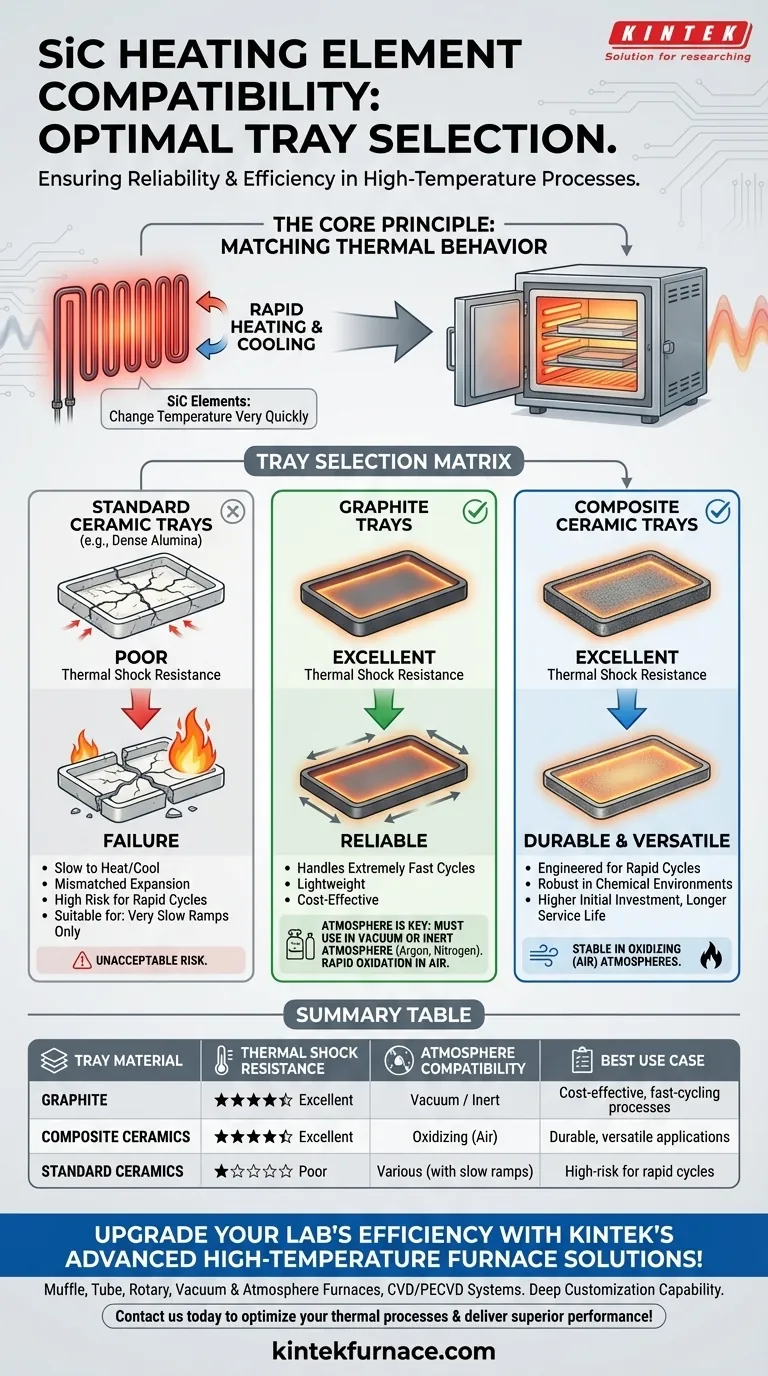
For SiC (silicon carbide) heating elements, you must use trays made from materials that can tolerate rapid temperature changes. The best choices are graphite and composite ceramic trays, as their ability to heat and cool quickly complements the inherent thermal behavior of SiC elements, preventing damage from thermal shock.
The critical factor is not just high-temperature resistance, but thermal compatibility. Your tray material must be able to keep pace with the fast heating and cooling cycles of SiC elements to ensure the reliability and efficiency of your entire thermal process.

The Core Principle: Matching Thermal Behavior
The defining characteristic of SiC heating elements is their ability to change temperature very quickly. This efficiency is a significant advantage, but it places a specific demand on all other components inside the furnace, especially the trays holding your product.
Why SiC Demands Specific Trays
SiC elements can be ramped up to temperature and cooled down far more rapidly than many traditional heating systems. This subjects everything in the furnace to significant thermal stress.
A tray material that cannot expand and contract at a compatible rate will fail. This failure is known as thermal shock.
The Problem with Mismatched Materials
Using a standard refractory tray, like one made of dense alumina, with fast-cycling SiC elements is a common and costly mistake.
The slow-to-heat, slow-to-cool nature of the dense tray conflicts with the rapid changes of the SiC elements. This mismatch creates internal stresses, leading to cracks, fractures, and ultimately, complete failure of the tray.
Recommended Tray Materials
To avoid system failure, you must select a tray material specifically designed for high thermal shock resistance.
Graphite Trays
Graphite is an excellent choice for its superior thermal shock resistance and light weight. It can handle extremely fast heating and cooling rates without cracking.
Its properties make it a natural partner for SiC elements, especially in cost-sensitive applications, which aligns with a common reason for choosing SiC in the first place.
Composite Ceramic Trays
These are advanced materials engineered specifically to overcome the thermal shock limitations of traditional ceramics.
They blend different ceramic materials to create a composite structure that offers excellent durability across rapid temperature cycles. They are often more robust than graphite in certain chemical environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material requires you to consider your specific process conditions, particularly the furnace atmosphere.
Graphite: Atmosphere is Key
The primary limitation of graphite is its reactivity with oxygen at high temperatures. Using graphite trays in an air atmosphere will cause them to oxidize rapidly, leading to degradation and failure.
Graphite is only suitable for processes run in a vacuum or an inert atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen).
Composite Ceramics: Cost vs. Versatility
Composite ceramic trays are generally more expensive than graphite. However, they are often formulated to be stable in oxidizing (air) atmospheres.
This makes them the superior choice for applications that require durability in air, justifying the higher initial investment through longer service life and process versatility.
Standard Ceramics: A High-Risk Choice
While inexpensive, standard high-alumina or other dense refractory trays are a poor match for the dynamic nature of SiC elements. Their low thermal shock resistance makes them suitable only for processes with very slow, controlled heating and cooling ramps.
For any application taking advantage of SiC's fast-cycling capability, these trays pose an unacceptable risk of failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by your specific operational environment and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency in a vacuum or inert gas furnace: Graphite trays offer the best performance and value by matching the thermal properties of your SiC elements.
- If your primary focus is durability in an air or oxidizing atmosphere: Invest in composite ceramic trays designed for high thermal shock resistance to ensure long-term reliability.
- If you are running rapid heating and cooling cycles: Absolutely avoid standard dense ceramic trays, as their poor thermal shock resistance will lead to cracking and process failure.
Matching your tray material to the thermal properties of your SiC elements is the foundation of a reliable and efficient high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Tray Material | Thermal Shock Resistance | Atmosphere Compatibility | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Excellent | Vacuum or Inert | Cost-effective, fast-cycling processes |
| Composite Ceramics | Excellent | Oxidizing (Air) | Durable, versatile applications |
| Standard Ceramics | Poor | Various (with slow ramps) | High-risk for rapid cycles |
Upgrade your lab's efficiency with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, including selecting the right trays for SiC heating elements to prevent thermal shock and enhance reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes and deliver superior performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















