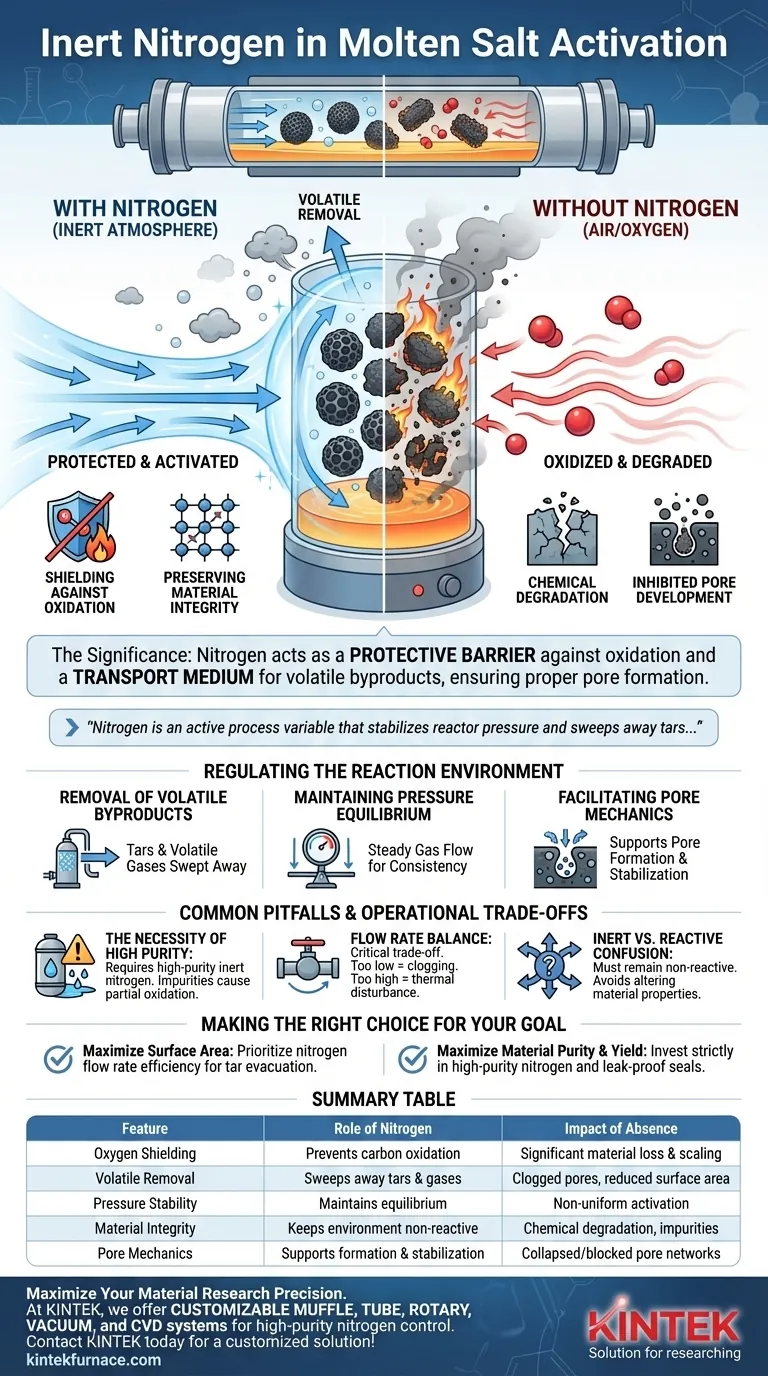
The significance of maintaining an inert nitrogen atmosphere during molten salt activation lies in its dual role: it acts as a protective barrier to prevent the destructive oxidation of carbon materials while simultaneously serving as a transport medium to remove volatile byproducts. Without this continuous flow, the high operational temperatures would cause the carbon source to burn away rather than activate, and trapped volatiles would inhibit proper pore structure development.
In the context of molten salt activation, nitrogen is not merely a passive gas; it is an active process variable that stabilizes reactor pressure and sweeps away tars, ensuring the precise mechanics of pore formation, growth, and stabilization proceed without interference.

Preventing Chemical Degradation
Shielding Against Oxidation
The most immediate risk during high-temperature activation is the presence of oxygen. High-purity nitrogen excludes oxygen from the furnace tube, preventing the carbon material from reacting with air. Without this shield, the carbon would simply burn (oxidize) into carbon dioxide or monoxide, resulting in significant yield loss and scaling rather than activation.
Preserving Material Integrity
By maintaining a chemically inert environment, nitrogen ensures that the chemical reactions remain restricted to the interaction between the precursor and the molten salt. This isolation prevents unwanted side reactions that could alter the material's properties, weaken its mechanical structure, or introduce impurities such as oxides.
Regulating the Reaction Environment
Removal of Volatile Byproducts
During the carbonization and activation phases, the material releases complex byproducts, including tars and volatile gases. The continuous flow of nitrogen acts as a carrier, physically sweeping these substances out of the hot zone. If these tars were allowed to stagnate, they could redeposit on the material, clogging the newly formed pores and degrading the final surface area.
Maintaining Pressure Equilibrium
The generation of gases inside the reactor can lead to pressure fluctuations. A steady nitrogen flow helps maintain pressure equilibrium within the reactor tube. This stability is crucial for process consistency, ensuring that the activation occurs uniformly across the entire batch of material.
Facilitating Pore Mechanics
The ultimate goal of molten salt activation is the creation of a specific porous architecture. The nitrogen atmosphere supports the mechanisms of pore formation, growth, and stabilization. By managing the removal of volatiles and preventing oxidation, the nitrogen environment allows the pores to develop their intended geometry without collapsing or being blocked by oxidation debris.
Common Pitfalls and Operational Trade-offs
The Necessity of High Purity
Not all nitrogen sources are created equal. The process explicitly requires high-purity inert nitrogen. Using industrial-grade nitrogen with trace amounts of oxygen or moisture can still lead to partial oxidation, compromising the "bright" finish and structural integrity of the carbon.
Flow Rate Balance
Achieving the correct flow rate is a critical trade-off.
- Too low: Tars and volatiles may not be evacuated efficiently, leading to blockage and pressure buildup.
- Too high: Excessive flow might disturb the temperature uniformity or physically displace lighter sample materials. The system relies on a balance that maintains the atmosphere without disrupting the thermal profile.
Inert vs. Reactive Confusion
It is vital to distinguish this process from treatments like carburizing or nitriding, where the atmosphere is designed to react with the surface. In molten salt activation, the atmosphere must remain strictly non-reactive. Introducing reactive elements intentionally (or accidentally via leaks) will fundamentally change the material properties, likely leading to failure of the activation process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your laboratory furnace setup for molten salt activation, consider these specific priorities:
- If your primary focus is maximizing surface area: Prioritize the nitrogen flow rate efficiency to ensure all tars and volatiles are immediately evacuated, preventing pore clogging.
- If your primary focus is material purity and yield: Invest strictly in high-purity nitrogen sources and leak-proof seals to eliminate any trace of oxygen ingress that causes burn-off.
The success of molten salt activation depends not just on temperature, but on the disciplined management of the inert atmosphere that makes the transformation possible.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role of Nitrogen in Activation | Impact of Absence |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Shielding | Prevents carbon oxidation/burn-off | Significant material loss and scaling |
| Volatile Removal | Sweeps away tars and reaction gases | Clogged pores and reduced surface area |
| Pressure Stability | Maintains equilibrium in the reactor | Non-uniform activation across the batch |
| Material Integrity | Keeps environment strictly non-reactive | Chemical degradation and introduction of impurities |
| Pore Mechanics | Supports formation and stabilization | Collapsed geometry or blocked pore networks |
Maximize Your Material Research Precision
Don’t let oxidation or poor atmosphere control compromise your activation results. At KINTEK, we understand that precise laboratory furnace environments are the foundation of high-performance materials. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to provide the high-purity nitrogen control and thermal stability your molten salt processes demand.
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities? Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Pu Yang, Feng Jiang. Phase Diagram‐Guided Molten Salt Engineering of Biocarbon Pores at Low Temperatures. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202501162
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is the problem of surface oxidation and decarburization addressed in conventional heat treatment? Learn the Machining Allowance Method
- What is the purpose of high-purity argon in heat treating Al-Cu-Mn-Zr-V alloys? Protect Your Material Integrity
- Why is a constant temperature drying oven utilized at 40 °C for clayey raw materials? Ensure Mineral Integrity.
- Why is precision constant temperature control required during the hardening stage of geopolymer mortar? Guide to Success
- How does a graphite furnace work? Achieve Ultra-Trace Element Analysis
- Why are different cooling methods compared for GFRP post-fire performance? Evaluate Thermal Shock & Safety Risks
- Why is Boron Nitride (BN) powder used as a diluent? Enhance Accuracy in Iron Oxidation Kinetics
- What is the significance of pre-equilibrating samples in silicate studies? Maximize Experimental Efficiency



















