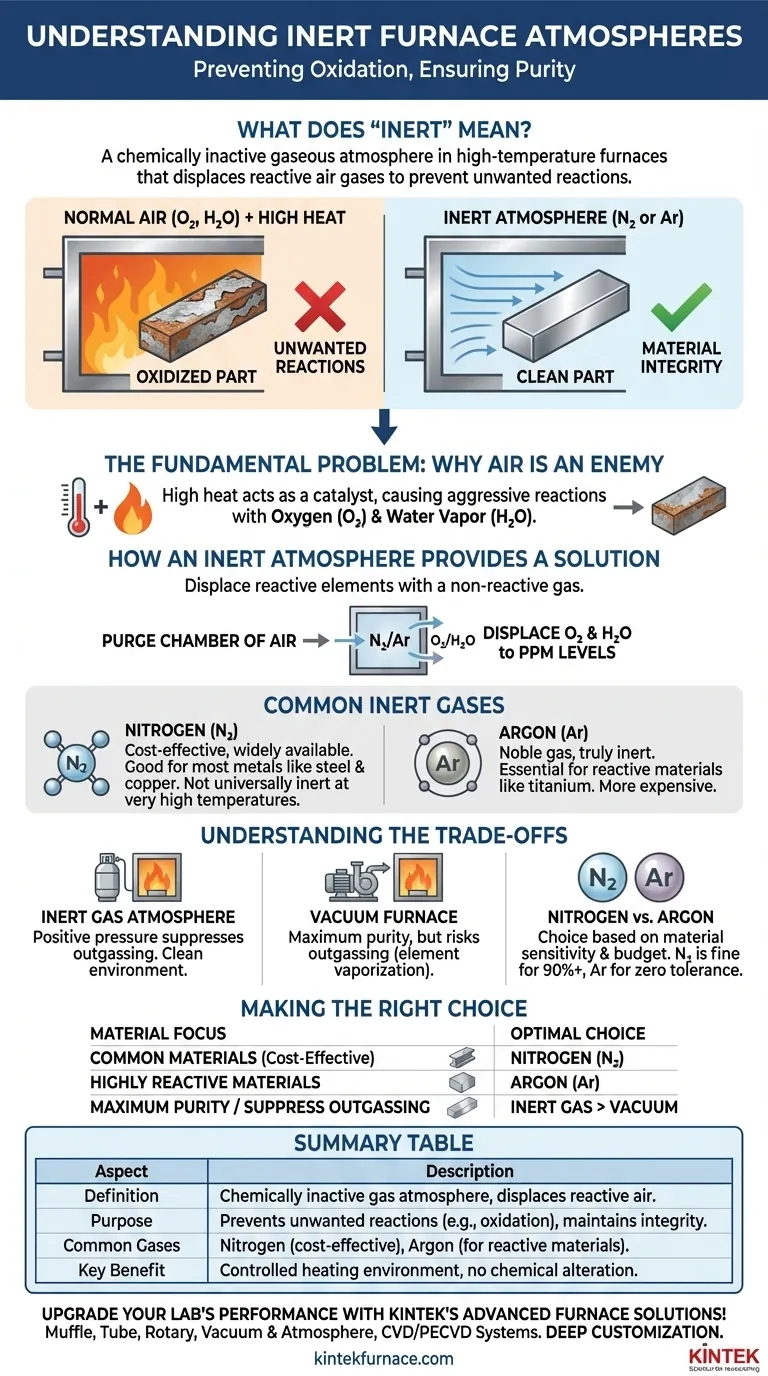
In the context of high-temperature furnaces, the term "inert" refers to a gaseous atmosphere that is chemically inactive. Its purpose is to displace the reactive gases found in normal air—primarily oxygen—to prevent unwanted chemical reactions like oxidation from occurring on the material being processed. This ensures the integrity, purity, and desired properties of the final product are maintained.
High temperatures act as a powerful catalyst for chemical reactions. An inert atmosphere serves as a protective shield, replacing reactive air with a non-reactive gas to create a controlled environment where materials can be heated without being chemically altered or damaged.

The Fundamental Problem: Why Air Is an Enemy
At room temperature, the oxygen in the air is relatively slow to react. However, inside a furnace, the rules change completely.
The Role of High Temperature
Heat provides the energy needed to overcome the activation barrier for chemical reactions. The hotter the furnace, the more aggressively the materials within it will try to react with any available gas molecules.
The Primary Threat: Oxidation
Oxygen is the most significant threat in most heat-treating processes. When a metal is heated in the presence of oxygen, it forms an oxide layer, commonly known as scale. This scale can ruin the surface finish, alter the component's dimensions, and compromise its mechanical properties.
Other Reactive Contaminants
While oxygen is the main concern, other gases in the air, such as water vapor (H₂O), can also be highly reactive at elevated temperatures, contributing to oxidation and other unwanted surface effects.
How an Inert Atmosphere Provides a Solution
The strategy behind using an inert atmosphere is straightforward: if you remove the reactive elements, the unwanted reactions cannot happen.
The Principle of Displacement
The process begins by purging the furnace chamber of ambient air. This is typically done by flushing the sealed chamber with a high-purity inert gas, which displaces the oxygen and water vapor until their concentration is reduced to a negligible level, often just a few parts per million (PPM).
Common Inert Gas: Nitrogen (N₂)
Nitrogen is the workhorse of inert atmospheres due to its wide availability and relatively low cost. For most applications, such as annealing steel or brazing copper, it is sufficiently non-reactive to prevent oxidation and produce a clean, bright part.
Common Inert Gas: Argon (Ar)
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is truly and completely inert under all conditions. While more expensive than nitrogen, it is essential for processing highly reactive materials like titanium, magnesium, and certain superalloys, which can form nitrides if processed in a nitrogen atmosphere at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right atmosphere is a balance of technical requirements, material properties, and cost.
Inert Gas vs. Vacuum
A vacuum furnace achieves a similar goal by physically removing almost all molecules from the chamber, creating an environment with nothing to react with. A vacuum is excellent for maximum purity but can sometimes cause "outgassing," where elements within the alloy itself (like zinc in brass) vaporize and are pulled out of the material. An inert gas atmosphere provides positive pressure, which helps suppress this phenomenon.
The Cost Factor: Nitrogen vs. Argon
The choice between nitrogen and argon is almost always driven by a combination of material sensitivity and budget. Nitrogen is sufficient for over 90% of inert atmosphere applications. Argon is reserved for processes where even the slightest reaction cannot be tolerated.
The Limits of "Inertness"
It is critical to remember that nitrogen is not universally inert. At very high temperatures, it will react with certain elements. Understanding your material's chemistry is essential to avoid creating brittle nitride compounds when you were only trying to prevent oxides.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection of a furnace atmosphere must be driven by the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for common materials: Nitrogen is the optimal choice for processes like annealing steels, copper, and most non-ferrous alloys.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive materials: Argon is necessary for materials like titanium, niobium, or certain refractory metals where nitrogen reactivity is a known risk.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and suppressing evaporation is a priority: An inert gas atmosphere is superior to a vacuum for alloys that are prone to outgassing.
Ultimately, controlling the furnace atmosphere is about controlling the chemical outcome, ensuring your material behaves exactly as intended.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Chemically inactive gas atmosphere that displaces reactive air gases like oxygen. |
| Purpose | Prevents unwanted reactions (e.g., oxidation) to maintain material integrity and purity. |
| Common Gases | Nitrogen (cost-effective for most metals), Argon (essential for highly reactive materials). |
| Key Benefit | Creates a controlled environment for heating without chemical alteration. |
Upgrade your lab's performance with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your process with reliable, tailored inert atmosphere systems!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality



















