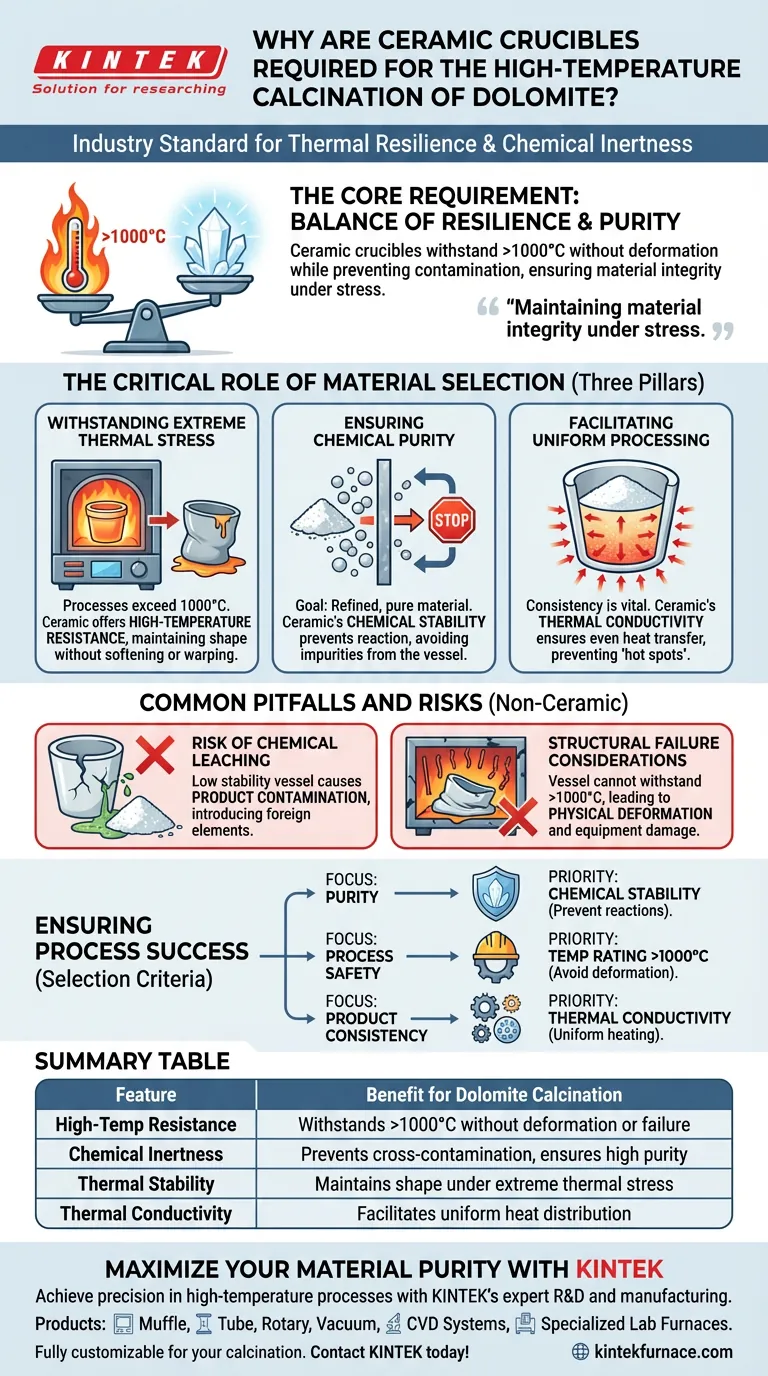
Ceramic crucibles are the industry standard for dolomite calcination due to their unique balance of thermal resilience and chemical inertness. They are specifically required to withstand processing temperatures exceeding 1000°C without physical deformation. Furthermore, their non-reactive nature prevents the vessel from contaminating the dolomite, ensuring the final material retains the high purity necessary for downstream applications.
The Core Requirement High-temperature calcination is not just about applying heat; it is about maintaining material integrity under stress. Ceramic crucibles provide the necessary stability to prevent cross-contamination and structural failure, ensuring the dolomite powder is modified without being compromised.
The Critical Role of Material Selection
To understand why ceramic is non-negotiable for this process, one must look at the specific physical and chemical demands placed on the vessel during calcination.
Withstanding Extreme Thermal Stress
Dolomite calcination requires processing environments where temperatures frequently exceed 1000°C.
At this intensity, many standard laboratory or industrial container materials would soften, warp, or lose their structural integrity. Ceramic crucibles possess excellent high-temperature resistance, allowing them to maintain their shape and hold the powder securely throughout the heating cycle without deformation.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
The goal of calcination is often to create a refined or modified material, which makes purity paramount.
At high temperatures, materials become more chemically active. A key advantage of ceramic is its chemical stability; it remains inert even under extreme heat. This prevents the crucible from reacting with the dolomite powder, thereby avoiding the introduction of impurities that would degrade the quality of the final product.
Facilitating Uniform Processing
Consistency is vital for successful calcination.
Ceramic crucibles offer specific thermal conductivity properties that assist in the calcination process. This ensures that heat is transferred evenly throughout the dolomite powder, preventing "hot spots" or uneven processing that could lead to an inconsistent final material.
Common Pitfalls and Risks
When selecting equipment for high-temperature processing, failure to prioritize vessel material can lead to critical process failures.
The Risk of Chemical Leaching
Using a vessel with low chemical stability is a primary cause of product contamination.
If a crucible reacts with the mineral load, it introduces foreign elements into the crystal lattice of the dolomite. As noted in similar high-purity applications, maintaining a non-reactive environment is the only way to ensure the resulting solid remains pure.
Structural Failure Considerations
The most immediate risk of using non-ceramic materials is physical deformation.
If a crucible cannot withstand the >1000°C threshold, it may collapse or warp inside the furnace. This not only ruins the batch of dolomite but can also damage the heating elements of the furnace itself.
Ensuring Process Success
To guarantee the quality of your calcined dolomite, apply the following selection criteria based on your project goals.
- If your primary focus is Purity: Prioritize ceramic crucibles for their chemical stability to prevent reactions between the vessel and the mineral powder.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: Ensure the crucible is rated for temperatures >1000°C to avoid deformation and equipment damage.
- If your primary focus is Product Consistency: Rely on the thermal conductivity of ceramic to ensure the powder is heated uniformly.
By selecting the correct ceramic vessel, you protect both the integrity of your equipment and the purity of your final material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for Dolomite Calcination |
|---|---|
| High-Temp Resistance | Withstands >1000°C without deformation or structural failure |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents cross-contamination and ensures high material purity |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains shape and integrity under extreme thermal stress |
| Thermal Conductivity | Facilitates uniform heat distribution for consistent processing |
Maximize Your Material Purity with KINTEK
Achieve precision in your high-temperature processes with KINTEK’s industry-leading thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique calcination requirements.
Whether you are processing dolomite or advanced minerals, our equipment ensures the chemical stability and thermal consistency your research demands. Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect furnace for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhaohui Li, Shangping Xu. Anionic Dye Alizarin Red S Removal Using Heat-Treated Dolomite. DOI: 10.3390/cryst14020187
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does the design of high-purity alumina capillaries influence bubble formation? Optimize Surface Tension Accuracy
- What role does a heated substrate platform play in the spray pyrolysis deposition? Optimize Your Thin Film Quality
- How does choosing alumina vs graphite crucibles affect Al-Si melting? Expert Guide to Data Integrity
- What are the thermal properties of alumina tubes? Discover Their High-Temp Durability and Stability
- What are the key characteristics of the alumina furnace tube? Essential for High-Temp Lab Success
- Why are support frames important for the alumina furnace tube? Prevent High-Temperature Deformation and Failure
- Why is ASTM A36 steel plate used for heat treatment furnace frameworks? Reliable Strength & Cost-Efficiency
- What is the primary function of an industrial vacuum drying oven in Si-RuO2 catalyst preparation? Achieve Uniformity.



















