In its most common application, a graphite furnace works by using a small graphite tube as a high-temperature chamber to transform a tiny liquid sample into a cloud of free atoms for analytical measurement. This process happens in a carefully controlled, multi-stage heating program under an inert gas atmosphere, allowing for the extremely sensitive detection of specific elements.
The core function of a graphite furnace is not just to heat a sample, but to meticulously isolate a target element from its surrounding material. It achieves this by sequentially drying, ashing, and finally flash-vaporizing the sample into a confined atomic vapor, purpose-built for spectroscopic analysis.
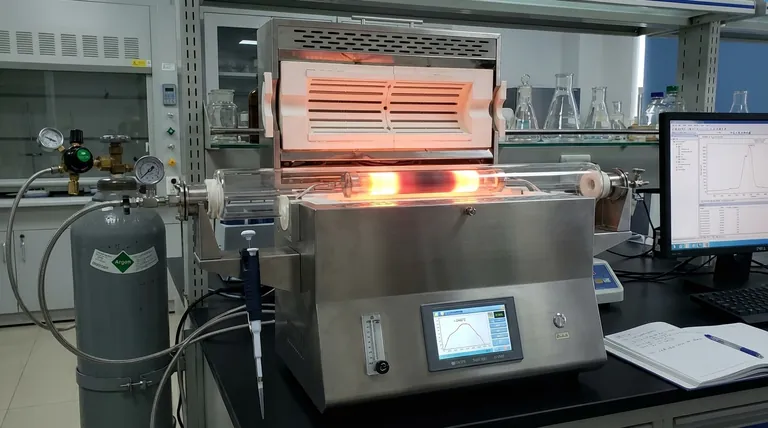

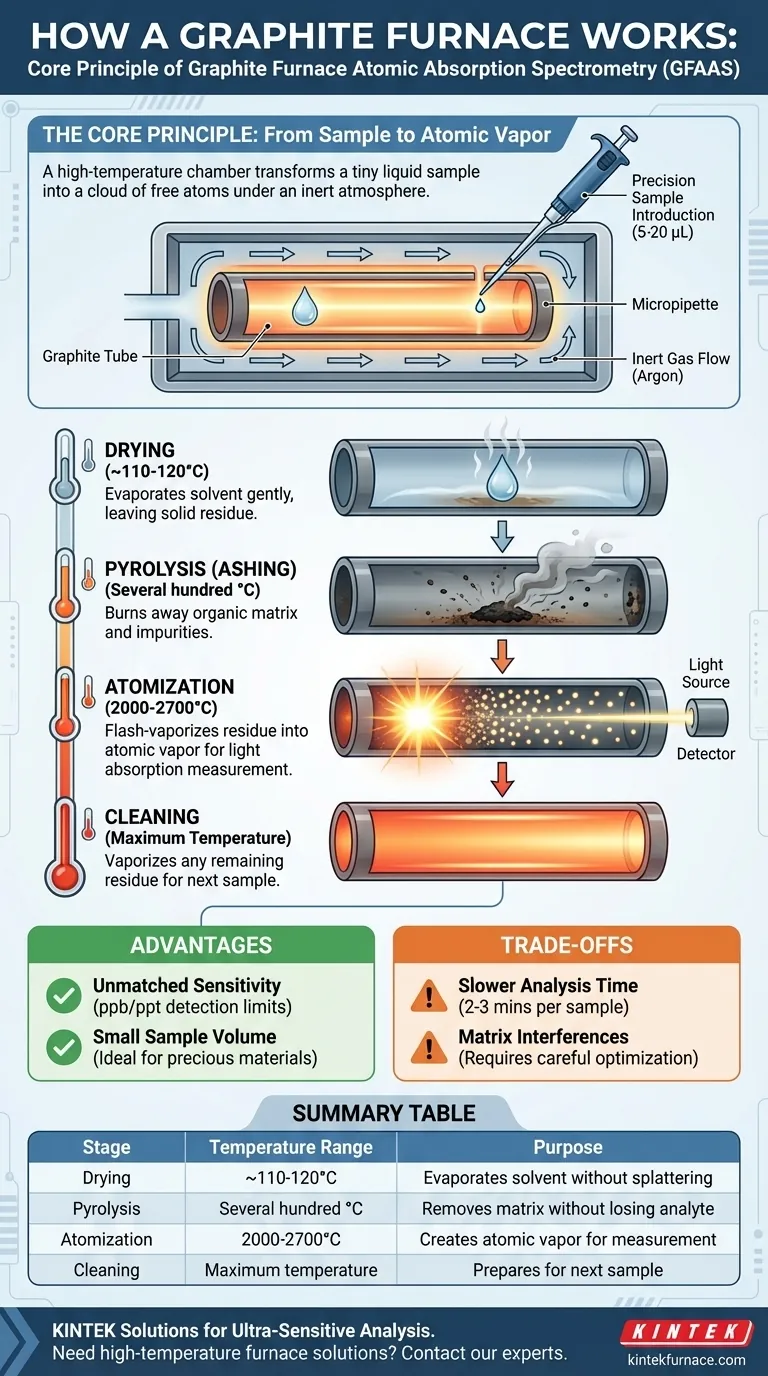
The Core Principle: From Sample to Atomic Vapor
A graphite furnace is the heart of a technique called Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (GFAAS). Its entire design is optimized for creating the ideal conditions for measuring trace amounts of an element.
The Graphite Tube
The central component is a hollow tube, typically a few centimeters long, made of high-purity graphite. This tube serves as both the sample container and the heating element. An electrical current is passed through the tube, causing it to heat up due to its own electrical resistance.
The Inert Atmosphere
The entire furnace is enclosed and continuously flushed with an inert gas, almost always argon. This is critical for two reasons: it prevents the hot graphite tube (which is carbon) from instantly burning up in the presence of oxygen, and it stops the target analyte from forming unwanted oxides that would interfere with the measurement.
Precision Sample Introduction
A very small, precise volume of the liquid sample, often just 5 to 20 microliters, is injected into the tube through a small hole. This is typically done with a highly accurate automated micropipette, ensuring a repeatable process.
The Multi-Stage Heating Program
The true power of the graphite furnace lies in its programmable temperature controller. Instead of just heating the sample, it takes it through a sequence of steps, each with a specific purpose.
Step 1: Drying
The program begins with a gentle ramp to a relatively low temperature, typically just above the boiling point of the sample's solvent (e.g., 110-120°C for water). This slowly evaporates the liquid without splattering, leaving behind a solid residue of the analyte and its surrounding matrix.
Step 2: Pyrolysis (Ashing)
Next, the temperature is increased significantly, often to several hundred degrees Celsius. The goal of this pyrolysis step is to char or burn away as much of the background material (like organic matter or volatile salts) as possible, without losing the target element you want to measure. This is a crucial cleanup stage.
Step 3: Atomization
This is the measurement step. The furnace temperature is ramped up almost instantaneously to a very high level (e.g., 2000-2700°C). This intense heat flash-vaporizes the remaining residue, breaking all chemical bonds and creating a dense, short-lived cloud of individual, neutral atoms of your target element. A beam of light is passed through the tube, and the amount of light absorbed by this atomic cloud is measured to determine its concentration.
Step 4: Cleaning
Finally, the temperature is raised to its maximum setting for a few seconds. This high-temperature "burnout" vaporizes any remaining residue, cleaning the tube and preparing it for the next sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the graphite furnace technique is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Advantage: Unmatched Sensitivity
The primary reason to use GFAAS is its phenomenal sensitivity. By atomizing the entire sample and temporarily trapping the atomic vapor in the light path, it can achieve detection limits thousands of times lower than other methods, often in the parts-per-billion (ppb) or even parts-per-trillion (ppt) range.
Advantage: Small Sample Volume
The ability to analyze mere microliters of a sample is a major benefit when dealing with precious, limited, or difficult-to-acquire materials, such as biological fluids or forensic evidence.
Trade-off: Slower Analysis Time
The multi-stage heating program, while precise, is time-consuming. A single analysis can take 2-3 minutes, making it much slower than techniques like Flame AAS, which can analyze samples in seconds. It is not well-suited for high-throughput screening.
Trade-off: Matrix Interferences
Despite the pyrolysis step, complex samples can still create chemical or spectral interferences that disrupt the measurement. Overcoming these often requires a deep understanding of the chemistry and careful optimization of the heating program.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding to use a graphite furnace depends entirely on your analytical requirements.
- If your primary focus is ultra-trace element detection: The high sensitivity of GFAAS makes it the superior choice for quantifying elements at parts-per-billion (ppb) or lower concentrations.
- If your sample volume is extremely limited: Its ability to work with microliter-sized samples is a major advantage for precious or clinical materials.
- If your analysis throughput is a secondary concern: The slower, sequential nature of GFAAS is a necessary trade-off for its high precision and low detection limits.
Ultimately, the graphite furnace is a specialized instrument designed to convert a complex liquid sample into a simple atomic vapor, enabling some of the most sensitive elemental analysis possible.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | ~110-120°C | Evaporates solvent without splattering |
| Pyrolysis (Ashing) | Several hundred °C | Removes organic matrix without losing analyte |
| Atomization | 2000-2700°C | Flash-vaporizes sample into atomic vapor for measurement |
| Cleaning | Maximum temperature | Vaporizes residue to prepare for next sample |
Need ultra-sensitive elemental analysis for your lab? KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including custom-designed Tube and Vacuum Furnaces, are engineered to meet the precise demands of GFAAS and other trace analysis techniques. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide robust, reliable heating platforms with the temperature control and inert atmosphere management critical for your research. Contact our experts today to discuss how our deep customization capabilities can optimize your analytical processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















