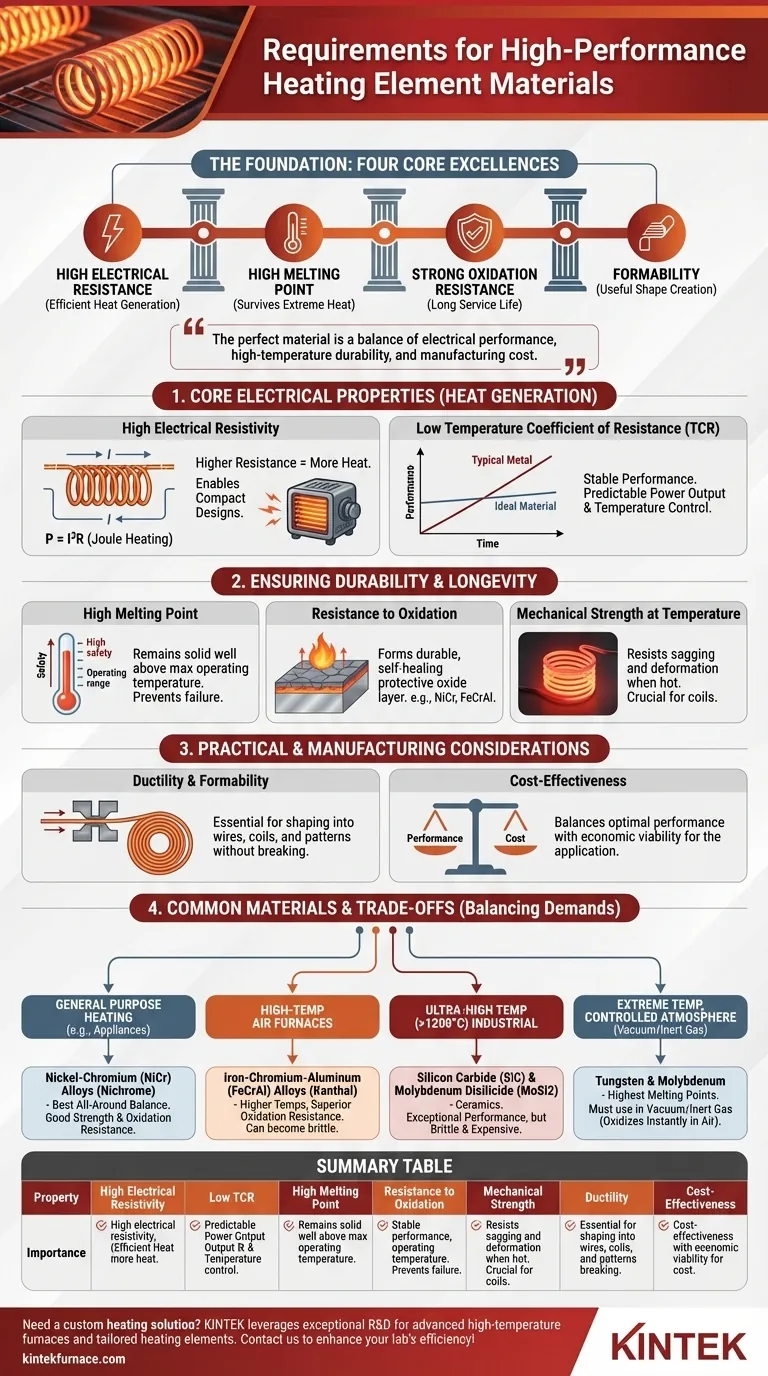
At its core, a good heating element material must excel at four things: it must have high electrical resistance to generate heat efficiently, a high melting point to survive its own heat, strong resistance to oxidation to ensure a long service life, and the ability to be formed into a useful shape. These properties are the foundation for creating a reliable and effective heating component.
The search for the perfect heating element material is not about finding a single "best" option. It is an engineering exercise in balancing conflicting requirements—electrical performance, high-temperature durability, and manufacturing cost—to fit the precise demands of the application.
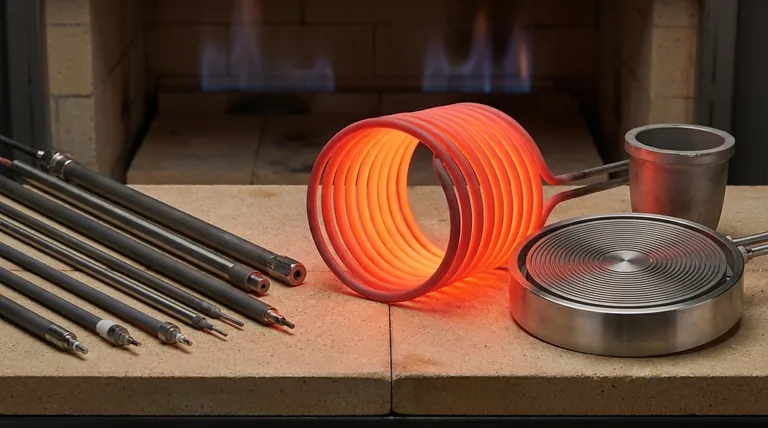

The Core Electrical Properties for Heat Generation
The primary function of a heating element is to convert electrical energy into thermal energy. This conversion is governed by two fundamental electrical properties.
High Electrical Resistivity
A material with high electrical resistivity (or specific resistance) is essential. This property determines how strongly a material opposes the flow of electric current.
According to the principle of Joule heating (Power = I²R), for a given electrical current (I), a higher resistance (R) produces significantly more heat. This allows for the design of compact, powerful heaters without needing excessively long wires.
Low Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR)
A low and predictable temperature coefficient of resistance is crucial for stable performance. TCR measures how much a material's resistance changes as its temperature changes.
While most metals have a positive TCR (resistance increases with heat), an ideal heating element's resistance remains relatively constant across its operating range. This stability ensures that the power output and temperature are predictable and controllable, preventing thermal runaway or performance dips.
Ensuring Durability and Longevity
A heating element must not only produce heat but also survive the extreme conditions it creates. Its lifespan is determined by its ability to withstand high temperatures and atmospheric exposure.
High Melting Point
The most obvious requirement is a high melting point. The material must remain solid and structurally sound well above its maximum intended operating temperature to provide a safe margin and prevent catastrophic failure.
Resistance to Oxidation
At high temperatures, most metals react rapidly with oxygen in the air, causing them to degrade and burn out. A premier heating element material must be highly resistant to oxidation.
Materials like Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) and Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) achieve this by forming a thin, durable, and self-healing layer of protective oxide on their surface. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing further oxygen from reaching the base metal.
Mechanical Strength at Temperature
Materials become softer and weaker as they heat up. A good heating element must maintain sufficient mechanical strength to hold its shape and resist sagging or stretching when glowing hot. This is critical for coiled elements, which can otherwise deform and cause short circuits.
Practical and Manufacturing Considerations
Beyond performance and durability, the material must be practical to manufacture and economically viable for the intended application.
Ductility and Formability
Ductility is the ability of a material to be stretched or drawn into a wire without breaking. This property is non-negotiable, as most heating elements are made from wires that are then wound into coils or formed into specific patterns.
Cost-Effectiveness
Engineering is always a balance of performance and cost. While materials like platinum offer excellent properties, their high cost makes them suitable only for specialized scientific or medical applications. The most widely used materials offer the best possible performance for an acceptable price.
Common Materials and Their Trade-offs
No single material is perfect for every situation. The choice is always a trade-off based on temperature, environment, and cost.
The Workhorse: Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) Alloys
Often known by the trade name Nichrome, NiCr alloys are the most common general-purpose heating materials. They offer a great balance of high resistivity, good oxidation resistance, and excellent mechanical strength when hot.
The High-Temp Alternative: Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) Alloys
Also known as Kanthal alloys, FeCrAl materials can operate at higher temperatures than NiCr and offer superior oxidation resistance. However, they can become brittle after repeated heating cycles, making them less suitable for applications involving vibration or frequent movement.
The Ultra-High Temperature Specialists: SiC and MoSi2
For industrial furnaces operating above 1200°C, metallic alloys reach their limits. Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) are ceramics that offer exceptional performance at extreme temperatures but are inherently brittle and more expensive.
The Extreme Case: Tungsten and Molybdenum
Tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal, making it ideal for the most extreme temperature applications. However, both Tungsten and Molybdenum oxidize almost instantly in air at high temperatures and must be used in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection must be guided by the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heating (e.g., appliances, lab equipment): Nickel-Chromium (NiCr) alloys provide the best all-around balance of cost, durability, and performance.
- If your primary focus is very high-temperature air furnaces: Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (FeCrAl) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) are superior choices for their exceptional oxidation resistance.
- If your primary focus is stability and precision: Prioritize materials with the lowest possible Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (TCR) to ensure predictable power output.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high temperatures in a controlled atmosphere: Tungsten or Molybdenum are the only viable options, provided you can operate in a vacuum or inert gas.
Ultimately, understanding these core material properties empowers you to select a heating element that is not just functional, but optimized for its purpose.
Summary Table:
| Property | Importance |
|---|---|
| High Electrical Resistivity | Efficient heat generation via Joule heating, enabling compact designs |
| Low Temperature Coefficient of Resistance | Stable performance and predictable power output |
| High Melting Point | Prevents failure at high temperatures |
| Resistance to Oxidation | Extends service life by preventing degradation |
| Mechanical Strength | Maintains shape and prevents sagging at high temperatures |
| Ductility and Formability | Allows shaping into wires and coils for manufacturing |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Balances performance with economic viability |
Need a custom heating solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and durability with tailored heating elements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability



















