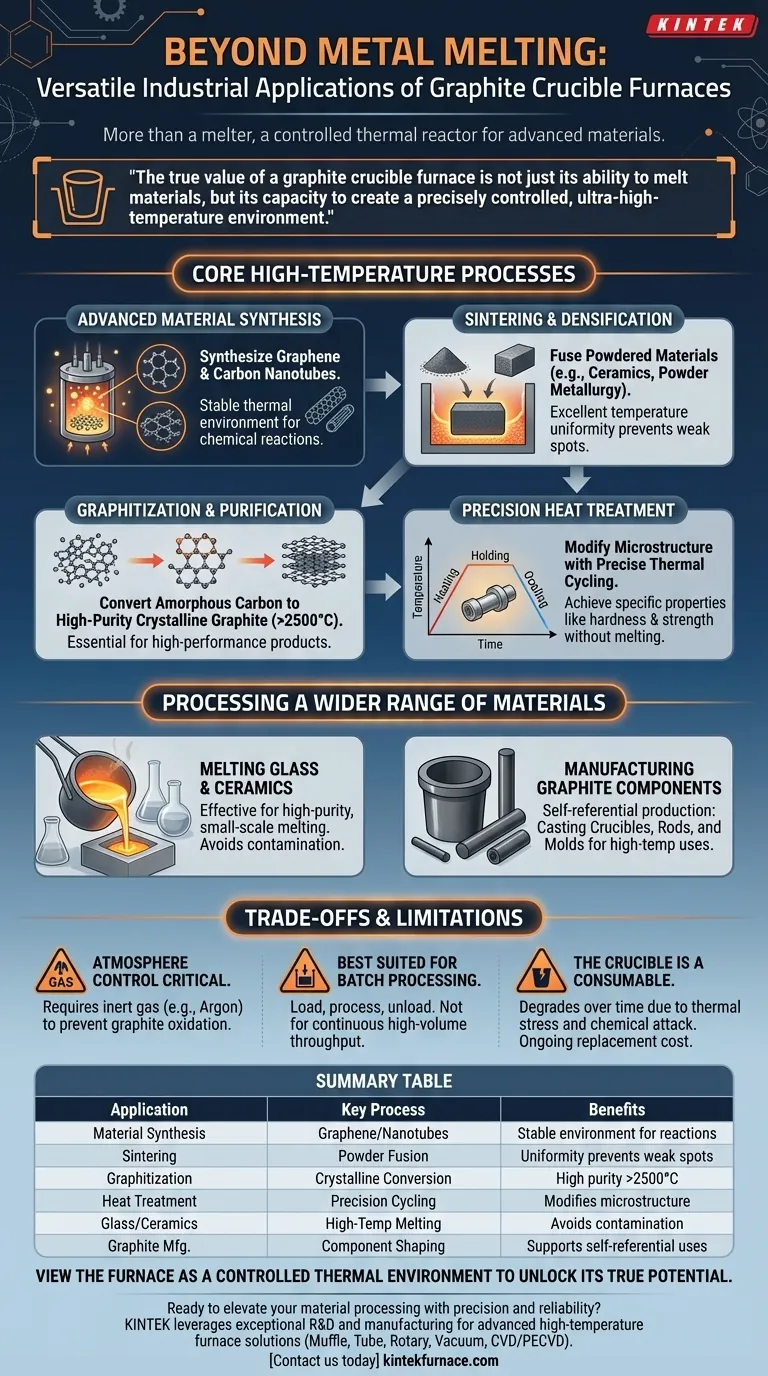
Beyond simple melting, a graphite crucible furnace serves as a versatile high-temperature reactor for advanced material science and manufacturing. Its primary applications outside of metal processing include the synthesis of new materials like graphene, specialized heat treatments such as sintering and graphitization, and the melting of non-metallic substances like glass and ceramics.
The true value of a graphite crucible furnace is not just its ability to melt materials, but its capacity to create a precisely controlled, ultra-high-temperature environment. This makes it a critical tool for fundamentally transforming the structure and properties of a wide range of materials.

Beyond Melting: Core High-Temperature Processes
The furnace's capabilities extend far beyond liquefying metals. Its core function is to provide a stable, high-heat environment, which is essential for several advanced industrial and scientific processes.
The Role in Advanced Material Synthesis
Graphite crucible furnaces are instrumental in producing next-generation materials. The synthesis of substances like graphene and carbon nanotubes requires consistently high temperatures to facilitate the necessary chemical reactions and structural formation. The furnace provides the stable thermal environment these delicate processes demand.
Sintering and Material Densification
Sintering is a process where a powdered material is heated to just below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse together and form a solid, dense mass. This is critical in powder metallurgy and ceramics. The excellent temperature uniformity of a graphite crucible furnace ensures the material is sintered evenly, preventing weak spots and internal stresses.
Graphitization and Purification
These furnaces are used in the graphitization process itself, where amorphous carbon materials are converted into high-purity, crystalline graphite at temperatures exceeding 2500°C. This is essential for manufacturing high-performance graphite products, including the very crucibles and heating elements used in the furnaces.
Precision Heat Treatment
Many materials require specific heat treatments to achieve desired properties like hardness, strength, or ductility. A graphite crucible furnace allows for precise thermal cycling—heating and cooling a material according to a strict profile—without melting it. This modifies the material's internal microstructure to meet exact engineering specifications.
Processing a Wider Range of Materials
The inert and high-temperature nature of graphite makes these furnaces suitable for more than just metals and carbon-based products.
Melting Glass and Ceramics
The ability to reach and maintain high temperatures makes crucible furnaces effective for melting and processing specialty glasses and ceramics. This is common in laboratory settings and for small-scale production of high-purity materials where contamination must be avoided.
Manufacturing Graphite Components
In a self-referential application, graphite crucible furnaces are used to process and shape other graphite products. This includes casting new crucible tanks, pull rods, and molds that will be used in other high-temperature applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly versatile, graphite crucible furnaces are not the universal solution for every high-temperature task. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Atmosphere Control is Critical
Graphite oxidizes (burns away) in the presence of oxygen at high temperatures. Therefore, many processes require the furnace to be operated with an inert gas atmosphere (like argon) to protect both the crucible and the material being processed. This adds a layer of complexity and cost.
Best Suited for Batch Processing
Crucible furnaces are inherently batch-based systems. You load a batch of material, run the process, and then unload it. They are not designed for the continuous, high-volume throughput that systems like tunnel kilns or rotary furnaces can provide.
The Crucible is a Consumable
The graphite crucible is subjected to extreme thermal stress and potential chemical attack from the materials it holds. It is a consumable component that degrades over time and must be replaced periodically, representing an ongoing operational cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a graphite crucible furnace is right for you, align its core strengths with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is R&D or new material synthesis: The furnace's precise temperature control and scalability from lab-to-pilot production are invaluable.
- If your primary focus is small-batch, high-purity manufacturing: The cost-effectiveness, operational simplicity, and ability to handle diverse materials make it an excellent choice.
- If your primary focus is very large-scale bulk processing: You should evaluate alternative furnace types, such as induction or arc furnaces, which are often better suited for continuous, high-volume operations.
Ultimately, viewing the graphite crucible furnace as a controlled thermal environment, rather than just a melting pot, unlocks its true potential across modern industry.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Graphene and carbon nanotube production | Stable high-temperature environment for chemical reactions |
| Sintering | Powder fusion for densification | Excellent temperature uniformity prevents weak spots |
| Graphitization | Conversion to crystalline graphite | High purity at temperatures over 2500°C |
| Heat Treatment | Precision thermal cycling | Modifies microstructure for enhanced properties |
| Glass/Ceramics Melting | High-temperature processing | Avoids contamination in small-scale production |
| Graphite Manufacturing | Shaping components like crucibles | Supports self-referential high-temperature applications |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and reliability? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in R&D, small-batch manufacturing, or need specialized thermal environments, KINTEK delivers efficiency and innovation. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can transform your operations and drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















