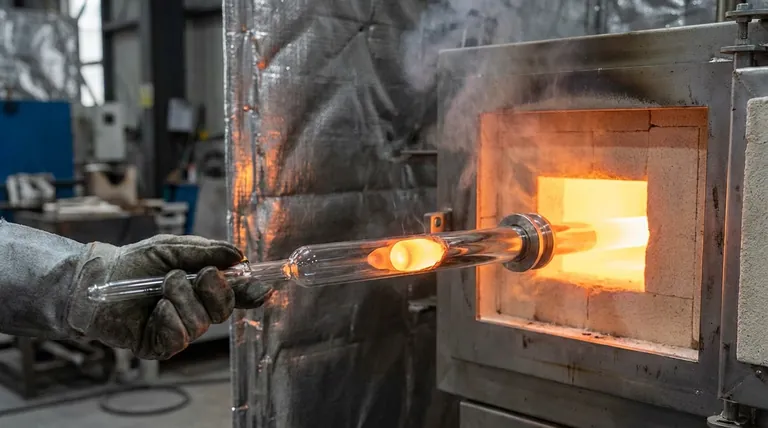
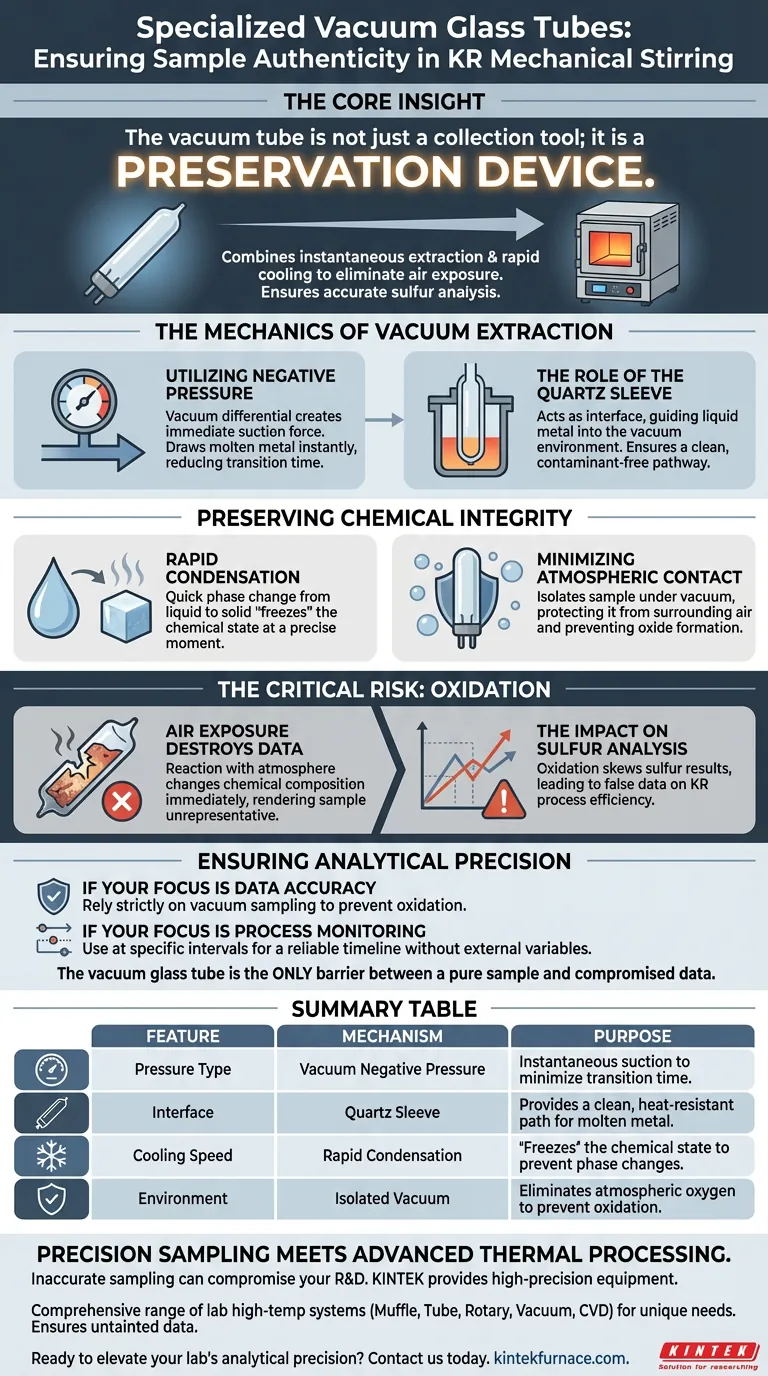
The primary purpose of specialized vacuum glass tubes in KR mechanical stirring is to guarantee the chemical authenticity of molten metal samples. These tubes utilize vacuum negative pressure to instantly draw liquid metal through a quartz sleeve and force rapid condensation. This specific mechanism is required to isolate the sample from the atmosphere, preventing oxidation that would otherwise corrupt subsequent sulfur content analysis.
The Core Insight: The vacuum tube is not just a collection tool; it is a preservation device. By combining instantaneous extraction with rapid cooling, it eliminates the variable of air exposure, ensuring that the sulfur levels measured in the lab match exactly what exists in the reactor.

The Mechanics of Vacuum Extraction
Utilizing Negative Pressure
The system relies on vacuum negative pressure rather than manual scooping or gravity.
This pressure differential creates an immediate suction force. It draws the molten metal into the tube instantly, reducing the time the metal spends in transition.
The Role of the Quartz Sleeve
The extraction takes place through a quartz sleeve acting as the interface between the reactor and the sampler.
This component guides the liquid metal into the vacuum environment. It ensures a clean pathway for the sample to enter the tube without picking up external contaminants.
Preserving Chemical Integrity
Rapid Condensation
Once the molten metal enters the tube, it undergoes rapid condensation.
This quick phase change from liquid to solid is deliberate. It "freezes" the chemical state of the metal at that precise moment in the stirring process.
Minimizing Atmospheric Contact
The defining feature of this method is the minimization of oxidation.
By keeping the sample under vacuum and cooling it quickly, the metal is protected from the surrounding air. This prevents the formation of oxides that would occur if the hot metal were exposed to oxygen during a slower cooling process.
The Critical Risk: Oxidation
Why Air Exposure Destroys Data
The primary pitfall in high-temperature metal sampling is the reaction between the metal and the atmosphere.
If a sample oxidizes, its chemical composition changes immediately. This alteration renders the sample unrepresentative of the actual batch in the reactor.
The Impact on Sulfur Analysis
The text explicitly links the use of vacuum tubes to the accuracy of sulfur content analysis.
Sulfur analysis is highly sensitive to the quality of the sample. Without the protection provided by the vacuum tube, oxidation would skew the results, leading to false data regarding the desulfurization efficiency of the KR process.
Ensuring Analytical Precision
To ensure your KR mechanical stirring data is actionable, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is Data Accuracy: Rely strictly on vacuum sampling to prevent oxidation from skewing your sulfur measurements.
- If your primary focus is Process Monitoring: Use these tubes at specific time intervals to create a reliable timeline of the stirring effect without external variables.
The vacuum glass tube is the only barrier standing between a pure sample and compromised data.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Mechanism | Purpose in KR Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Type | Vacuum Negative Pressure | Instantaneous suction to minimize transition time |
| Interface | Quartz Sleeve | Provides a clean, heat-resistant path for molten metal |
| Cooling Speed | Rapid Condensation | "Freezes" the chemical state to prevent phase changes |
| Environment | Isolated Vacuum | Eliminates atmospheric oxygen to prevent oxidation |
Precision Sampling Meets Advanced Thermal Processing
Inaccurate sampling can compromise your entire R&D or production timeline. KINTEK provides the high-precision equipment necessary to maintain the integrity of your most sensitive materials.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of lab high-temp systems—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you are conducting KR mechanical stirring experiments or advanced metallurgy, our solutions ensure your data remains untainted by environmental variables.
Ready to elevate your lab's analytical precision? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace requirements.
Visual Guide
References
- Jyun-Ming Shen, Weite Wu. Effects of Different CaO/Al2O3 Ratios on the Phase Composition and Desulfurization Ability of CaO-Based Desulfurizers in Hot Metal. DOI: 10.3390/met14030363
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a ceramic protection tube in a furnace? Protect High-Temp Measurements and Equipment
- How do the quartz crucible and descending device function in Bridgman method? Precision Growth for CsPbBr3 Crystals
- What are the placement requirements for high-precision standard thermocouples? Master Sensor Calibration Accuracy
- Why is it necessary to use alumina or ceramic crucibles during the high-temperature evaporation of magnesium? Ensure Purity and Process Integrity
- Why are fly ash geopolymer specimens subjected to 60 °C drying? Master Accelerated Curing for Maximum Strength
- What is the specific purpose of using a graphite crucible equipped with a plug during the melting process of Mg3Sb2?
- How does the dispersion of ruthenium precursors on alumina carriers affect thermal processing in a lab furnace?
- What other industrial applications do graphite crucible furnaces have beyond metal melting? Unlock Advanced Material Processing



















