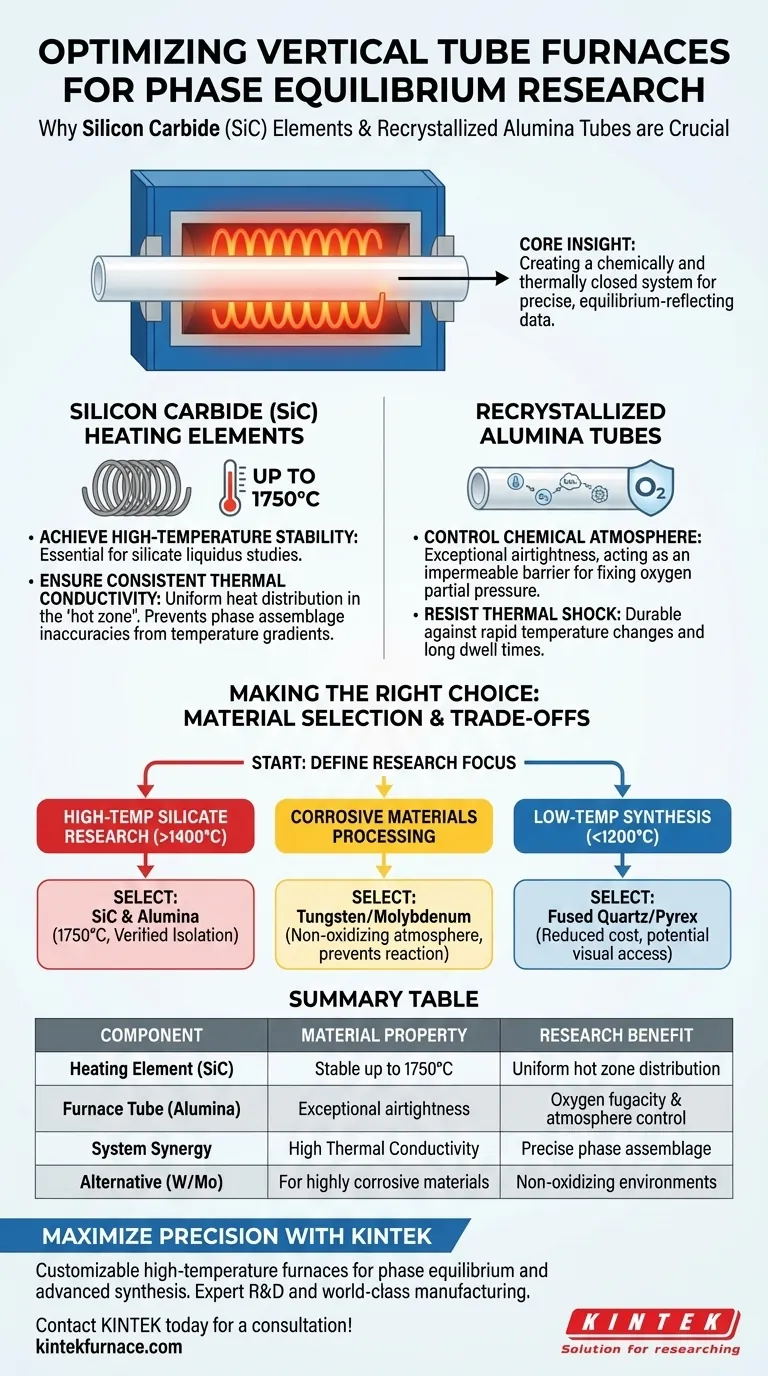
Achieving precise phase equilibrium data requires a furnace configuration that prioritizes thermal stability and atmospheric isolation. Silicon Carbide (SiC) heating elements are strictly chosen for their ability to maintain stable operating temperatures up to 1750°C, a requirement for high-temperature silicate liquidus studies. Recrystallized alumina tubes are paired with these elements primarily for their airtightness, which is critical for maintaining the specific air atmospheres needed to validate thermodynamic experiments.
Core Insight Phase equilibrium research is not just about heating a sample; it is about establishing a chemically and thermally closed system. The combination of SiC elements and recrystallized alumina tubes creates a robust environment where temperature and oxygen fugacity can be strictly controlled, ensuring the resulting data reflects true equilibrium conditions.

The Role of Silicon Carbide (SiC) Heating Elements
Achieving High-Temperature Stability
Standard metallic heating elements often fail or degrade rapidly at the temperatures required for geological or advanced ceramics research.
Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements are utilized specifically because they remain stable and operational up to 1750°C. This high ceiling is essential for silicate liquidus studies, where materials must be melted and equilibrated at extreme heat.
Ensuring Consistent Thermal Conductivity
SiC is chosen for its high thermal conductivity and high-temperature strength.
This ensures that the heat distribution within the "hot zone" of the furnace remains uniform. In phase equilibrium studies, even minor temperature gradients can alter the phase assemblage, rendering the data inaccurate.
The Function of Recrystallized Alumina Tubes
Controlling the Chemical Atmosphere
The primary reason for selecting recrystallized alumina is its exceptional airtightness.
To study phase equilibrium, researchers often need to fix the atmosphere (e.g., controlling oxygen partial pressure). The alumina tube acts as an impermeable barrier, isolating the internal experiment from the external lab environment.
Resisting Thermal Shock
Experiments often involve rapid temperature changes or long dwell times.
Recrystallized alumina is engineered to possess high thermal shock resistance. This durability prevents the tube from cracking during the heating and cooling cycles inherent to thermodynamic experiments, protecting both the sample and the heating elements.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Material Limitations
While recrystallized alumina is excellent for air and inert atmospheres, it is not a universal solution.
Supplementary data indicates that for processes involving highly corrosive materials, alumina may degrade. In such specific cases, tubes made from tungsten or molybdenum are preferred, though they often require non-oxidizing atmospheres to prevent the tube itself from oxidizing.
Application Specificity
SiC and alumina are optimized for high-temperature stability, but they may be overkill for lower-temperature applications.
For research below 1200°C or where transparency is required, materials like fused quartz or Pyrex are commonly used. Choosing SiC/Alumina implies a specific need for the >1400°C range and strict atmosphere control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring a vertical tube furnace, your material selection dictates the validity of your research data.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature silicate research: Rely on the SiC and Recrystallized Alumina combination to reach 1750°C with verified atmospheric isolation.
- If your primary focus is processing corrosive materials: Move away from standard alumina and investigate tungsten or molybdenum tubes to prevent reaction with the containment vessel.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature synthesis: Consider fused quartz or Pyrex to reduce costs and potentially gain visual access to the sample, provided the temperature remains moderate.
Select your components based not just on maximum temperature, but on the chemical strictness required by your thermodynamic model.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material Property | Research Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Stable operation up to 1750°C; uniform hot zone distribution |
| Furnace Tube | Recrystallized Alumina | Exceptional airtightness for oxygen fugacity & atmosphere control |
| System Synergy | High Thermal Conductivity | Ensures precise phase assemblage by minimizing temperature gradients |
| Alternative | Tungsten/Molybdenum | Required for highly corrosive materials in non-oxidizing environments |
Maximize Your Research Precision with KINTEK
Ensure the integrity of your thermodynamic data with high-performance heating solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems.
Our lab high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet the rigorous demands of phase equilibrium studies and advanced material synthesis. Whether you need the extreme stability of SiC elements or specialized tube materials for corrosive environments, our technical team is ready to build the perfect system for your unique needs.
Ready to upgrade your laboratory capabilities? Contact KINTEK today for a custom consultation!
Visual Guide
References
- Georgii Khartcyzov, Evgueni Jak. Integrated Experimental and Thermodynamic Modelling Study of Phase Equilibria in the PbO-AlO1.5-SiO2 System in Air. DOI: 10.1007/s12540-024-01878-4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- What happens when a ceramic heating element reaches its preset temperature? Discover Self-Regulating Safety and Efficiency
- What is the basic concept behind heating elements? Discover How They Efficiently Convert Electricity to Heat
- What is a key property of silicon carbide as a ceramic material? Discover Its High-Temp and Thermal Conductivity Edge
- How does the lifespan of MoSi2 heating elements compare to Silicon Carbide elements? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the durability benefits of high temperature heating elements? Superior Lifespan and Lower Costs
- In which industries are quartz tubes commonly used? Essential for High-Tech and Clean Processes
- What are resistance heating elements made of and where are they used? Discover Materials for Efficient Heat Generation
- What are the requirements for good heating element materials? Optimize Your Heating Solutions with Expert Insights



















