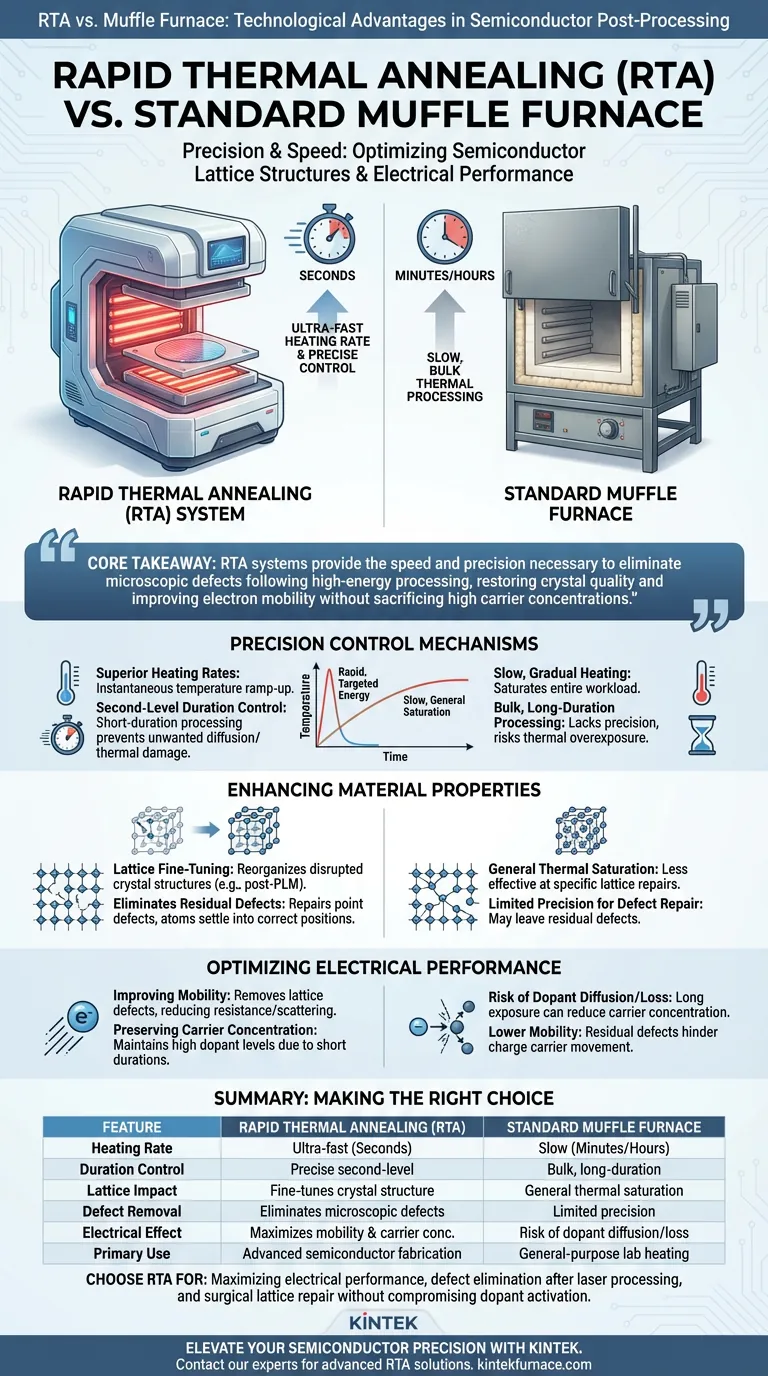
The primary technological advantage of a Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) system over a standard muffle furnace is its ability to deliver significantly faster heating rates combined with precise, second-level duration control. Unlike the slow, bulk thermal processing of a muffle furnace, an RTA system provides the targeted energy required to fine-tune semiconductor lattice structures without prolonged exposure to heat.
Core Takeaway While standard furnaces offer general bulk heating, RTA systems provide the speed and precision necessary to eliminate microscopic defects following high-energy processing. This capability allows for the restoration of crystal quality and improved electron mobility without sacrificing high carrier concentrations.
Precision Control Mechanisms
Superior Heating Rates
The most immediate distinction between the two systems is the speed of thermal delivery. A standard muffle furnace relies on slow, gradual heating which saturates the entire workload.
In contrast, an RTA system is engineered for rapid temperature ramp-ups. This allows the system to reach target temperatures almost instantly, preventing the thermal lag associated with traditional furnaces.
Second-Level Duration Control
Precision in semiconductor processing often comes down to timing. RTA systems allow for temperature control measured in seconds.
This short-duration processing is critical. It ensures the material is exposed to heat only as long as necessary to trigger specific physical changes, preventing unwanted diffusion or thermal damage.
Enhancing Material Properties
Lattice Fine-Tuning
The RTA system is particularly effective when used as a post-processing step for techniques like Pulsed Laser Melting (PLM).
The thermal energy provided by the RTA drives a process known as "lattice fine-tuning." This mechanism essentially reorganizes the crystal structure that may have been disrupted during previous high-energy steps.
Eliminating Residual Defects
One of the critical challenges in semiconductor fabrication is the presence of "point defects"—imperfections in the crystal lattice.
RTA processing effectively eliminates these residual point defects left behind by the PLM stage. By briefly energizing the lattice, the system allows atoms to settle into their correct positions, repairing the crystal structure.
Optimizing Electrical Performance
Improving Mobility
The structural repairs effected by the RTA system translate directly into electrical performance.
By removing lattice defects, the system significantly improves hole or electron mobility. This allows charge carriers to move through the semiconductor material with less resistance/scattering.
Preserving Carrier Concentration
Usually, thermal processing involves a trade-off where annealing improves structure but reduces the concentration of dopants (carriers).
RTA systems overcome this by using short durations. They maintain the high carrier concentrations achieved during the melting phase while still delivering the thermal energy needed for structural repair.
Understanding the Context and Trade-offs
Specificity of Application
It is important to note that the advantages of RTA are most pronounced in advanced applications, such as post-Pulsed Laser Melting (PLM).
A standard muffle furnace is a general-purpose tool suitable for broad, non-critical heating tasks. However, it lacks the finesse required to drive specific lattice repairs without altering other material properties.
The Cost of Precision
While RTA offers superior control, it implies a more complex process window.
The system requires precise calibration to ensure the "second-level" duration is exact. A standard furnace, being slower, is more forgiving but incapable of achieving the high-mobility, high-concentration results of RTA.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine whether an RTA system is required for your specific application, consider your performance metrics:
- If your primary focus is maximizing electrical performance: Choose RTA to improve electron/hole mobility while retaining high carrier concentrations.
- If your primary focus is defect elimination after laser processing: Choose RTA to drive lattice fine-tuning and remove residual point defects from the PLM stage.
- If your primary focus is general bulk heating: A standard muffle furnace may suffice, but it will lack the ability to perform rapid, short-duration structural repairs.
The RTA system is the definitive choice when the goal is to surgically repair crystal structures to boost device speed without compromising dopant activation.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Rapid Thermal Annealing (RTA) | Standard Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate | Ultra-fast ramp-up (Seconds) | Slow, gradual heating (Minutes/Hours) |
| Duration Control | Precise second-level control | Bulk, long-duration processing |
| Lattice Impact | Fine-tunes crystal structure | General thermal saturation |
| Defect Removal | Eliminates microscopic point defects | Limited precision for defect repair |
| Electrical Effect | Maximizes mobility & carrier concentration | Risk of dopant diffusion/loss |
| Primary Use | Advanced semiconductor fabrication | General-purpose lab heating |
Elevate Your Semiconductor Precision with KINTEK
Maximize your material's electrical performance and achieve flawless lattice structures with KINTEK’s advanced thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of high-temperature laboratory equipment, including specialized RTA-capable systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique semiconductor and research needs.
Don't settle for general heating when your project demands precision. Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace for your high-mobility applications and experience the KINTEK advantage in thermal engineering.
Visual Guide
References
- K. M. Yu, W. Walukiewicz. Overcoming the doping limit in GaAs by ion implantation and pulsed laser melting. DOI: 10.1063/5.0190600
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of maintaining an inert nitrogen atmosphere during molten salt activation? Ensure Pore Purity
- What are some drawbacks of electric heating methods? High Costs and Grid Dependence Explained
- Why is an optical pyrometer necessary for monitoring nickel-aluminum alloy synthesis? Capture Rapid Thermal Explosions
- What is the function of a magnetron sputtering system for WS2 thin films? Master Nano-Scale Deposition Control
- Why is a laboratory vacuum oven utilized for ZnO-FL drying? Preserving Delicate Nanoparticle Morphologies
- What function does high-purity argon gas serve in BPEA PVT preparation? Ensure High-Quality Crystal Growth
- How does a forced-air drying oven contribute to the transformation of GaN precursor resins? Ensure Material Uniformity
- How does high-temperature filtration equipment facilitate molten salt separation? Boost Your Slag Treatment Recovery



















