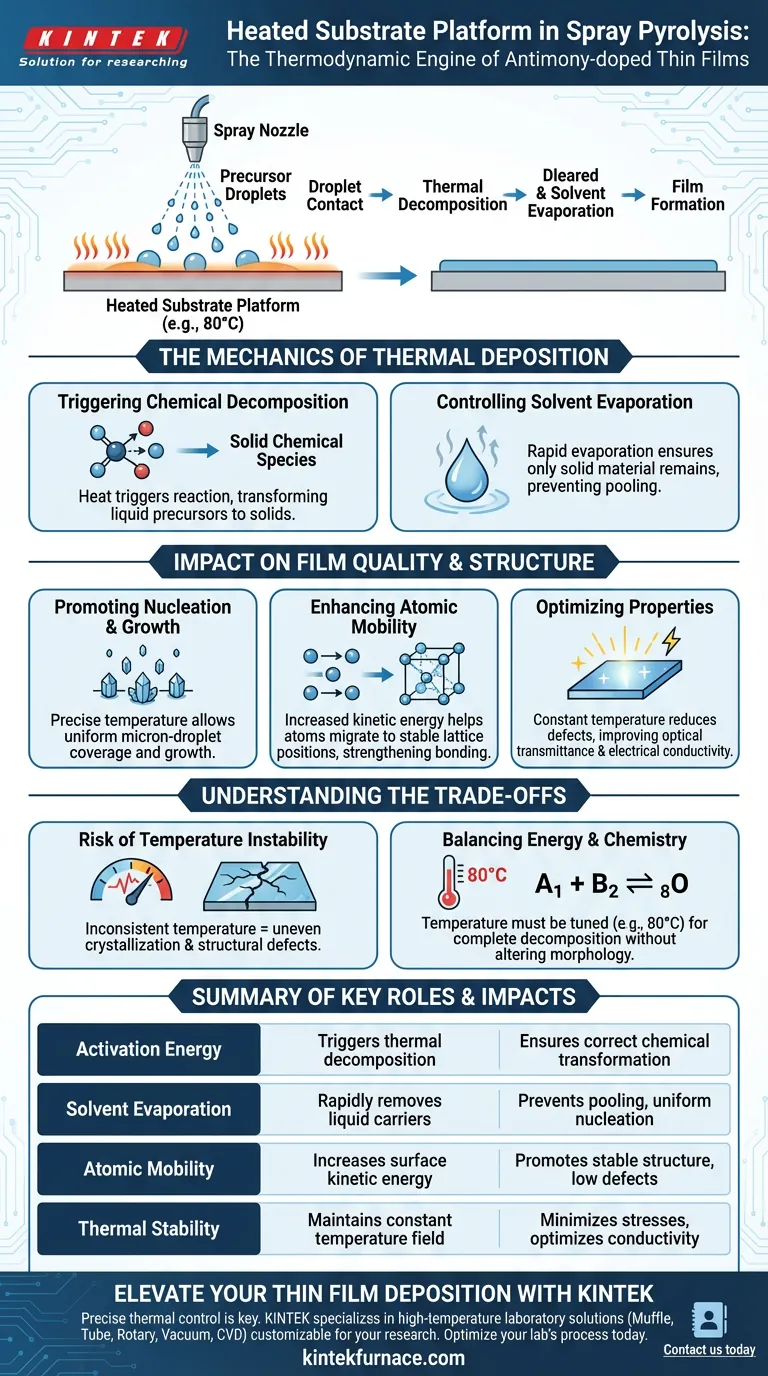
The heated substrate platform acts as the thermodynamic engine of the spray pyrolysis system. Its primary role is to maintain a specific temperature, often around 80°C for these specific materials, which supplies the necessary activation energy to thermally decompose precursor droplets and drive the rapid evaporation of solvents.
By maintaining a precise thermal environment, the platform ensures that precursor droplets undergo controlled chemical changes immediately upon contact. This thermal regulation is the deciding factor in nucleating high-quality Antimony-doped ZnSe or PbSe thin films with desirable structural properties.
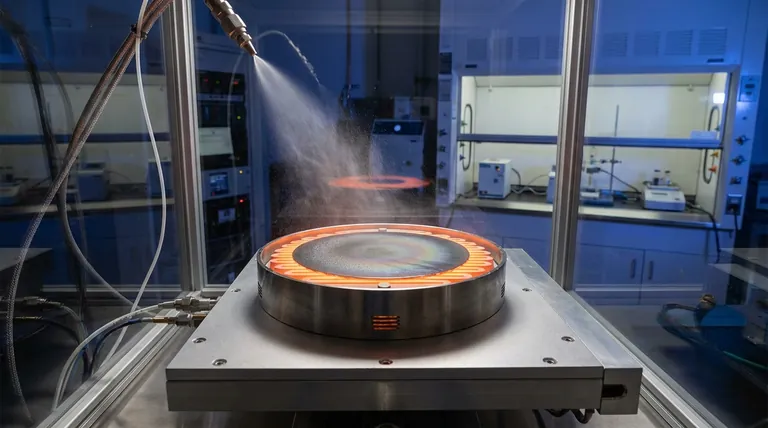

The Mechanics of Thermal Deposition
Triggering Chemical Decomposition
The fundamental purpose of the heated platform is to provide activation energy.
When the atomized precursor droplets strike the substrate, the heat triggers a thermal decomposition reaction. This transforms the liquid precursors into the solid chemical species required for the film.
Controlling Solvent Evaporation
Simultaneously, the heated surface drives the rapid evaporation of the solvent carrying the precursor material.
Effective evaporation is critical. It ensures that only the solid Antimony-doped material (such as ZnSe or PbSe) remains to nucleate and grow on the substrate surface, preventing liquid pooling or runoff.
Impact on Film Quality and Structure
Promoting Nucleation and Growth
The heat does not just dry the film; it actively facilitates the nucleation process.
By keeping the substrate at a precise temperature (e.g., 80°C), the system allows the solid film to grow effectively. This controlled environment ensures that the micron-sized droplets cover the surface uniformly.
Enhancing Atomic Mobility
Thermal energy significantly impacts how atoms arrange themselves after deposition.
The heat increases the kinetic energy of atoms on the surface. This mobility allows atoms to migrate to low-energy lattice positions, promoting a stable crystalline structure and stronger interfacial bonding between the film and the substrate.
Optimizing Optical and Electrical Properties
Temperature stability directly influences the final performance of the thin film.
A constant temperature field allows molecules to grow along specific crystal orientations, which reduces internal stresses and defects. Fewer defects translate to improved initial optical transmittance and better electrical conductivity in the final doped film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Temperature Instability
The precision of the heating platform is as important as the heat itself.
If the temperature fluctuates, the solvent evaporation rate becomes inconsistent. This can lead to uneven crystallization, structural defects, or variations in film thickness across the substrate.
Balancing Energy and Chemistry
While heat is necessary, the specific temperature must be tuned to the material.
The primary reference notes an 80°C requirement for these specific Antimony-doped films. Deviating significantly from the required activation temperature can result in incomplete decomposition (if too low) or potentially alter the film's morphology purely due to rapid kinetic changes (if too high).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure successful deposition of Antimony-doped thin films, consider the following based on your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Prioritize a heating system with high-precision temperature control to minimize internal stresses and defects.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Composition: Ensure the platform can maintain the specific activation temperature (e.g., 80°C) required to fully decompose your specific precursors without overheating.
Ultimately, the heated platform is not just a passive holder, but an active participant that dictates the crystalline quality and performance of your final device.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Role in Spray Pyrolysis | Impact on Film Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Activation Energy | Triggers thermal decomposition of precursors | Ensures correct chemical species transformation |
| Solvent Evaporation | Rapidly removes liquid carriers upon contact | Prevents liquid pooling and ensures uniform nucleation |
| Atomic Mobility | Increases kinetic energy of surface atoms | Promotes stable crystalline structure and low defects |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains a constant temperature field | Minimizes internal stresses and optimizes conductivity |
Elevate Your Thin Film Deposition with KINTEK
Precise thermal control is the difference between a defective layer and a high-performance Antimony-doped thin film. At KINTEK, we specialize in the advanced R&D and manufacturing of high-temperature laboratory solutions designed for rigorous research environments.
Whether you need Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our equipment is fully customizable to meet your specific activation energy and temperature stability requirements.
Ready to optimize your lab's deposition process? Contact us today to discuss how our customizable furnace systems can enhance your material growth and research outcomes.
Visual Guide
References
- Ikechukwu Christian Nworie, B. Ojobo. Comparative Assessment of Optical and Solid-State Characteristics in Antimony-Doped Chalcogenide Thin Films of ZnSe and PbSe to Boost Photovoltaic Performance in Solar Cells. DOI: 10.62292/njp.v33i1.2024.202
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why are fume hoods and sealed quartz tubes mandatory for BiF3 and SbF3? Safety in High-Temp Fluoride Reactions
- What is the function of a vacuum drying oven for biochar FTIR analysis? Ensure High-Purity Sample Preparation
- What are the primary functions of a Quartz Flow Reactor? Enhance Precision in Oxidation Research
- Why are high-performance insulation accessories necessary during the microwave sintering of zirconia ceramics?
- What is the necessity of using an alumina closed-end tube? Protect Your Aluminum Alloy Melting Process
- Why is a benchtop forced air drying oven preferred for microalgae-based nanomaterials? Enhance Powder Quality
- What functions do carbon black and carbon fiber felt serve as insulation? Maximize Efficiency in 3000°C Furnaces
- Why is a ceramic crucible necessary for the thermal processing of silica extracted from sugarcane bagasse?















