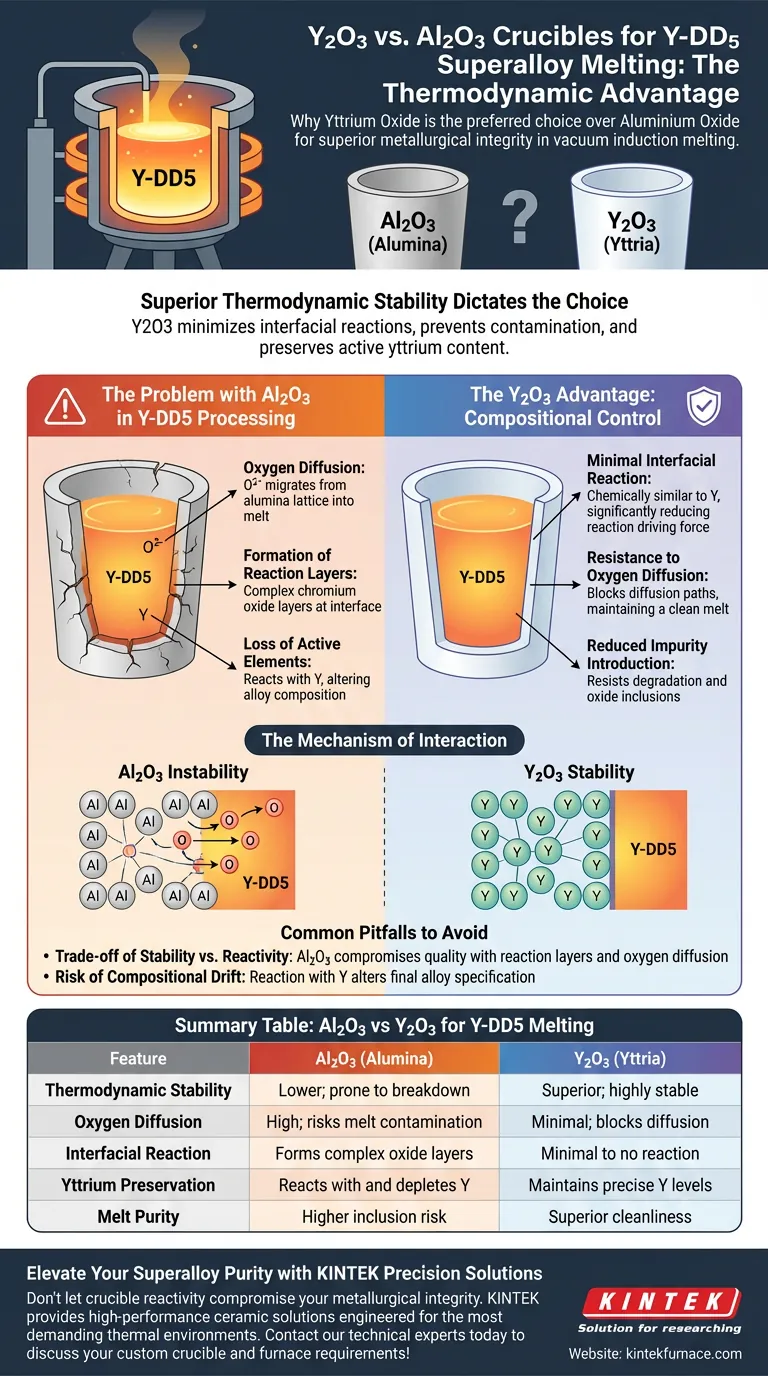
Superior thermodynamic stability dictates the choice. Y2O3 (Yttrium Oxide) ceramic crucibles are preferred over Al2O3 (Aluminium Oxide) because they significantly minimize interfacial reactions with the melt. While Al2O3 suffers from oxygen diffusion and chemical breakdown, Y2O3 remains inert, preventing the contamination of the superalloy and ensuring the active yttrium content within the Y-DD5 alloy is preserved.
The primary advantage of Y2O3 is its inertness towards melts containing active yttrium. By preventing the formation of complex oxide reaction layers common with Al2O3, Y2O3 crucibles preserve the purity and precise stoichiometry of high-performance superalloys.

The Mechanism of Crucible Interaction
To understand why Y2O3 is the superior vessel, one must look at how the crucible material interacts chemically with the molten alloy at high temperatures.
Thermodynamic Stability
Y2O3 offers superior thermodynamic stability compared to Al2O3. In the context of vacuum induction melting, the crucible must resist breaking down under intense heat and vacuum conditions. Yttria (Y2O3) maintains its structural and chemical integrity, whereas alumina (Al2O3) is more prone to instability when in contact with reactive superalloy melts.
Resistance to Oxygen Diffusion
A critical failure mode of Al2O3 crucibles is oxygen diffusion. During the melting process, oxygen from the alumina lattice can migrate into the melt.
This diffusion introduces impurities that compromise the mechanical properties of the final superalloy. Y2O3 crucibles effectively block this diffusion path, maintaining a cleaner melt environment.
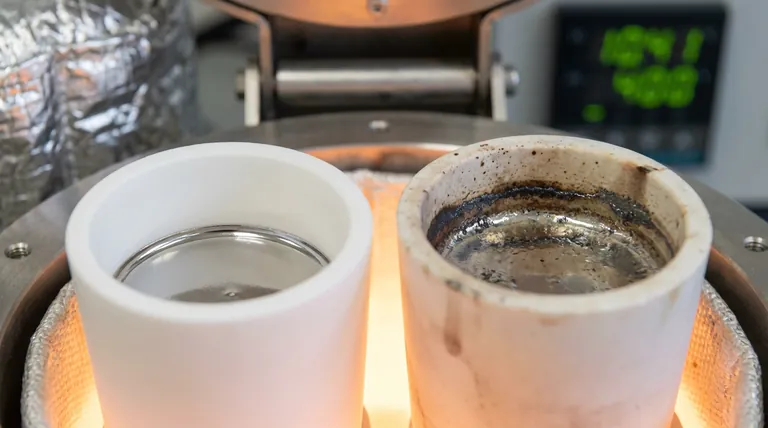
The Problem with Al2O3 in Y-DD5 Processing
Using Al2O3 crucibles for Y-DD5 superalloys triggers specific chemical reactions that degrade the alloy's quality.
Formation of Reaction Layers
When Al2O3 interacts with the melt, it tends to form complex chromium oxide reaction layers at the interface. This physical reaction layer is evidence of the crucible material degrading and chemically bonding with the alloy constituents.
Loss of Active Elements
The most significant drawback of Al2O3 is its reactivity with active yttrium. The Y-DD5 alloy relies on a precise concentration of yttrium for its performance. Al2O3 crucibles react with this active element, effectively stripping it from the melt and altering the alloy's intended composition.
The Y2O3 Advantage: Compositional Control
Y2O3 crucibles are specifically selected to solve the issues created by alumina.
Minimal Interfacial Reaction
Y2O3 shows minimal reaction with melts containing active yttrium. Because the crucible is chemically similar to the active element in the alloy, the driving force for a chemical reaction is significantly reduced.
Reduced Impurity Introduction
By resisting degradation and reaction layer formation, Y2O3 drastically reduces the introduction of oxide inclusions and other impurities. This results in a "cleaner" metal that adheres strictly to metallurgical standards.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
When selecting crucible materials, it is vital to understand the consequences of choosing a less stable oxide like Al2O3.
The Trade-off of Stability vs. Reactivity
While Al2O3 is a standard refractory material, its use in this specific application represents a compromise in quality. The "cost" of using Al2O3 is the formation of reaction layers and the uncontrolled diffusion of oxygen.
The Risk of Compositional Drift
The most dangerous pitfall is compositional drift. If the crucible reacts with the active yttrium, the final product will not match the Y-DD5 specification. Using Y2O3 is the only reliable way to maintain the stability of the alloy composition throughout the melting process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the integrity of your Y-DD5 superalloy production, prioritize the crucible material based on your specific metallurgical requirements.
- If your primary focus is impurity control: Choose Y2O3 to eliminate oxygen diffusion and prevent the introduction of foreign oxides into the melt.
- If your primary focus is compositional accuracy: Select Y2O3 to prevent the loss of active yttrium and ensure the final alloy matches its precise chemical specification.
For critical vacuum induction melting of Y-DD5, Y2O3 provides the necessary chemical inertness to guarantee metallurgical integrity.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Al2O3 (Alumina) | Y2O3 (Yttria) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermodynamic Stability | Lower; prone to breakdown | Superior; highly stable |
| Oxygen Diffusion | High; risks melt contamination | Minimal; blocks diffusion |
| Interfacial Reaction | Forms complex oxide layers | Minimal to no reaction |
| Yttrium Preservation | Reacts with and depletes Y | Maintains precise Y levels |
| Melt Purity | Higher inclusion risk | Superior cleanliness |
Elevate Your Superalloy Purity with KINTEK Precision Solutions
Don't let crucible reactivity compromise your metallurgical integrity. KINTEK provides high-performance ceramic solutions engineered for the most demanding thermal environments. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable for your unique material needs.
Ensure perfect stoichiometry and zero contamination in your next melt. Contact our technical experts today to discuss your custom crucible and furnace requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Fuwei Wang, Hu Zhang. The Influence of Yttrium Content and Ceramic Crucible Materials on Desulfurization during Vacuum Induction Melting of DD5 Superalloys. DOI: 10.3390/met14030353
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What are the specific functions of a magnetic stirrer and a condenser reflux apparatus in the synthesis of KCC-1? Expert Insights
- What is the sucking rate for a single tap on the water circulating vacuum pump? Get Key Specs for Your Lab
- What role do high-purity graphite molds and punches play during the sintering of silicon carbide ceramics in SPS?
- Why is a cylindrical mold made of SS400 steel utilized for slag casting experiments? Explained
- What is the role of providing a uniform heating environment? Achieve Perfect Deep Eutectic Solvent Formation
- How do sealed boxes and backfill materials function during high-temperature powder metallurgy sintering?
- What is the function of a honeycomb-shaped firing tray? Master Thermal Equilibrium in Ceramic Sintering
- How does the density of alumina ceramics compare to steel? Uncover Lighter, High-Performance Material Solutions



















