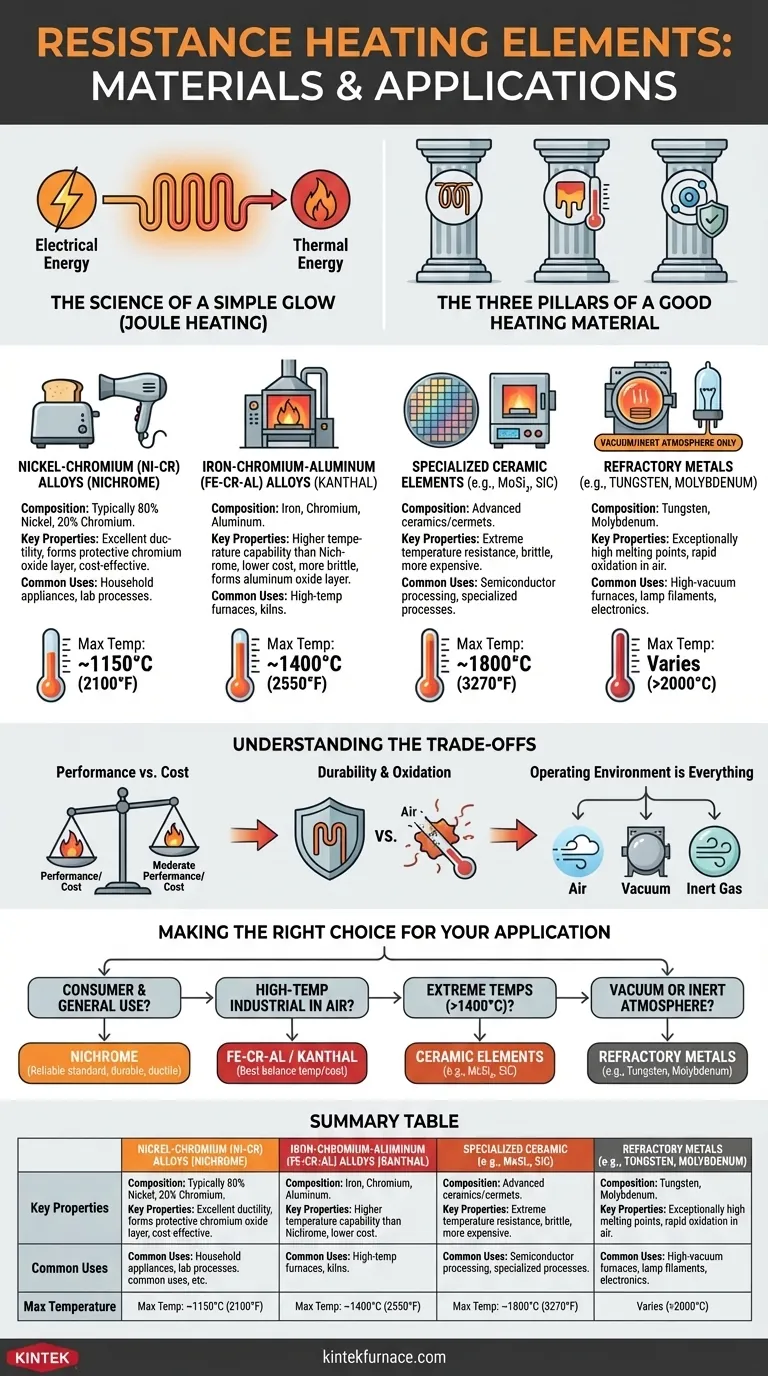
At their core, resistance heating elements are made from specialized materials—most commonly metal alloys like Nichrome and Kanthal or advanced ceramics—that are chosen for their ability to convert electrical energy into heat efficiently and reliably. This principle, known as Joule heating, is the foundation for countless devices, from everyday household appliances like toasters and water heaters to high-temperature industrial furnaces.
The specific material used for a heating element is never an arbitrary choice. It is a deliberate engineering decision based on a critical balance of electrical resistance, the ability to withstand high temperatures without oxidizing or degrading, and overall cost for the intended application.

The Science of a Simple Glow
The function of a resistance heating element is governed by a simple physical principle. When an electric current flows through a material with electrical resistance, a portion of that electrical energy is converted directly into thermal energy, or heat.
The Three Pillars of a Good Heating Material
For a material to be effective as a heating element, it must possess three key properties:
- High Electrical Resistivity: A higher resistance means more heat is generated for a given electrical current, allowing for more compact and efficient element design.
- High-Temperature Stability: The material must not melt, soften, or deform at its intended operating temperature.
- Resistance to Oxidation: This is perhaps the most critical factor for elements operating in open air. The material must resist reacting with oxygen at high temperatures, which would cause it to degrade and fail quickly.
A Breakdown of Key Element Materials
Heating element materials can be grouped into distinct families, each suited for different operating conditions and temperature ranges.
Nickel-Chromium (Ni-Cr) Alloys: The Industry Workhorse
Often known by the trade name Nichrome, this family of alloys (typically 80% nickel, 20% chromium) is the most common material for a vast range of heating applications.
Its popularity comes from its excellent combination of ductility (it's easy to form into coils and wires) and its ability to form a protective, adherent outer layer of chromium oxide when heated. This passive layer prevents oxygen from reaching the underlying metal, dramatically extending the element's lifespan.
Common Uses: Toasters, hair dryers, heat guns, and many lab and industrial heating processes up to about 1150°C (2100°F).
Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (Fe-Cr-Al) Alloys: The High-Temp Competitor
Frequently sold under the name Kanthal, this alloy family is the primary alternative to Nichrome, especially for higher-temperature applications.
Fe-Cr-Al alloys can operate at higher temperatures than Nichrome (up to 1400°C / 2550°F) and do so at a lower material cost. They also form a protective oxide layer, though it is based on aluminum oxide. The main trade-off is that these alloys tend to be more brittle than Nichrome.
Common Uses: High-temperature industrial furnaces, kilns for ceramics and glass, and other demanding heat-treatment applications.
Specialized Ceramic Elements: For Extreme Environments
For temperatures beyond what metal alloys can handle, engineers turn to advanced ceramic or cermet (ceramic-metal composite) materials.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are two prominent examples. These materials can operate at extremely high temperatures in air but are significantly more expensive and brittle than metal alloys, requiring careful handling and system design.
Common Uses: Semiconductor processing, laboratory furnaces, and specialized industrial processes requiring temperatures from 1400°C to 1800°C (2550°F to 3270°F).
Refractory Metals: The Vacuum Specialists
Metals like Tungsten and Molybdenum have exceptionally high melting points but a fatal flaw: they oxidize almost instantly at high temperatures in the presence of air.
Therefore, their use is restricted to environments where oxygen is absent, such as a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen).
Common Uses: High-vacuum furnaces, filaments in certain types of lamps, and specific electronics manufacturing processes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element is an exercise in managing engineering compromises. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for the job.
Performance vs. Cost
There is a direct correlation between temperature capability and cost. Nichrome provides excellent, reliable performance at a moderate cost. Kanthal offers higher temperatures for a slightly lower cost but with reduced ductility. Ceramic and refractory metal elements provide extreme performance at a significantly higher price point.
Durability and Oxidation
The lifespan of an element operating in air is almost entirely determined by its resistance to oxidation. Ni-Cr and Fe-Cr-Al alloys are designed to create their own protective oxide shields. Materials without this capability, like tungsten, will simply burn up.
Operating Environment is Everything
The single most important factor is the element's environment. Will it be exposed to air? Will it be in a vacuum? Will it be subject to mechanical shock or vibration? Answering these questions immediately narrows the list of suitable materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to understand why a certain material is chosen for a specific purpose.
- If the primary focus is consumer appliances and general use: Nichrome is the reliable standard due to its excellent durability, ductility, and cost-effectiveness for moderate temperatures.
- If the primary focus is high-temperature industrial furnaces in air: Fe-Cr-Al (Kanthal) alloys typically offer the best balance of high-temperature capability and material cost.
- If the primary focus is extreme temperatures above 1400°C (2550°F): Specialized ceramic elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) are required.
- If the primary focus is operating in a vacuum or inert atmosphere: Refractory metals like Tungsten and Molybdenum are the only viable choices for reaching the highest possible temperatures.
Ultimately, material selection for resistance heating is a direct reflection of the physical and economic demands of the final application.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Common Uses | Max Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Chromium (Ni-Cr) Alloys | High ductility, forms chromium oxide layer | Toasters, hair dryers, lab processes | 1150°C |
| Iron-Chromium-Aluminum (Fe-Cr-Al) Alloys | Higher temp capability, brittle, forms aluminum oxide layer | Industrial furnaces, kilns | 1400°C |
| Ceramic Elements (e.g., MoSi₂, SiC) | Extreme temp resistance, brittle, expensive | Semiconductor processing, lab furnaces | 1800°C |
| Refractory Metals (e.g., Tungsten, Molybdenum) | Very high melting points, requires vacuum/inert atmosphere | High-vacuum furnaces, electronics | Varies (e.g., >2000°C) |
Need a custom high-temperature furnace solution? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced heating systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether for industrial processes or specialized labs. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?



















