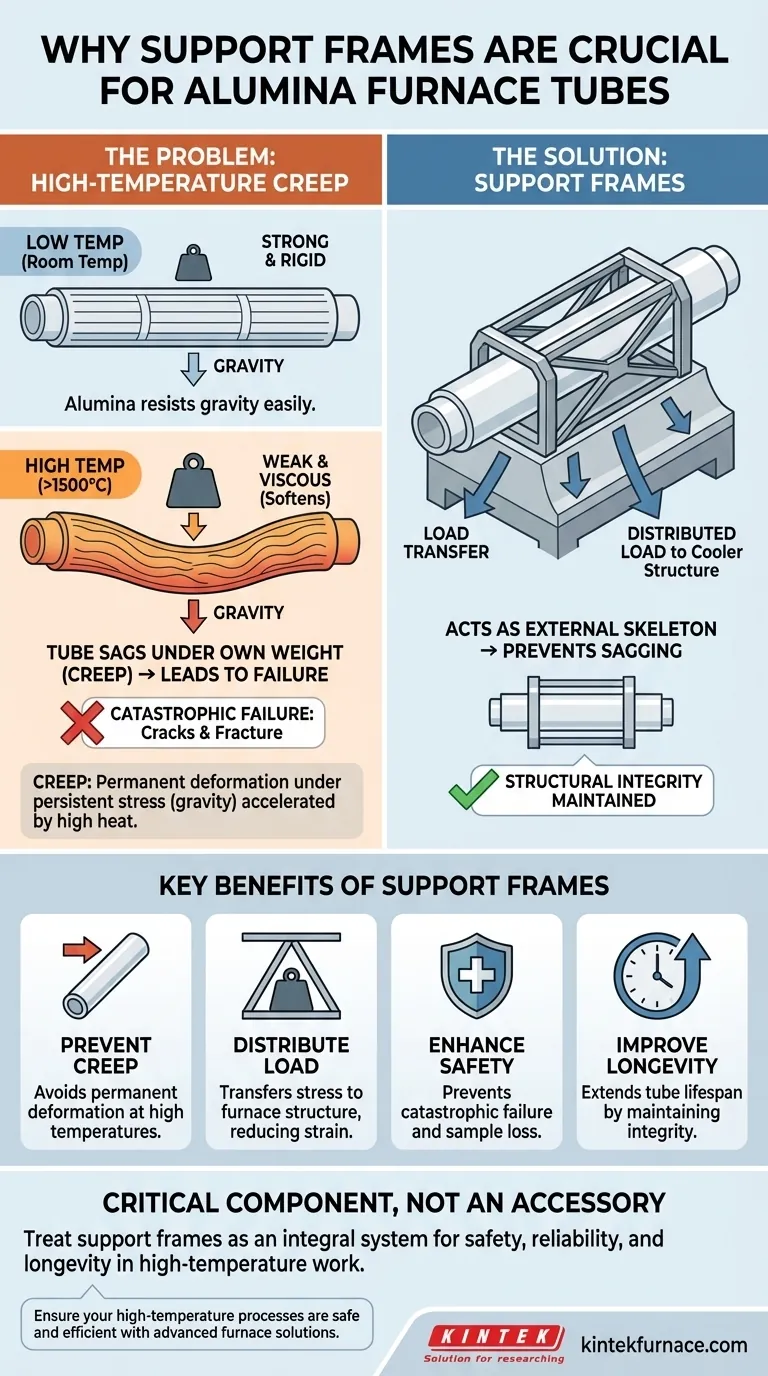
At their core, support frames are essential to prevent an alumina furnace tube from deforming and breaking under its own weight at high temperatures. While alumina is incredibly strong at room temperature, it loses a significant amount of its structural integrity when heated above 1,500°C, making it vulnerable to the constant, subtle force of gravity.
At the extreme temperatures where alumina tubes operate, the material begins to behave less like a rigid ceramic and more like a highly viscous fluid. Support frames are not just accessories; they are the critical structural countermeasure to gravity-induced sag, known as creep, which would otherwise lead to catastrophic tube failure.

The Core Problem: High-Temperature Creep
To understand the role of support frames, you must first understand the primary threat they are designed to fight: creep. This phenomenon is the central reason why unsupported horizontal tubes fail.
What is Creep?
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress. It is a time-dependent deformation that becomes highly accelerated at elevated temperatures.
Think of a plastic ruler placed between two books. At room temperature, it can support its own weight indefinitely. But if you add a small weight to its center and leave it in a hot car, you will eventually find it has permanently bent. This is creep.
Why Alumina is Susceptible
Alumina (Al₂O₃) is chosen for its exceptional resistance to heat, with a working temperature often exceeding 1600°C. However, this is precisely the temperature range where its mechanical strength diminishes and creep becomes a significant factor.
The material essentially softens, losing its rigidity. The very property that makes it useful—its ability to withstand high heat—also makes it vulnerable to structural deformation over time.
Gravity's Unseen Force
For a long, horizontal tube, its own weight creates a constant bending stress that is most concentrated at its midpoint. At room temperature, the alumina's strength easily resists this stress.
At 1600°C, this same, unchanging force of gravity is now acting on a much weaker, softer material. The tube begins to sag under its own weight, leading to deformation.
How Support Frames Solve the Problem
Support frames are a direct and effective engineering solution to the problem of high-temperature creep.
Providing Structural Reinforcement
The frames act as an external skeleton for the tube. By providing contact points along its length, they physically hold the tube in its intended horizontal position, preventing it from sagging.
Distributing the Load
Most importantly, the support frames transfer the tube's weight away from the tube itself and onto the main, cooler structure of the furnace. This effectively neutralizes the bending stress that would otherwise cause the tube to deform.
Preventing Catastrophic Failure
Without support, the initial sag (creep) will eventually lead to cracks as the deformation exceeds the material's limits. Because alumina is a brittle ceramic, it does not bend gracefully; it fractures. This failure can result in loss of the sample, damage to the furnace's heating elements, and a significant safety hazard.
Understanding the Material's Limits
The need for support frames highlights a critical trade-off in material science. While alumina is a superior material for high-temperature work, it is not without its weaknesses.
The Inherent Brittleness of Alumina
References note that alumina has poor thermal shock resistance. This points to its brittle nature. Brittle materials are very strong under compression but weak under tension.
When a tube sags, the top surface is compressed, but the bottom surface is pulled into tension. This tensile stress is what ultimately causes a crack to form and propagate, leading to a sudden fracture.
The Frames' Single Purpose
It is crucial to recognize that support frames only solve the problem of mechanical stress from creep. They do nothing to prevent failure from thermal stress.
Rapid heating or cooling will still create internal stresses that can crack the tube, a phenomenon known as thermal shock. Proper temperature ramping protocols are just as critical as mechanical support.
Applying This to Your Work
Your approach to furnace operation should treat the support frame as an integral system component, not an optional add-on.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity and safety: Always use and properly maintain support frames for any horizontally oriented alumina tube operating near its maximum temperature.
- If your primary focus is process reliability: View the supports as essential for preventing catastrophic failure that leads to sample loss and costly downtime.
- If you are designing or specifying a furnace: Insist on integrated support structures, especially for longer tubes, to counteract high-temperature creep from the outset.
Understanding this principle transforms the support frame from a simple accessory into a critical component for safe and successful high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prevent Creep | Avoids permanent deformation from gravity at high temperatures |
| Distribute Load | Transfers stress to furnace structure, reducing tube strain |
| Enhance Safety | Prevents catastrophic tube failure and sample loss |
| Improve Longevity | Extends tube lifespan by maintaining structural integrity |
Ensure your high-temperature processes are safe and efficient with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace options, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability precisely meets your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your lab's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control



















