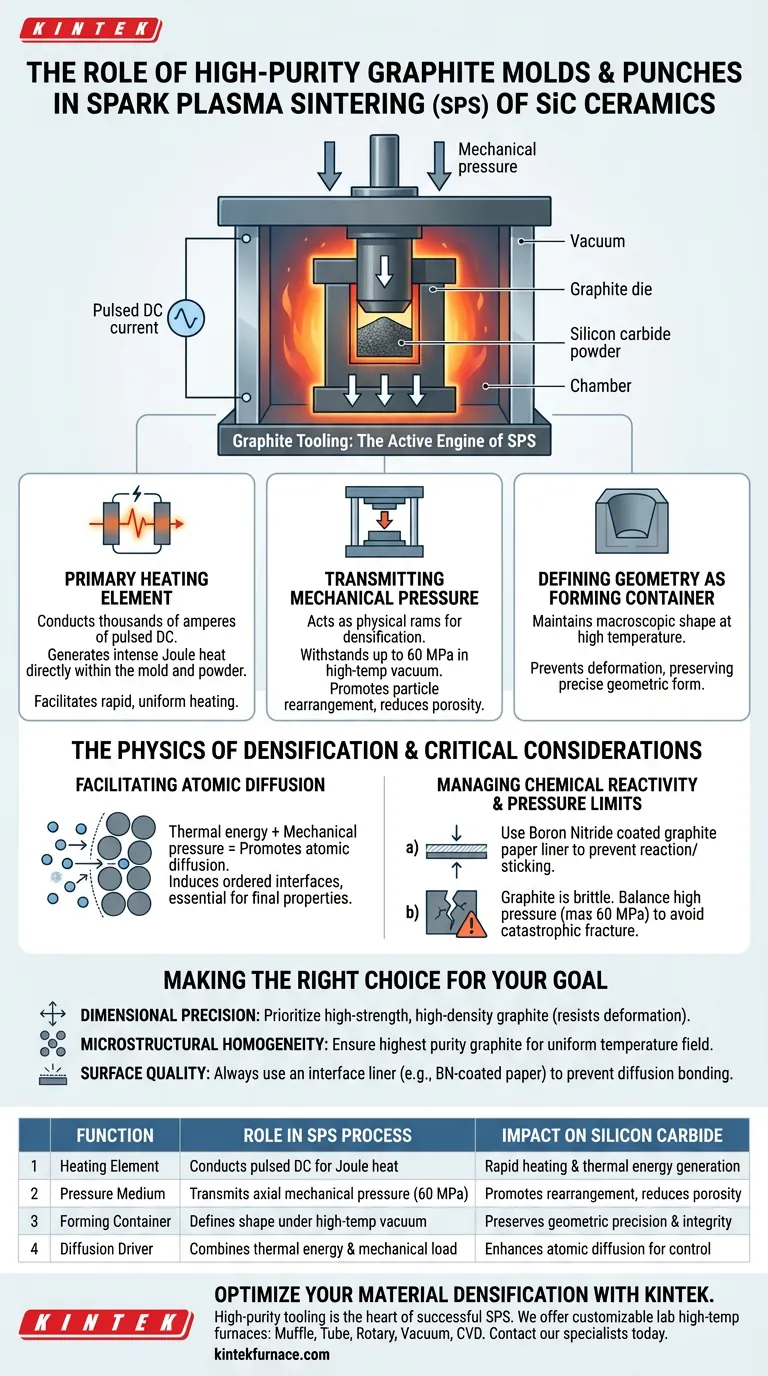
High-purity graphite molds and punches serve as the active engine of the Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) process, functioning as far more than simple containment vessels. In the sintering of silicon carbide, these components perform a simultaneous triple duty: they define the geometric form, act as the primary resistive heating elements, and serve as the transmission medium for high mechanical pressure.
Core Takeaway Graphite tooling is the critical interface in SPS systems that converts electrical energy into thermal energy while simultaneously applying mechanical load, enabling the precise densification and microstructural control of silicon carbide ceramics under vacuum conditions.
The Triple Function of Graphite Tooling
Acting as the Primary Heating Element
In an SPS system, the graphite mold is part of the electrical circuit. It utilizes its high electrical conductivity to allow thousands of amperes of pulsed direct current to pass through the assembly.
This current generates intense Joule heat directly within the mold and around the powder. Unlike conventional sintering which heats from the outside in, the graphite mold ensures thermal energy is generated immediately adjacent to the sample, facilitating rapid heating rates.
Transmitting Mechanical Pressure
The punches within the graphite mold assembly act as the physical rams for densification. They must withstand significant axial pressures—typically up to 60 MPa—while operating in a high-temperature vacuum environment.
This pressure transmission is vital for mechanically compressing the powder particles. It promotes particle rearrangement and reduces porosity, ensuring the final silicon carbide ceramic achieves uniform density distribution.
Defining Geometry as a Forming Container
While managing heat and pressure, the mold maintains the macroscopic shape of the ceramic. The high-temperature strength of the graphite ensures that the mold does not deform under stress, preserving the precise geometry of the sample throughout the sintering cycle.
The Physics of Densification
Facilitating Atomic Diffusion
The combination of direct thermal energy and mechanical pressure promotes atomic diffusion at the particle boundaries. This helps induce the formation of ordered interfaces with semi-coherent characteristics.
These specific microstructural features are essential for the material's final properties, such as minimizing lattice thermal conductivity in the silicon carbide.
Ensuring Thermal Uniformity
The purity and density of the graphite material are not arbitrary specifications; they directly dictate the uniformity of the sintering temperature field.
High-purity graphite ensures consistent electrical and thermal conductivity throughout the mold. This prevents "hot spots" or uneven heating, which could otherwise lead to cracks or density gradients in the final composite.
Critical Considerations and Trade-offs
Managing Chemical Reactivity
While graphite is excellent for heating, it can react with silicon carbide or stick to the sample at high temperatures. This is a common failure point in the process.
To mitigate this, graphite paper—often coated with boron nitride—is used as an isolation layer. This liner prevents adhesion, ensures easier demolding, and protects the surface quality of the ceramic without impeding electrical flow.
Pressure Limitations
Graphite is strong, but it is brittle. While it can handle 60 MPa, exceeding this threshold risks catastrophic fracture of the mold.
Operators must balance the need for high pressure (to maximize density) against the mechanical limits of the graphite tooling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is Dimensional Precision: Prioritize high-strength, high-density graphite grades that resist deformation under the 60 MPa load limit.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Homogeneity: Ensure you use the highest purity graphite available to guarantee a perfectly uniform temperature field across the sample.
- If your primary focus is Surface Quality: Always utilize an interface liner like boron nitride-coated graphite paper to prevent diffusion bonding between the sample and the punch.
The success of your SPS process relies less on the machine itself and more on the integrity and design of your graphite tooling interface.
Summary Table:
| Function | Role in SPS Process | Impact on Silicon Carbide |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | Conducts pulsed DC to generate Joule heat | Facilitates rapid heating and thermal energy generation |
| Pressure Medium | Transmits axial mechanical pressure (up to 60 MPa) | Promotes particle rearrangement and reduces porosity |
| Forming Container | Defines macroscopic shape under high-temp vacuum | Preserves geometric precision and structural integrity |
| Diffusion Driver | Combines thermal energy and mechanical load | Enhances atomic diffusion for microstructural control |
Optimize Your Material Densification with KINTEK
High-purity tooling is the heart of successful Spark Plasma Sintering. At KINTEK, we understand that the integrity of your silicon carbide ceramics depends on the precision of your equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of lab high-temp furnaces—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique research and production needs.
Ready to achieve superior microstructural homogeneity? Contact our specialists today to discover how our customizable sintering solutions can elevate your lab's efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Tribological properties of silicon carbide ceramic surfaces modified by polishing, grinding and laser radiation. DOI: 10.1007/s42452-024-06004-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the maximum working pressure specifications for water circulating vacuum pumps? Ensure Safe Operation and Avoid Failure
- What core environmental protection does an argon-protected glove box provide for sodium-ion batteries? Maximize Safety
- What are the functions of a high vacuum mechanical pump in Ga2O3 PETO? Ensure Purity in Film Preparation
- What are the performance parameters of a circulating water vacuum pump? Optimize Your Lab's Vacuum Efficiency
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles required for the cook-off method? Ensure Safety & Catalyst Purity
- What is the purpose of waveguide-to-coax adapters? Key Roles in High-Temperature Measurement Chains
- Why is an alumina crucible required for bauxite residue thermal analysis? Ensure Stability and Data Purity Up to 1400°C
- What types of trays are compatible with SiC heating elements? Choose Graphite or Composite Ceramics for Thermal Shock Resistance


















