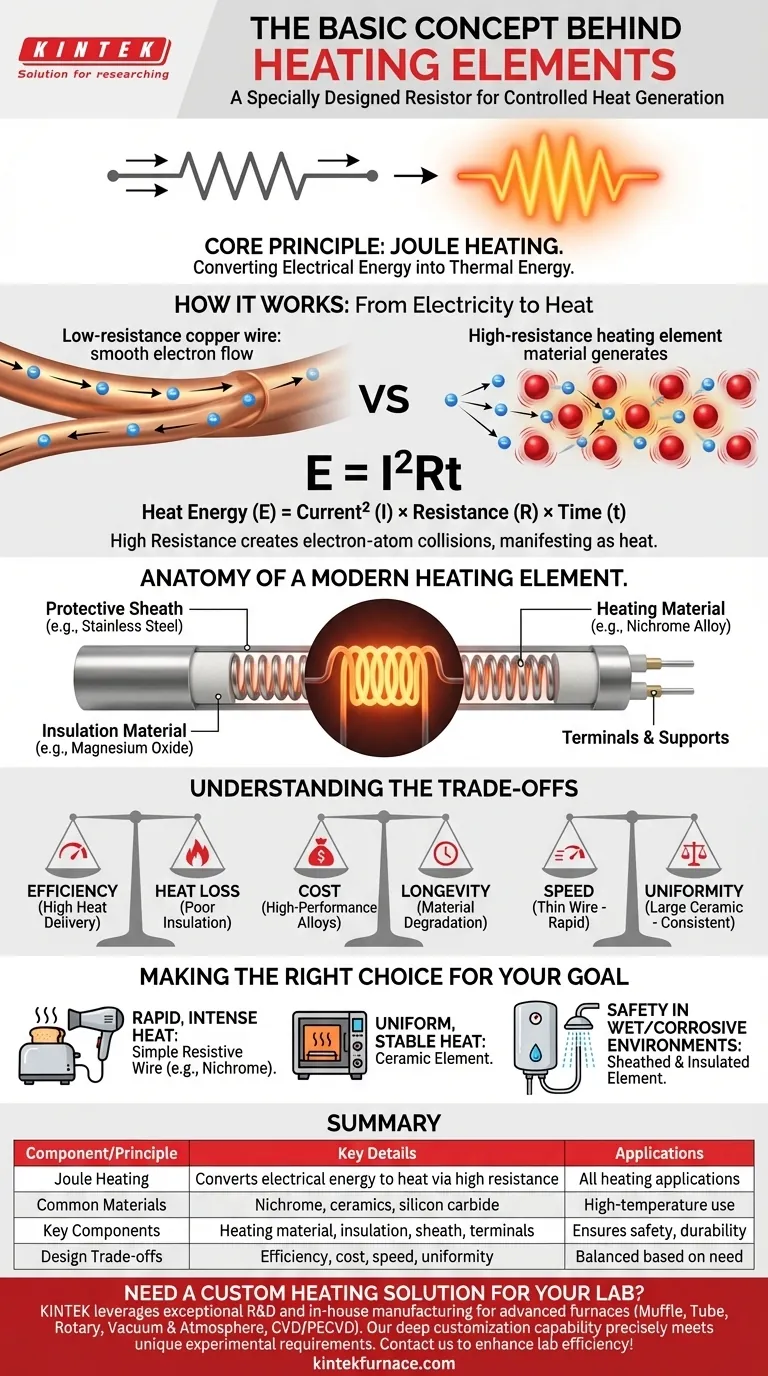
At its core, a heating element is a specially designed resistor. It works by intentionally converting electrical energy into heat energy through a principle known as Joule heating. When an electric current flows through a material with high electrical resistance, the electrons struggle to pass through, causing friction at an atomic level that manifests as heat. This allows for precise, controllable heat generation, turning electricity into a modern, manageable form of fire.
A heating element is simply a material that is a poor conductor of electricity. By forcing current through this high-resistance path, electrical energy is transformed directly into thermal energy, providing a clean and controllable source of heat for countless applications.

The Core Principle: Joule Heating
The function of every electrical heating element is governed by a fundamental law of physics. Understanding this principle is key to seeing why these components are so effective.
From Electricity to Heat
When electricity flows through a conductor, electrons move through the material. In a material with high resistance, these electrons constantly collide with the atoms of the material.
Each collision transfers kinetic energy from the electron to the atom, causing the atom to vibrate more intensely. This increased atomic vibration is what we perceive as heat.
The Formula for Heat
This relationship is quantified by the formula E = I²Rt.
In simple terms, this means the heat energy (E) generated is a product of the electrical current (I) squared, the material's resistance (R), and the time (t) the current flows. Increasing the resistance or the current dramatically increases the heat output.
Why Not Just Any Wire?
A standard copper wire is designed to have very low resistance to conduct electricity efficiently with minimal heat loss.
A heating element does the exact opposite. It uses materials with inherently high resistance specifically to maximize heat generation, turning an electrical inefficiency into a useful feature.
Anatomy of a Modern Heating Element
While the principle is simple, a practical heating element is an engineered system with several key components designed for safety, durability, and performance.
The Heating Material
This is the heart of the element. Materials are chosen for their ability to resist current and withstand high temperatures. Common examples include metallic alloys like Nichrome (an alloy of nickel and chromium) or non-metallic materials like ceramics and silicon carbide.
The Insulation Material
The resistive material is often encased in a high-temperature electrical insulator, such as magnesium oxide powder or ceramic beads. This prevents the energized coil from shorting out against its own protective sheath and helps direct the heat outwards.
The Protective Sheath
A metal tube, or sheath, typically made of stainless steel or another corrosion-resistant alloy, encloses the core components. This sheath protects the element from moisture, physical damage, and chemical corrosion, making it safe for use in appliances like water heaters and ovens.
Terminals and Supports
Terminals provide a safe and secure point to connect the element to the power source. Internal supports and brackets ensure the resistive wire remains stable and doesn't deform or break under the stress of repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting or designing a heating element involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" material or design; the optimal choice depends entirely on the application.
Efficiency vs. Heat Loss
The conversion of electricity to heat at the element itself is nearly 100% efficient. However, the practical efficiency of the appliance depends on how well that heat is delivered to its target. Poor insulation or design can lead to significant heat loss to the surrounding environment, wasting energy.
Cost vs. Longevity
High-performance alloys that resist oxidation at extreme temperatures are more expensive. Cheaper materials may work well initially but can quickly degrade, become brittle, and fail, especially when exposed to air while hot. Longevity is a direct function of material quality.
Speed vs. Uniformity
A thin wire element, like in a toaster, heats up almost instantly, providing rapid and intense heat. A larger ceramic element, found in some space heaters, takes longer to warm up but radiates heat more evenly and consistently over a wider area.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The design of a heating element is dictated by its intended use. By understanding the core requirements of your task, you can recognize why a specific type of element is used.
- If your primary focus is rapid, intense heat: A simple resistive wire element, like the Nichrome coils in a hair dryer or toaster, is the most direct and effective solution.
- If your primary focus is uniform, stable heat: A ceramic element, which heats evenly and radiates consistently, is superior for applications like kilns or high-end space heaters.
- If your primary focus is safety in a wet or corrosive environment: A sheathed element with robust insulation, such as those in electric showers or water heaters, is essential for protecting the electrical components and ensuring safe operation.
Ultimately, the heating element is a perfect example of turning a fundamental physical principle into a reliable and indispensable modern technology.
Summary Table:
| Component/Principle | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Joule heating converts electrical energy to heat via high resistance. |
| Common Materials | Nichrome alloys, ceramics, silicon carbide for high-temperature use. |
| Key Components | Heating material, insulation (e.g., magnesium oxide), protective sheath, terminals. |
| Design Trade-offs | Efficiency vs. heat loss, cost vs. longevity, speed vs. uniformity. |
| Applications | Rapid heat (toasters), uniform heat (kilns), safe use in wet environments (water heaters). |
Need a custom heating solution for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace contribute to the thermal treatment process of chalcopyrite ore?
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in HZSM-5 preparation? Master Catalytic Activation
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- How is the thermal stability of KBaBi compounds evaluated? Discover Precise XRD & Heat Treatment Limits



















