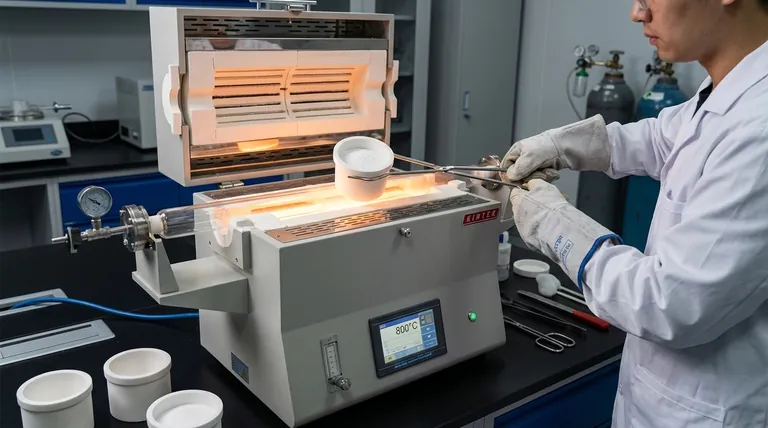
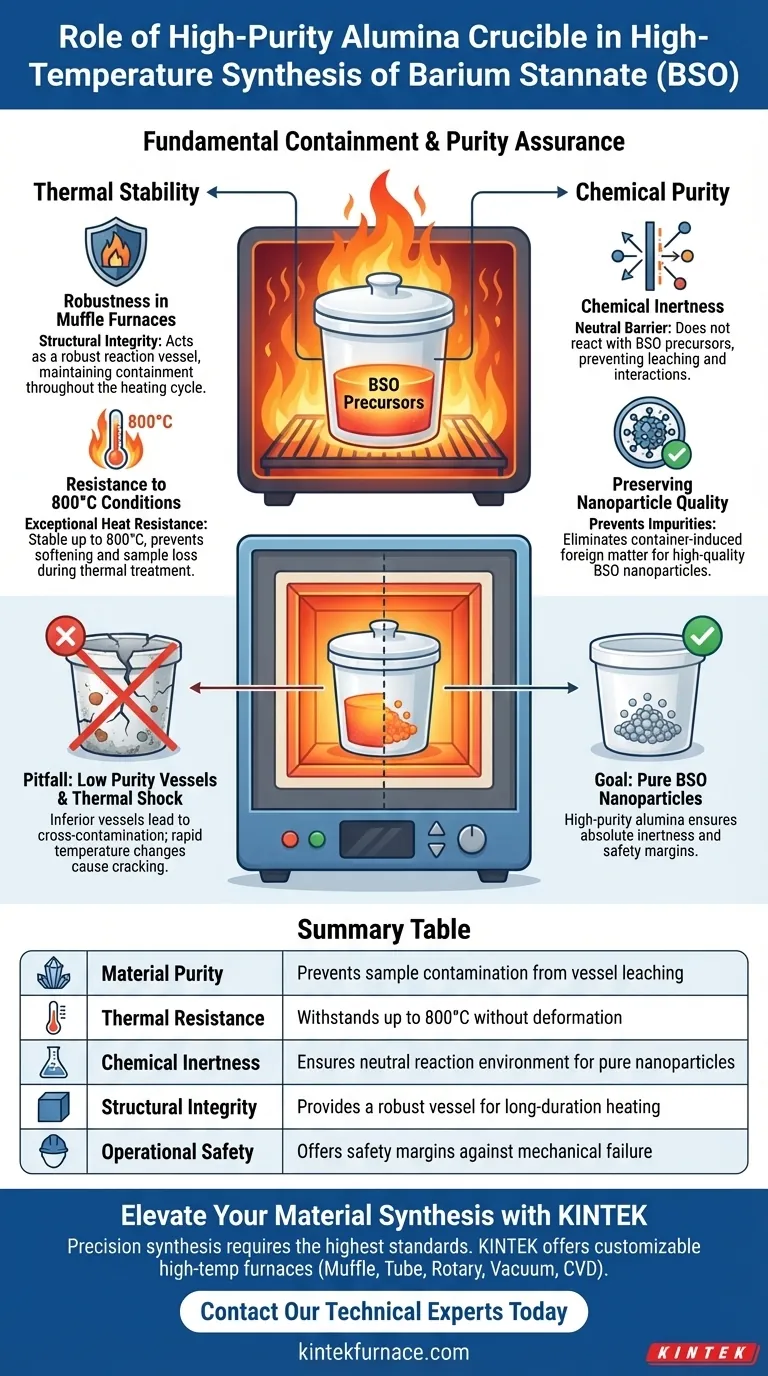
A high-purity alumina crucible serves as the fundamental containment vessel during the synthesis of Barium Stannate (BSO). It is specifically engineered to hold chemical samples within a muffle furnace, ensuring they withstand thermal treatment up to 800°C without physical degradation or chemical interaction.
The crucible’s primary value lies in its exceptional chemical inertness. By preventing reactions between the vessel and the heated sample, it guarantees that the final Barium Stannate nanoparticles remain free of container-induced impurities.

The Mechanics of Thermal Stability
Robustness in Muffle Furnaces
The synthesis of Barium Stannate requires sustained exposure to high heat to facilitate the necessary chemical changes.
A high-purity alumina crucible is designed to act as a robust reaction vessel within this harsh environment. It provides the structural integrity needed to carry the samples into a muffle furnace and maintain containment throughout the heating cycle.
Resistance to 800°C Conditions
Standard laboratory glassware or lower-grade ceramics often fail or soften at the temperatures required for BSO synthesis.
High-purity alumina possesses exceptional heat resistance, allowing it to remain stable at temperatures as high as 800°C. This ensures the vessel retains its shape and mechanical strength, preventing sample loss during the critical thermal treatment phase.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
Chemical Inertness
At elevated temperatures, many materials become reactive, potentially leaching elements into the sample they contain.
The defining characteristic of this crucible is its chemical stability. It does not react with the Barium Stannate precursors, acting as a neutral barrier rather than a participant in the chemical reaction.
Preserving Nanoparticle Quality
The goal of this synthesis is the creation of high-quality BSO nanoparticles. Any foreign matter introduced during heating would compromise the electronic or structural properties of these particles.
By eliminating the risk of reaction between the container and the sample, the crucible prevents the introduction of impurities. This ensures the final output is pure Barium Stannate, rather than a contaminated compound.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of Lower Purity Vessels
It is a common error to assume that all ceramic crucibles perform equally.
Crucibles with lower alumina purity or higher silica content often lack the necessary inertness for high-precision synthesis. Using an inferior vessel can lead to cross-contamination, where elements from the crucible wall migrate into the melt, fundamentally altering the composition of your final product.
Thermal Shock Sensitivity
While alumina is heat resistant, it is technically a ceramic and subject to thermal shock if heated or cooled too rapidly.
Operators must manage the temperature ramp rates in the muffle furnace carefully. Rapid temperature changes can crack the crucible, risking the loss of the Barium Stannate sample inside.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the success of your high-temperature synthesis, align your equipment choice with your specific scientific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Prioritize crucibles with the highest available alumina content to ensure absolute inertness and prevent impurity leaching.
- If your primary focus is Process Stability: Ensure the crucible is rated for temperatures significantly higher than your 800°C target to provide a safety margin against thermal failure.
The quality of your Barium Stannate nanoparticles is ultimately limited by the quality of the vessel in which they are created.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit in BSO Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Material Purity | Prevents sample contamination from vessel leaching |
| Thermal Resistance | Withstands temperatures up to 800°C without deformation |
| Chemical Inertness | Ensures neutral reaction environment for pure nanoparticles |
| Structural Integrity | Provides a robust vessel for long-duration muffle furnace heating |
| Operational Safety | Offers safety margins against mechanical failure at high heat |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision synthesis of Barium Stannate requires the highest standards of thermal and chemical stability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab high-temp furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Don't let vessel impurities compromise your nanoparticle quality. Partner with KINTEK for reliable, high-purity laboratory solutions designed for high-precision results.
Contact Our Technical Experts Today
Visual Guide
References
- Nehal Ashok Waghchoure, Halan Prakash. Removal of tetracycline antibiotic activity in water by stable cubic phase barium stannate-perovskite nanoparticles under energy-efficient blue light LED irradiation. DOI: 10.1039/d5ra02938d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the considerations for using vacuum-sealed quartz tubes for Ti-xCr-2Ge alloys? Ensure Peak Alloy Performance
- What is the main purpose of BN coating on graphite in Ti-6Al-4V hot pressing? Ensure Purity & Easy Release
- What is the importance of a water-cooled injector in DTF experiments? Ensure Precise Ignition Delay Measurement
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles preferred? Secure Unmatched Purity and Data Integrity in Lab Synthesis
- What is the purpose of using specialized vacuum glass tubes for sampling? Ensure KR Stirring Chemical Integrity
- What are the main reasons for the alumina furnace tube being prone to breaking? Prevent Costly Failures with Expert Tips
- What is the function of alumina crucibles in YBCO synthesis? Ensure Purity & Stability in Superconductor Production
- What are the technical considerations for using alumina crucibles? Optimize High-Entropy Alloy Purity & Microstructure



















