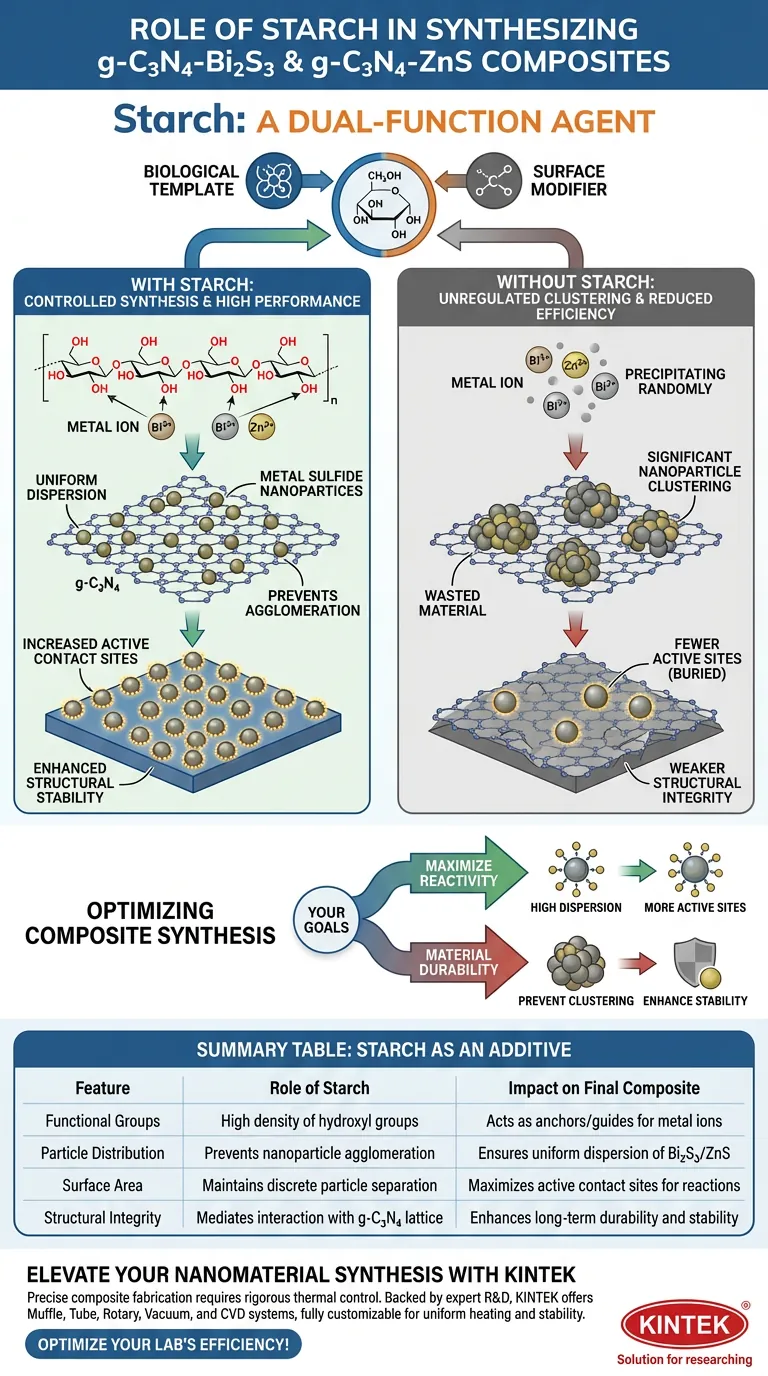
Starch acts as a dual-function agent in the synthesis of g-C3N4-Bi2S3 and g-C3N4-ZnS composites, serving as both a biological template and a surface modifier. By leveraging its abundant hydroxyl functional groups, starch interacts directly with metal ions to control the growth and placement of nanoparticles on the substrate.
Starch prevents nanoparticle agglomeration by ensuring the uniform dispersion of metal sulfides across the graphitic carbon nitride surface, significantly enhancing both the active contact sites and the overall structural stability of the composite.

The Mechanism of Starch Interaction
Utilizing Hydroxyl Groups
Starch is not merely a passive filler; it is chemically active due to its high density of functional groups.
Specifically, the hydroxyl groups inherent in the starch structure play a critical role. These groups actively interact with metal ions during the synthesis process, acting as anchors or guides.
Facilitating Uniform Dispersion
This chemical interaction governs the physical distribution of the material.
Starch ensures that metal sulfide nanoparticles (specifically Bi2S3 and ZnS) are spread evenly across the graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) support. It prevents the metal ions from precipitating randomly or unevenly.
Impact on Material Performance
Preventing Agglomeration
One of the primary challenges in nanocomposite synthesis is the natural tendency of particles to clump together.
Starch acts as a barrier to this significant nanoparticle clustering. By mediating the interaction between the metal sulfides and the support matrix, it maintains discrete particle separation.
Increasing Active Sites
The efficiency of a composite material often depends on its available surface area.
Because starch enforces a high degree of dispersion, more surface area of the metal sulfides is exposed. This directly maximizes the number of active contact sites available for subsequent chemical or physical reactions.
Enhancing Structural Stability
Beyond mere placement, the presence of starch contributes to the durability of the final product.
The resulting composites exhibit enhanced overall structural stability. This implies a more robust integration between the metal sulfide nanoparticles and the g-C3N4 lattice.
The Consequence of Omitting Starch
Unregulated Particle Clustering
Without the templating effect of starch, the synthesis process lacks a critical control mechanism.
This absence typically leads to significant clustering of the Bi2S3 or ZnS nanoparticles. Clustered particles have a lower surface-to-volume ratio, effectively wasting material.
Reduced Composite Efficiency
When nanoparticles agglomerate, active sites are buried inside the clusters and become inaccessible.
Therefore, omitting starch results in a material with fewer active contact sites and potentially weaker structural integrity, compromising the performance of the composite.
Optimizing Composite Synthesis
To achieve high-performance g-C3N4 composites, consider your specific fabrication goals:
- If your primary focus is Maximizing Reactivity: Utilize starch to ensure high dispersion, which directly increases the number of available active contact sites.
- If your primary focus is Material Durability: Incorporate starch as a modifying agent to prevent clustering and enhance the long-term structural stability of the composite.
By using starch as a biological template, you transform a chaotic precipitation process into a controlled synthesis that yields a highly stable and active material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role of Starch as an Additive | Impact on Final Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Functional Groups | High density of hydroxyl groups | Acts as anchors/guides for metal ions |
| Particle Distribution | Prevents nanoparticle agglomeration | Ensures uniform dispersion of Bi2S3/ZnS |
| Surface Area | Maintains discrete particle separation | Maximizes active contact sites for reactions |
| Structural Integrity | Mediates interaction with g-C3N4 lattice | Enhances long-term durability and stability |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise composite fabrication requires rigorous thermal control and specialized equipment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as other lab high-temperature furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Whether you are synthesizing g-C3N4 composites or developing advanced biological templates, our high-performance solutions ensure the uniform heating and stability your materials demand. Contact us today to optimize your lab's efficiency!
Visual Guide
References
- Shoaib Mukhtar, Ottó Horváth. g-C3N4 Modified with Metal Sulfides for Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants. DOI: 10.3390/molecules30020253
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a precise heating system during the hydrolysis of palm kernel oil? Optimize Your Fatty Acid Yield
- What industries commonly use batch furnaces? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Electronics
- What is the primary purpose of using a laboratory constant temperature drying oven for fuel sample preparation?
- What role does an RTA system play in processing SiN thin films? Unlock High-Performance Quantum & Optical Materials
- Why is X-ray diffraction (XRD) required for lithium iron phosphate synthesis? Ensuring Phase Purity & Structure
- What are the technological advantages of using a Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) system? Precision for Semiconductors
- Why does high-phenyl conductive silicone rubber require secondary vulcanization? Essential Stability Guide
- How does a circulating mineral oil jacket heating system function? Ensure Precision in Wood Thermal Modification



















