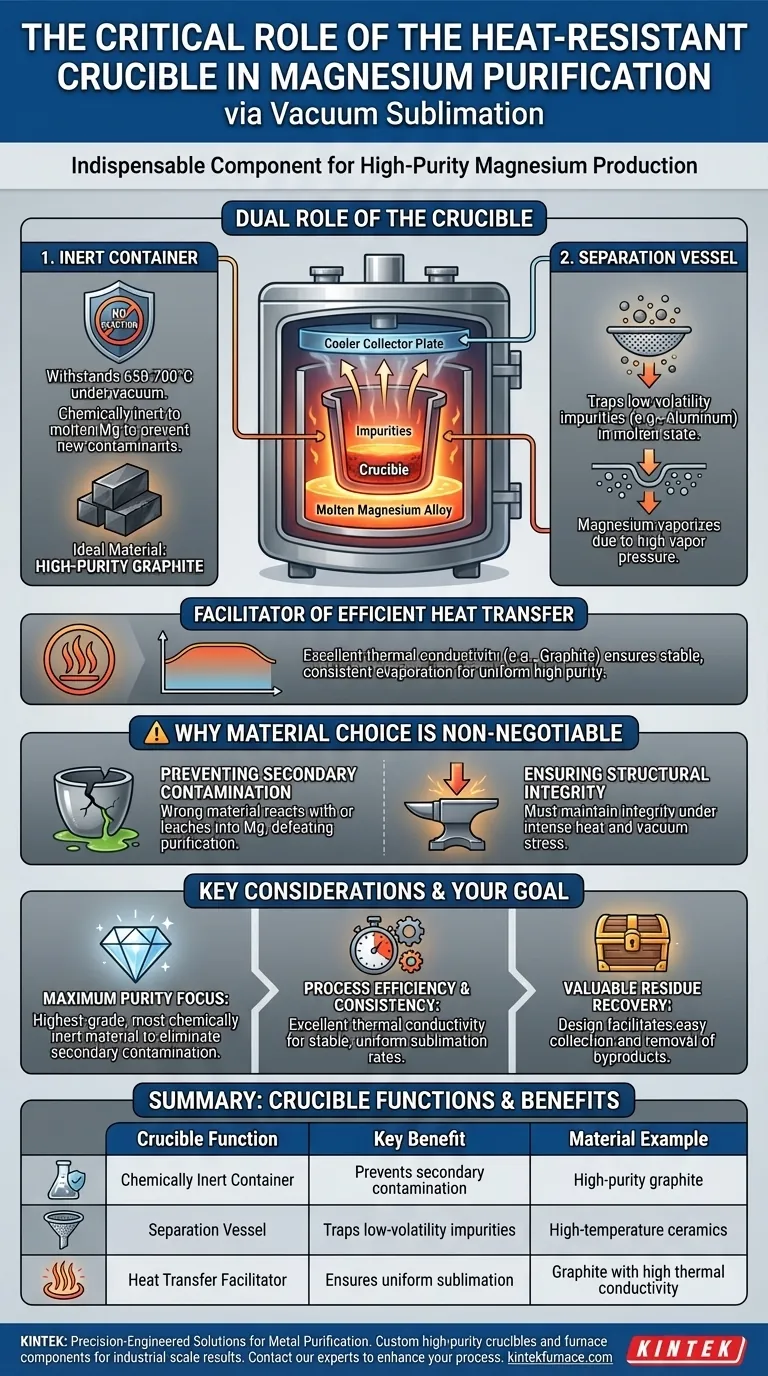
A heat-resistant crucible is indispensable in the vacuum sublimation of magnesium because it performs two critical, simultaneous functions. It acts as a chemically inert container that can withstand extreme temperatures without reacting with the molten metal, and it serves as the physical separation unit where low-volatility impurities are left behind.
The crucible is more than just a container; it is the core component that enables the entire purification strategy. Its material properties—specifically its chemical inertness and thermal stability—are what make it possible to separate pure magnesium from its alloys without introducing new contaminants.

The Dual Role of the Crucible in Purification
To understand the crucible's importance, we must look at its two distinct jobs in the vacuum sublimation process, which relies on the different vapor pressures of metals to achieve separation.
A High-Temperature, Inert Container
The process operates at high temperatures, typically around 650-700°C, and under a vacuum. The crucible must hold the raw, molten magnesium alloy without melting, softening, or degrading.
Most importantly, it must be chemically inert. Any reaction between the crucible and the molten magnesium would introduce new impurities, defeating the entire purpose of purification. This is why high-purity graphite is an ideal material.
A Critical Separation Vessel
Sublimation separates elements based on how easily they turn into a gas. Magnesium has a relatively high vapor pressure, allowing it to vaporize under vacuum at these temperatures.
Impurities like aluminum, however, have a very low vapor pressure and remain behind in the molten state. The crucible physically contains these leftover residues, effectively acting as the collection point that completes the separation.
A Facilitator of Efficient Heat Transfer
The crucible's material properties also impact process efficiency. Materials like graphite have good thermal conductivity, which helps transfer heat uniformly to the raw magnesium.
This even heating ensures a stable and consistent evaporation rate, which is critical for controlling the process and producing a final product of uniformly high purity.
Why Material Choice is Non-Negotiable
The selection of the crucible material is not a minor detail; it is fundamental to the success of the operation. The wrong choice can compromise the integrity of the entire purification cycle.
Preventing Secondary Contamination
The primary goal is purification. Using a crucible made from a material that could react with or leach into the molten magnesium would be counterproductive. High-purity graphite is favored specifically because it avoids this secondary contamination.
Ensuring Structural Integrity under Stress
The combination of intense heat and a vacuum environment places significant stress on the equipment. The crucible must maintain its structural integrity under these conditions to prevent process failure.
Understanding the Key Considerations
While the concept is straightforward, practical application involves important details that determine the outcome. Choosing the right crucible means balancing several factors.
The Purity of the Crucible Itself
The emphasis on high-purity graphite is crucial. A lower-grade graphite crucible could contain its own ash or impurities, which could then contaminate the magnesium. The purity of the tool must exceed the desired purity of the product.
Chemical Stability is Paramount
The defining characteristic of a suitable crucible is its chemical stability in the presence of the specific molten metals being processed. It must remain a neutral bystander in the chemical reaction, serving only as the vessel.
Thermal Performance and Consistency
A crucible that heats unevenly will create an unstable sublimation process, potentially reducing both yield and purity. High and uniform thermal conductivity is a key performance attribute for predictable, industrial-scale results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective in the purification process will guide your crucible selection and focus.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum purity: Prioritize the highest-grade, most chemically inert crucible material available to eliminate any risk of secondary contamination.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and consistency: Select a crucible material with excellent thermal conductivity, like high-purity graphite, to ensure stable and uniform sublimation rates.
- If your primary focus is recovering valuable residues: Choose a crucible with a design and material that facilitates the easy collection and removal of byproducts like enriched aluminum.
Ultimately, the crucible is the silent, foundational component that enables the entire principle of vacuum sublimation to work effectively.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Function | Key Benefit | Material Example |
|---|---|---|
| Chemically Inert Container | Prevents secondary contamination | High-purity graphite |
| Separation Vessel | Traps low-volatility impurities | High-temperature ceramics |
| Heat Transfer Facilitator | Ensures uniform sublimation | Graphite with high thermal conductivity |
Achieve Maximum Purity and Efficiency in Your Metal Purification Processes
Choosing the right crucible is critical for successful vacuum sublimation. At KINTEK, we understand that your goals—whether maximum purity, process consistency, or efficient residue recovery—demand precision-engineered solutions.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-purity graphite crucibles and other lab high-temp furnace components, all customizable for your unique needs. Our products ensure chemical inertness, structural integrity under extreme conditions, and optimal thermal performance for predictable, industrial-scale results.
Ready to enhance your purification process? Contact our experts today to discuss how our tailored solutions can meet your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios



















