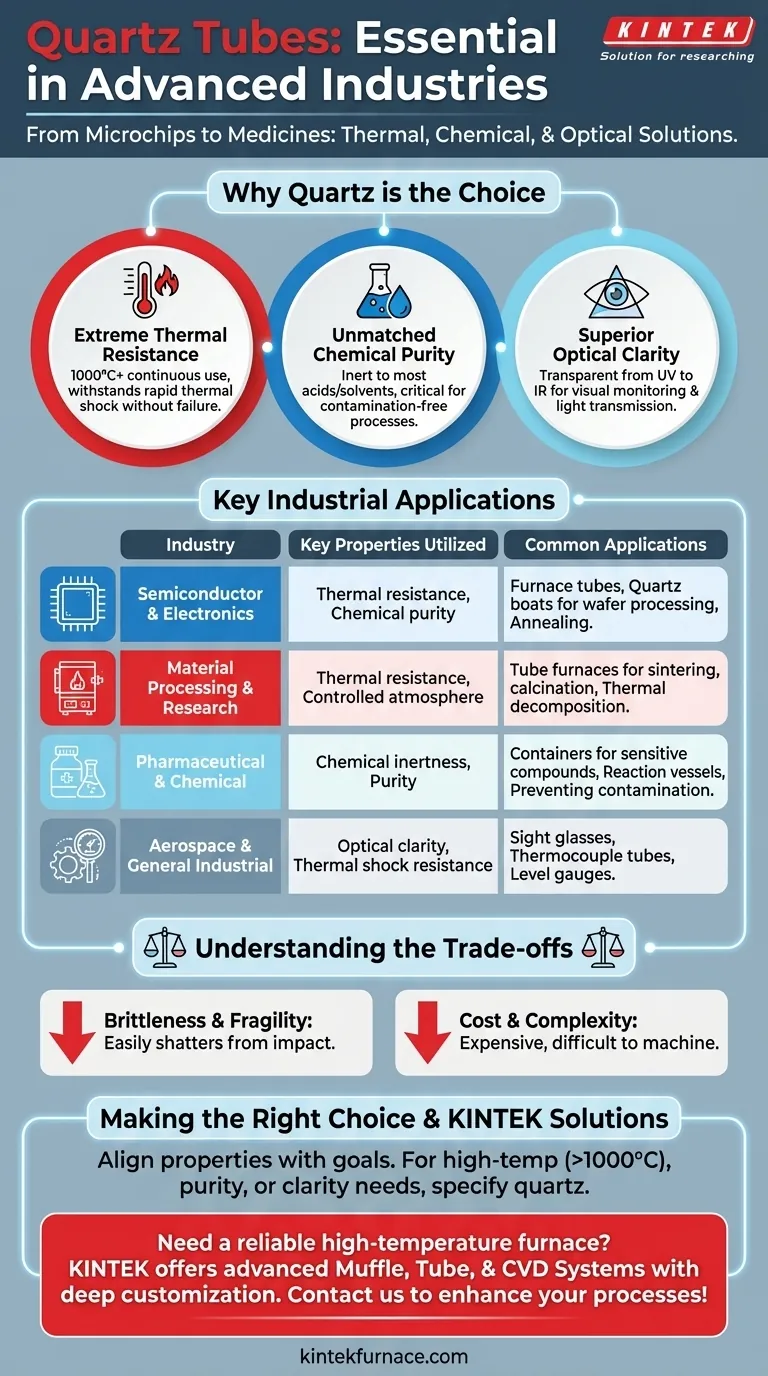
From creating microchips to developing new medicines, quartz tubes are indispensable components across a wide range of advanced industries. Their primary applications are found in semiconductor manufacturing, material processing, research laboratories, and the pharmaceutical sector, with additional uses in aerospace and general industrial settings. This wide adoption is due to a unique combination of thermal, chemical, and optical properties.
The widespread use of quartz tubes is not arbitrary; it's a direct result of their three core properties: exceptional thermal resistance, high chemical purity, and optical clarity. Industries choose quartz wherever a process demands a contamination-free, transparent material that can withstand extreme heat and chemical exposure.

Why Quartz is the Material of Choice
The value of quartz tubes is rooted in a few fundamental characteristics that make them superior to other materials like standard glass or ceramics in specific, demanding environments.
Extreme Thermal Resistance
Quartz, specifically fused quartz, possesses an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it can endure rapid and extreme temperature changes—known as thermal shock—without cracking or failing.
It maintains its structural integrity at continuous operating temperatures well above 1000°C, making it essential for high-temperature furnaces and processing equipment.
Unmatched Chemical Purity and Inertness
Quartz is composed of silicon dioxide in a very pure, non-crystalline form. It is highly chemically inert, meaning it does not react with most acids, solvents, or other chemicals.
This purity is critical in applications like semiconductor and pharmaceutical manufacturing, where even microscopic levels of contamination from the container can ruin an entire batch or process.
Superior Optical Clarity
Quartz is transparent to a wide spectrum of light, from ultraviolet (UV) to infrared (IR). This clarity allows it to be used in applications where visual monitoring or light transmission is necessary.
Key Industrial Applications by Function
Different industries leverage specific properties of quartz to solve critical operational challenges. The application dictates which property is most important.
In Semiconductor and Electronics Manufacturing
This is one of the largest markets for quartz. It is used for furnace tubes, wafer carriers (quartz boats), and end caps in processes like annealing and chemical vapor deposition.
Here, both high purity and thermal resistance are non-negotiable. The material must withstand extreme heat cycles while ensuring the silicon wafer environment remains absolutely free of contaminants.
In Material Processing and Research Furnaces
Tube furnaces are a staple in metallurgy, new energy research (like lithium batteries), and materials science labs. Quartz tubes form the central reaction chamber.
They create a controlled atmosphere for processes like sintering, calcination, and thermal decomposition, where high temperatures are required to transform materials.
In Pharmaceutical and Chemical Production
The chemical inertness of quartz is its most valued trait in this sector. It ensures that sensitive compounds and high-purity chemicals are not contaminated by elements leaching from their container.
This maintains the safety, stability, and efficacy of the final pharmaceutical product.
As Critical Industrial Components
In broader industrial settings, quartz serves specialized roles. It is used for sight glasses and level gauges on high-temperature or corrosive chemical tanks, allowing for safe visual monitoring.
It also acts as protective thermocouple tubes, sheathing delicate temperature sensors from harsh environments so they can provide accurate readings without being damaged.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, quartz is not the solution for every problem. Being an effective advisor means acknowledging limitations.
Brittleness and Mechanical Fragility
Despite its thermal strength, quartz is a brittle material. It can easily shatter from a sharp mechanical impact. It requires careful handling and installation to prevent breakage.
Cost and Machining Complexity
Fused quartz is significantly more expensive than common materials like borosilicate glass. It is also a very hard material, making it difficult and costly to machine into complex shapes. This often limits its use to applications where its unique properties are strictly necessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the right material, you must align its properties with your primary technical and business goals.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing (>1000°C) in a controlled atmosphere: A quartz furnace tube is the industry-standard solution.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute purity in a chemical or semiconductor process: The inertness and purity of quartz make it an essential material to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is visual monitoring of a harsh, high-heat process: A quartz sight glass provides the necessary optical clarity and thermal shock resistance.
- If your application is below 500°C and does not have strict purity requirements: Borosilicate glass is often a more economical and suitable alternative.
By understanding these core principles, you can confidently specify quartz for applications where performance and purity cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Properties Utilized | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductor & Electronics | Thermal resistance, Chemical purity | Furnace tubes, Quartz boats for wafer processing |
| Material Processing & Research | Thermal resistance, Controlled atmosphere | Tube furnaces for sintering, calcination |
| Pharmaceutical & Chemical | Chemical inertness, Purity | Containers for sensitive compounds, Reaction vessels |
| Aerospace & General Industrial | Optical clarity, Thermal shock resistance | Sight glasses, Thermocouple tubes |
Need a reliable high-temperature furnace solution for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet unique experimental requirements in industries like semiconductor, pharmaceutical, and material processing. Contact us today to enhance your processes with tailored quartz tube applications and more!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role do tube furnaces play in semiconductor and battery production? Unlock Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What materials are used for the tubes in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Choose the Right Tube for Your Lab
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the function of high-vacuum encapsulated quartz tubes for Ce2(Fe, Co)17? Ensure Phase Purity and Stability
- What is the primary function of high-purity quartz sealed tubes? Master Sb-Te Alloy Synthesis with Precision Isolation



















