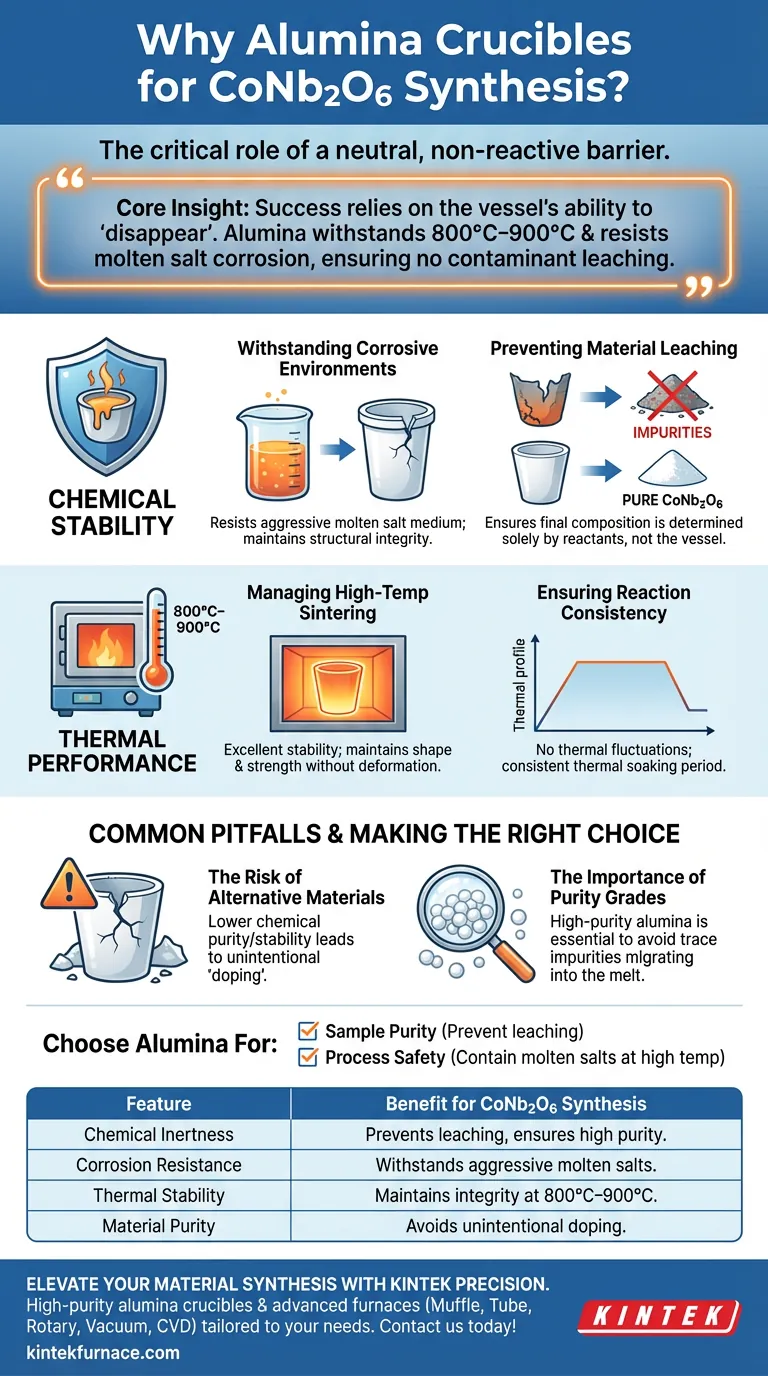
The primary reason for using alumina crucibles during the synthesis of CoNb2O6 ceramic powders is their ability to act as a neutral, non-reactive barrier. Specifically, they provide the necessary chemical inertness to withstand the corrosive molten salt medium used in the reaction without introducing impurities into the final product.
Core Insight: The success of synthesizing high-purity CoNb2O6 relies entirely on the vessel's ability to "disappear" from the chemical equation. Alumina is selected because it withstands temperatures of 800°C–900°C and resists corrosion from molten salts, ensuring the crucible does not leach contaminants into the ceramic powder.
The Critical Role of Chemical Stability
Withstanding Corrosive Environments
The synthesis of CoNb2O6 involves a molten salt medium, which creates a highly aggressive chemical environment.
Standard reaction vessels often degrade when exposed to these liquified salts. Alumina crucibles are specifically utilized because they possess excellent resistance to this type of corrosion, maintaining their structural integrity throughout the process.
Preventing Material Leaching
The ultimate goal of this synthesis is to produce pure CoNb2O6 ceramic powders.
If a crucible reacts with the molten salts or metal oxides, components of the vessel wall will leach into the mixture. Alumina prevents this vessel degradation, ensuring that the chemical composition of the final powder is dictated solely by the reactants, not the container.
Thermal Performance and Process Integrity
Managing High-Temperature Sintering
The synthesis process for CoNb2O6 requires a sintering phase with temperatures ranging between 800°C and 900°C.
Alumina is chosen for its exceptional thermal stability within and above this range. It maintains its shape and strength without softening or deforming, which is critical for containing the molten contents safely.
Ensuring Reaction Consistency
In high-temperature synthesis, the reaction vessel must not act as a heat sink or a variable in the thermal profile.
Alumina's stability ensures that the thermal soaking period—which can be extensive in ceramic synthesis—remains consistent. This allows the CoNb2O6 to form correctly without thermal fluctuations caused by material failure.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of Alternative Materials
Choosing a crucible with lower chemical purity or stability often leads to "doping" the sample unintentionally.
While other materials might withstand the heat, they frequently fail against the corrosive nature of molten salts. This results in unintended elements entering the crystal lattice of the ceramic, potentially altering its electronic or physical properties.
The Importance of Purity Grades
Not all alumina is created equal; the specific application requires high-purity alumina.
Using lower-grade ceramics can introduce trace impurities that migrate into the melt at 800°C. To guarantee the outcome described in the primary reference, the crucible itself must be free of contaminants that could release during the heating cycle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting reaction vessels for ceramic synthesis, your choice depends on the specific stressors of your environment.
- If your primary focus is Sample Purity: Select alumina crucibles to prevent vessel components from leaching into the CoNb2O6 powder during reaction.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: Rely on alumina for its ability to contain molten salts at 800°C–900°C without succumbing to corrosive structural failure.
The selection of alumina is not merely about holding the material; it is about ensuring the vessel remains chemically invisible throughout the transformation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for CoNb2O6 Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents leaching and ensures high purity of ceramic powders. |
| Corrosion Resistance | Withstands aggressive molten salt mediums without degrading. |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains structural integrity at sintering temperatures (800°C–900°C). |
| Material Purity | High-grade alumina avoids unintentional doping of the crystal lattice. |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Don't let crucible contamination compromise your research or production quality. KINTEK provides high-purity alumina crucibles and advanced laboratory equipment designed to withstand the most aggressive chemical environments.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with customizable high-temp furnaces tailored to your unique specifications. Ensure the integrity of your CoNb2O6 ceramic powders and other advanced materials with our industry-leading solutions.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processes? Contact us today to discuss your custom needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Mustafa İlhan, Kadir Esmer. Structural and dielectric properties of Eu3+,B3+ co-doped CoNb2O6 ceramic. DOI: 10.18596/jotcsa.1397311
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a carrier gas flow control system necessary for thermal sludge treatment? Ensure Precision & Protect Equipment
- What role does a precision drying oven play in the pre-treatment of Bi-Fe oxide powders? Safeguard Your Nano-Morphology
- How does an electromechanical vibrator assist in fuel feeding? Enhance Coal and Biomass Combustion Stability
- What are the advantages of 0.7 mm quartz capillaries for SXRD? Optimize High-Energy In-Situ X-ray Experiments
- What is the sucking rate for a single tap on the water circulating vacuum pump? Get Key Specs for Your Lab
- What processes is the circulating water multifunctional vacuum pump suitable for? Ideal for Clean, Economical Lab Vacuum Needs
- What are some key terms related to Laboratory Furnaces? Demystify Types Like Muffle and Tube Furnaces
- What is the function of an alumina boat during high-temperature activation of porous carbon? Durable Lab Solutions



















