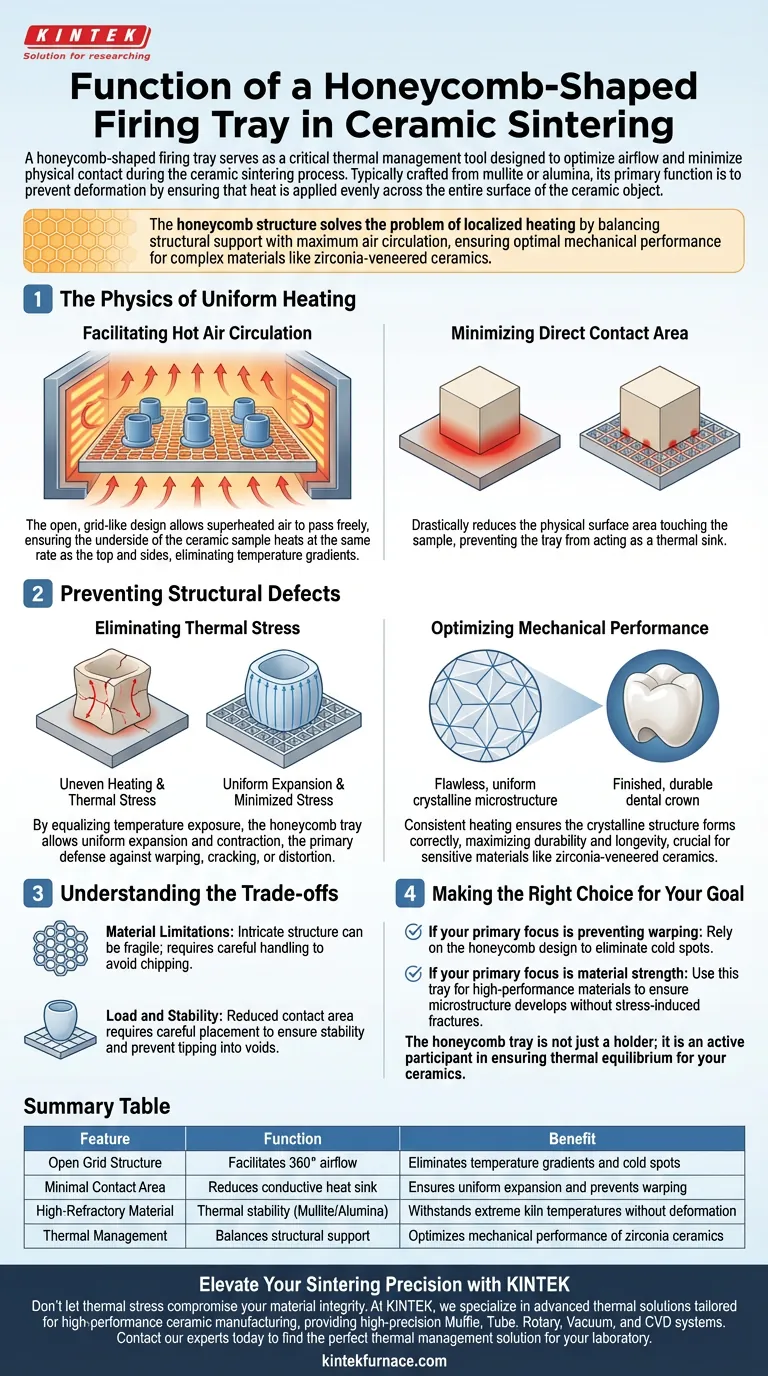
A honeycomb-shaped firing tray serves as a critical thermal management tool designed to optimize airflow and minimize physical contact during the ceramic sintering process. Typically crafted from heat-resistant materials like mullite or alumina, its primary function is to prevent deformation by ensuring that heat is applied evenly across the entire surface of the ceramic object.
The honeycomb structure solves the problem of localized heating by balancing structural support with maximum air circulation. This design ensures that complex materials, such as zirconia-veneered ceramics, achieve optimal mechanical performance without succumbing to thermal stress.

The Physics of Uniform Heating
Facilitating Hot Air Circulation
The defining feature of these trays is their open, grid-like design. This structure allows superheated air to pass freely through the tray rather than being blocked by a solid surface.
By permitting airflow from beneath, the tray ensures that the underside of the ceramic sample heats at the same rate as the top and sides. This eliminates the temperature gradients that often occur on solid firing plates.
Minimizing Direct Contact Area
A solid tray creates a large contact patch that can act as a thermal sink, drawing heat away from the ceramic or heating up slower than the surrounding air.
The honeycomb design drastically reduces the physical surface area touching the sample. This isolation ensures the ceramic is influenced primarily by the ambient kiln temperature, not the conductive properties of the tray itself.
Preventing Structural Defects
Eliminating Thermal Stress
When a ceramic object heats unevenly, different parts of the material expand at different rates. This creates internal tension known as thermal stress.
By equalizing the temperature exposure, the honeycomb tray allows the material to expand and contract uniformly. This is the primary defense against warping, cracking, or distortion during the firing cycle.
Optimizing Mechanical Performance
The ultimate goal of sintering is to achieve specific material properties, such as hardness and fracture toughness.
For sensitive materials like zirconia-veneered ceramics, consistent heating is non-negotiable. The honeycomb tray ensures the crystalline structure forms correctly, maximizing the durability and longevity of the final restoration.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Material Limitations
While the design is efficient, the materials used to make these trays—mullite and alumina—are chosen for thermal stability, not infinite durability.
The intricate honeycomb structure can be more fragile than solid slabs. They require careful handling to avoid chipping the thin grid walls, which could create uneven surfaces for future firings.
Load and Stability
The reduced contact area is excellent for thermodynamics but requires careful placement of the ceramic samples.
Because the support is not continuous, the operator must ensure the ceramic is stable and not liable to tip into the voids of the grid.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To get the most out of your sintering process, align your equipment choice with your specific quality targets.
- If your primary focus is preventing warping: Rely on the honeycomb design to eliminate cold spots and ensure the underside of the ceramic heats synchronously with the rest of the unit.
- If your primary focus is material strength: Use this tray type for high-performance materials like zirconia to ensure the microstructure develops without stress-induced fractures.
The honeycomb tray is not just a holder; it is an active participant in ensuring thermal equilibrium for your ceramics.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Open Grid Structure | Facilitates 360° airflow | Eliminates temperature gradients and cold spots |
| Minimal Contact Area | Reduces conductive heat sink | Ensures uniform expansion and prevents warping |
| High-Refractory Material | Thermal stability (Mullite/Alumina) | Withstands extreme kiln temperatures without deformation |
| Thermal Management | Balances structural support | Optimizes mechanical performance of zirconia ceramics |
Elevate Your Sintering Precision with KINTEK
Don’t let thermal stress compromise your material integrity. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced thermal solutions tailored for high-performance ceramic manufacturing. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable lab high-temp furnaces designed to meet your unique sintering needs.
Ready to achieve superior mechanical properties? Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal management solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Moritz Hoffmann, Bogna Stawarczyk. Mechanical Properties of High- and Low-Fusing Zirconia Veneering Ceramics Fired on Different Trays and Substrates. DOI: 10.3390/ma17102261
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the performance parameters of a circulating water vacuum pump? Optimize Your Lab's Vacuum Efficiency
- Why is a cylindrical mold made of SS400 steel utilized for slag casting experiments? Explained
- How does a water circulating vacuum pump create negative pressure? Discover the Liquid-Ring Mechanism for Efficient Lab Vacuum
- Why is an alumina crucible required for bauxite residue thermal analysis? Ensure Stability and Data Purity Up to 1400°C
- What is the function of the substrate heating system for WS2 thin films? Optimize Crystallinity and Adhesion
- Why is a vacuum drying oven essential for Pd-Ni/ZrO2 catalyst preparation? Ensure Uniform Metal Distribution
- What is the function of high-purity graphite molds during SPS of Cu2Se? Essential Tips for Superior Sintering
- What key functions do high-strength graphite molds perform? Optimize Al2O3/TiC Hot Press Sintering Success



















