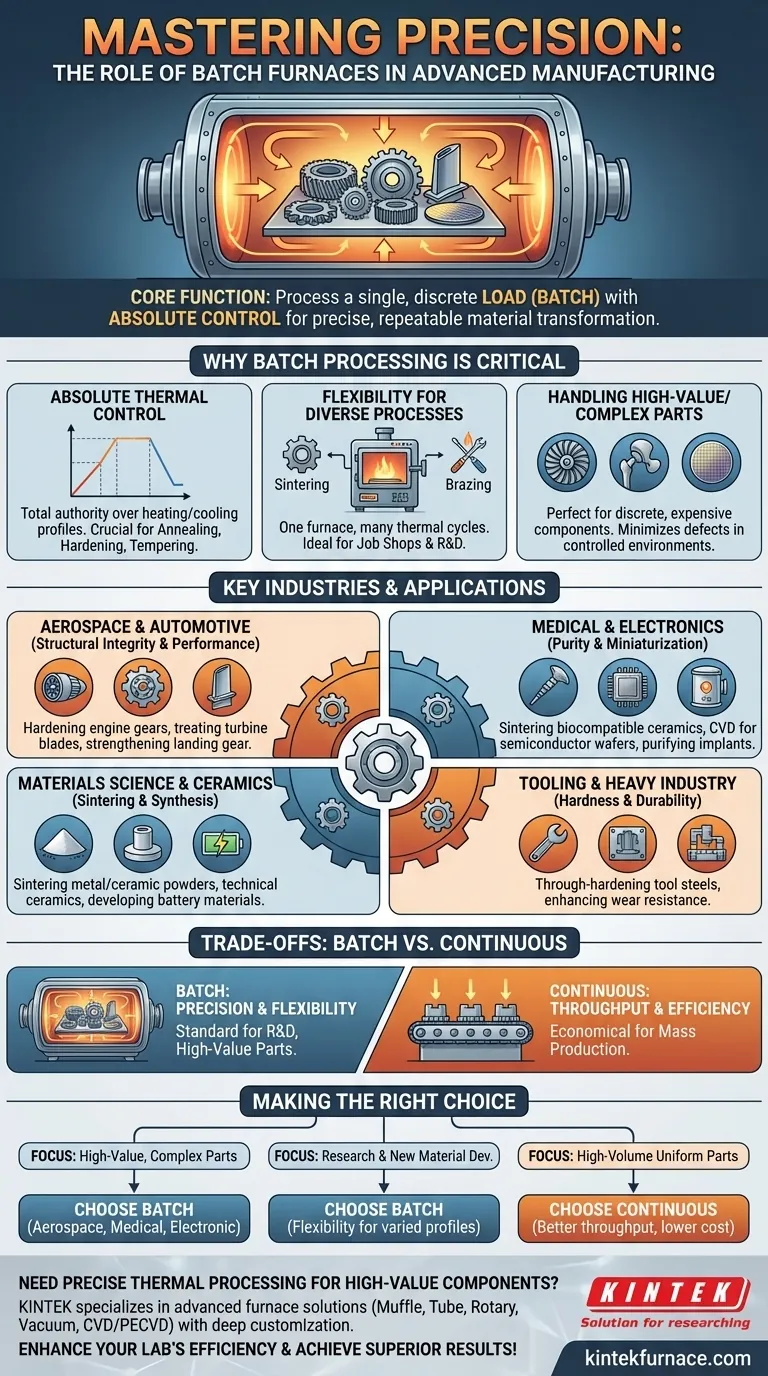
At their core, batch furnaces are indispensable in industries where material transformation must be precise, repeatable, and controlled. They are foundational pieces of equipment in advanced manufacturing sectors, including aerospace, automotive, medical device manufacturing, and electronics. The defining characteristic is their ability to process a single, discrete load—or "batch"—of parts through a complete thermal cycle, ensuring every piece receives the exact same treatment.
The specific industry is less important than the required process. Batch furnaces are chosen not for the industry itself, but for applications demanding exceptional control over temperature, atmosphere, and time for high-value or complex components.

Why Batch Processing is Critical for Advanced Manufacturing
The decision to use a batch furnace over a continuous-type furnace is driven by the need for process integrity. For high-stakes components, uniformity and precision are paramount.
Absolute Control Over the Thermal Cycle
A batch furnace gives operators total authority over the entire heating and cooling profile. This includes precise control over ramp rates (how fast the temperature rises), soak times (how long it's held at a specific temperature), and cooling rates.
This level of control is non-negotiable for metallurgical processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering, where slight deviations can compromise a material's structural integrity.
Flexibility for Diverse Processes
A single batch furnace can be programmed to run vastly different thermal cycles. One day it might perform a high-temperature sintering process for ceramics, and the next it could be used for a lower-temperature brazing cycle for joining metals.
This versatility makes them ideal for job shops, research and development labs, and facilities that produce a wide range of products rather than a single, high-volume item.
Handling of High-Value or Complex Parts
Batch furnaces are perfectly suited for processing discrete, high-value components. Think of aerospace turbine blades, surgical implants, or semiconductor wafers.
The value of each part justifies the focused, controlled environment of a batch process to minimize the risk of defects. The loading process also accommodates complex shapes and sizes that may not be suitable for a continuous conveyor system.
A Breakdown of Key Industries and Applications
While the applications are vast, they can be grouped by the primary goal of the thermal process.
Aerospace and Automotive: Structural Integrity and Performance
These industries rely on batch furnaces for the heat treatment of critical metal components. The goal is to create parts that are lightweight yet incredibly strong and resistant to fatigue and extreme temperatures.
Applications include hardening engine gears, strengthening landing gear components, and treating turbine blades in vacuum furnaces to achieve the required purity and grain structure.
Medical and Electronics: Purity and Miniaturization
In both medical device and semiconductor manufacturing, the primary concern is purity. Batch furnaces with controlled atmospheres or high-vacuum capabilities are essential to prevent contamination.
These furnaces are used to create high-purity metals for surgical implants, sinter biocompatible ceramics, and grow crystalline films on semiconductor wafers through processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Materials Science and Ceramics: Sintering and Synthesis
This is a broad category focused on creating new materials or consolidating powders into solid forms.
Batch furnaces are used for sintering metal and ceramic powders to create dense, strong parts, producing technical ceramics, developing materials for lithium batteries, and creating specialized glass and abrasive tools.
Tooling and Heavy Industry: Hardness and Durability
For manufacturing tools, dies, and components for heavy machinery, the goal is maximum hardness and wear resistance.
Batch furnaces are used for the through-hardening of tool steels and other alloys, ensuring that cutting tools, molds, and mechanical parts can withstand intense operational stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Batch vs. Continuous
No single solution is perfect for every scenario. The choice between a batch and a continuous furnace is a fundamental engineering and business decision.
The Strength of Batch: Precision and Flexibility
As discussed, batch furnaces excel where precision is critical and production runs involve varied parts or processes. They are the standard for R&D, aerospace, and medical applications.
The Strength of Continuous: Throughput and Efficiency
Continuous furnaces move parts on a conveyor through different temperature zones. They are designed for one specific thermal profile and run constantly.
For the mass production of identical, low-cost parts (like screws, fasteners, or simple stampings), a continuous furnace offers far greater throughput and lower per-unit labor costs, making it the more economical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the right furnace type, you must first define your primary manufacturing objective.
- If your primary focus is high-value, complex components: A batch furnace provides the non-negotiable process control and precision required for aerospace, medical, or advanced electronic parts.
- If your primary focus is research and new material development: The inherent flexibility of a batch furnace to run varied thermal profiles makes it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing of uniform parts: A continuous furnace will almost always deliver better throughput and lower operational costs for mass production.
Ultimately, choosing the correct thermal processing equipment is about aligning the tool's capabilities directly with the value and requirements of your product.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace & Automotive | Hardening engine gears, treating turbine blades, strengthening landing gear |
| Medical & Electronics | Sintering biocompatible ceramics, growing films on semiconductor wafers, purifying surgical implants |
| Materials Science & Ceramics | Sintering metal/ceramic powders, developing battery materials, producing technical ceramics |
| Tooling & Heavy Industry | Through-hardening tool steels, enhancing wear resistance for molds and mechanical parts |
Need precise thermal processing for high-value components? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to industries like aerospace, medical, and electronics. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What factors should be considered when purchasing a quartz tube furnace? Ensure Reliable High-Temperature Processing
- How should a quartz tube furnace be cleaned? Essential Steps for Safe, Contamination-Free Maintenance
- What is a quartz tube furnace and what is its primary use? Essential for Controlled High-Temp Processing
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance
- How does the work process of a quartz tube furnace typically proceed? Master Precision Heating for Advanced Materials



















