When discussing laboratory furnaces, several key terms are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion. The most common names you will encounter are Muffle Furnace, Ashing Furnace, Chamber Furnace, and Tube Furnace, which describe either the furnace's core design or its specific application. These are generally all forms of electrically-heated, high-temperature ovens designed for laboratory work.
While terms like 'ash furnace' and 'chamber furnace' seem distinct, most describe variations of the fundamental muffle furnace design. The key is to understand that the terminology is based on either the furnace's construction, its intended application, or its physical size.
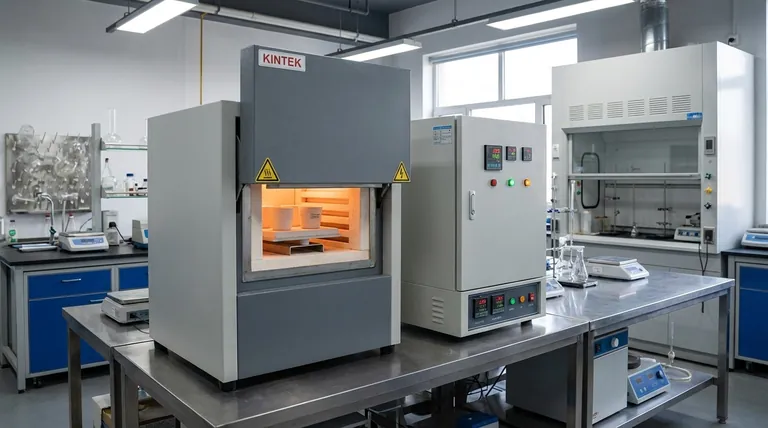

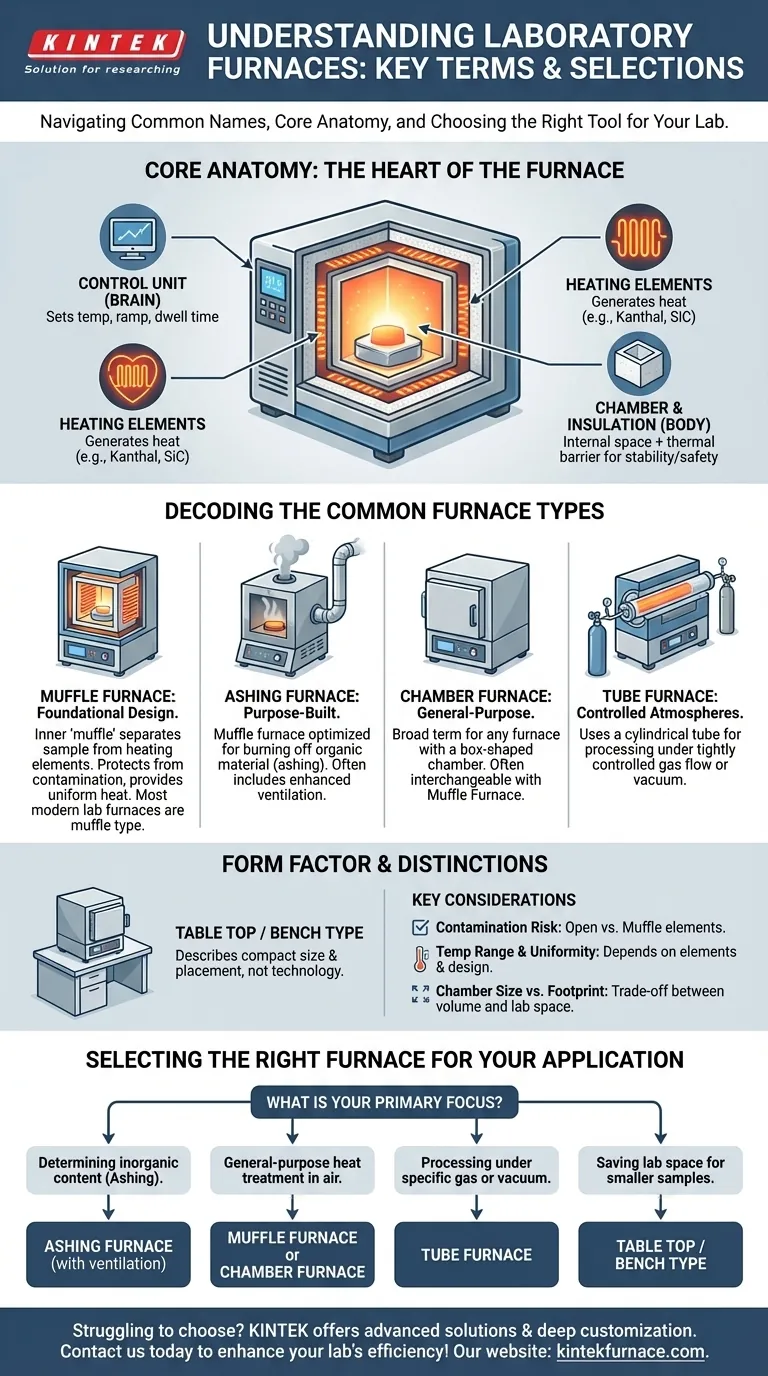
The Core Anatomy of a Laboratory Furnace
Before decoding the types, it's essential to understand the four primary components that constitute nearly every modern laboratory furnace.
The Control Unit: The Brain
This is the electronic interface for the furnace. It allows the user to set the target temperature, ramp rate (how quickly it heats up), and dwell time (how long it stays at a specific temperature).
Heating Elements: The Heart
These are the components that generate heat when electricity is passed through them. They are typically made of high-resistance alloys like Kanthal or, for higher temperatures, materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2).
The Chamber & Insulation: The Body
The chamber is the internal space where the sample is placed. This is surrounded by high-density ceramic fiber insulation to prevent heat loss, ensure temperature stability, and keep the exterior of the furnace cool and safe to touch.
Decoding the Common Furnace Types
The various names for laboratory furnaces typically describe one of three things: the core heating technology, the primary use case, or the physical form factor.
The Muffle Furnace: The Foundational Design
This is the most crucial term to understand. A muffle furnace features an inner chamber (the "muffle") that separates the sample from the heating elements. This design protects samples from contamination from the elements and provides more uniform radiant heat. Most modern lab furnaces are, by definition, muffle furnaces.
Ashing Furnace: A Purpose-Built Muffle Furnace
An Ashing Furnace is simply a muffle furnace optimized for ashing—the process of burning off organic material to determine the non-combustible inorganic content (ash) of a sample. They often have enhanced ventilation to handle the fumes produced during combustion.
Chamber Furnace: A General-Purpose Term
This is a broader, more descriptive term. It refers to any furnace with a box-shaped heating chamber. The term Chamber Furnace is often used interchangeably with Muffle Furnace because the vast majority of chamber furnaces utilize a muffle design.
Tube Furnace: For Controlled Atmospheres
A Tube Furnace is structurally different. Instead of a box-like chamber, it uses a cylindrical tube (often made of ceramic or quartz) around which the heating elements are placed. Its primary advantage is the ability to process samples under a tightly controlled atmosphere by flowing specific gases through the tube or pulling a vacuum.
Table Top / Bench Type: Describing the Form Factor
These terms do not describe the heating technology but rather the furnace's size and placement. A Table Top or Bench Type furnace is simply a compact unit designed to sit on a standard laboratory bench.
Understanding Key Distinctions and Limitations
Choosing a furnace requires looking past the names and understanding the practical differences in their design and capabilities.
Open Elements vs. Muffle: Contamination Risk
While most modern furnaces have a muffle, some older or simpler designs may have exposed heating elements inside the chamber. This creates a risk of sample contamination and is generally less desirable for sensitive analytical work.
Temperature Range and Uniformity
Different furnaces are rated for different maximum temperatures, which is determined by the type of heating elements and insulation used. Furthermore, temperature uniformity—how consistent the temperature is throughout the chamber—can vary significantly between models.
Chamber Size vs. Footprint
There is a direct trade-off between the internal working volume of the furnace and the amount of valuable lab space it consumes. A larger chamber is more versatile but requires more space and energy.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on the work you need to accomplish.
- If your primary focus is determining inorganic content (ashing): An Ashing Furnace with good ventilation is specifically designed for this task.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment in air: A standard Muffle Furnace or Chamber Furnace is your reliable workhorse.
- If your primary focus is processing samples under a specific gas or vacuum: A Tube Furnace is the only correct choice for this requirement.
- If your primary focus is saving lab space for smaller samples: A Table Top or Bench Type furnace provides full functionality in a compact design.
Understanding these core terms transforms a confusing market into a clear set of tools, empowering you to select the precise instrument for your work.
Summary Table:
| Term | Description | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|
| Muffle Furnace | Inner chamber separates sample from heating elements for uniform heat and contamination protection | General-purpose heat treatment in air |
| Ashing Furnace | Muffle furnace optimized for burning off organic material with enhanced ventilation | Determining inorganic content (ashing) |
| Chamber Furnace | Box-shaped heating chamber, often interchangeable with muffle furnace | General-purpose applications |
| Tube Furnace | Cylindrical tube design for controlled atmospheres with gas flow or vacuum | Processing under specific gases or vacuum |
| Table Top / Bench Type | Compact unit for small samples, saving lab space | Smaller-scale heat treatments |
Struggling to choose the right laboratory furnace for your unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your experimental requirements. Whether you need precise temperature control, contamination-free heating, or specialized atmosphere processing, we can help. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















