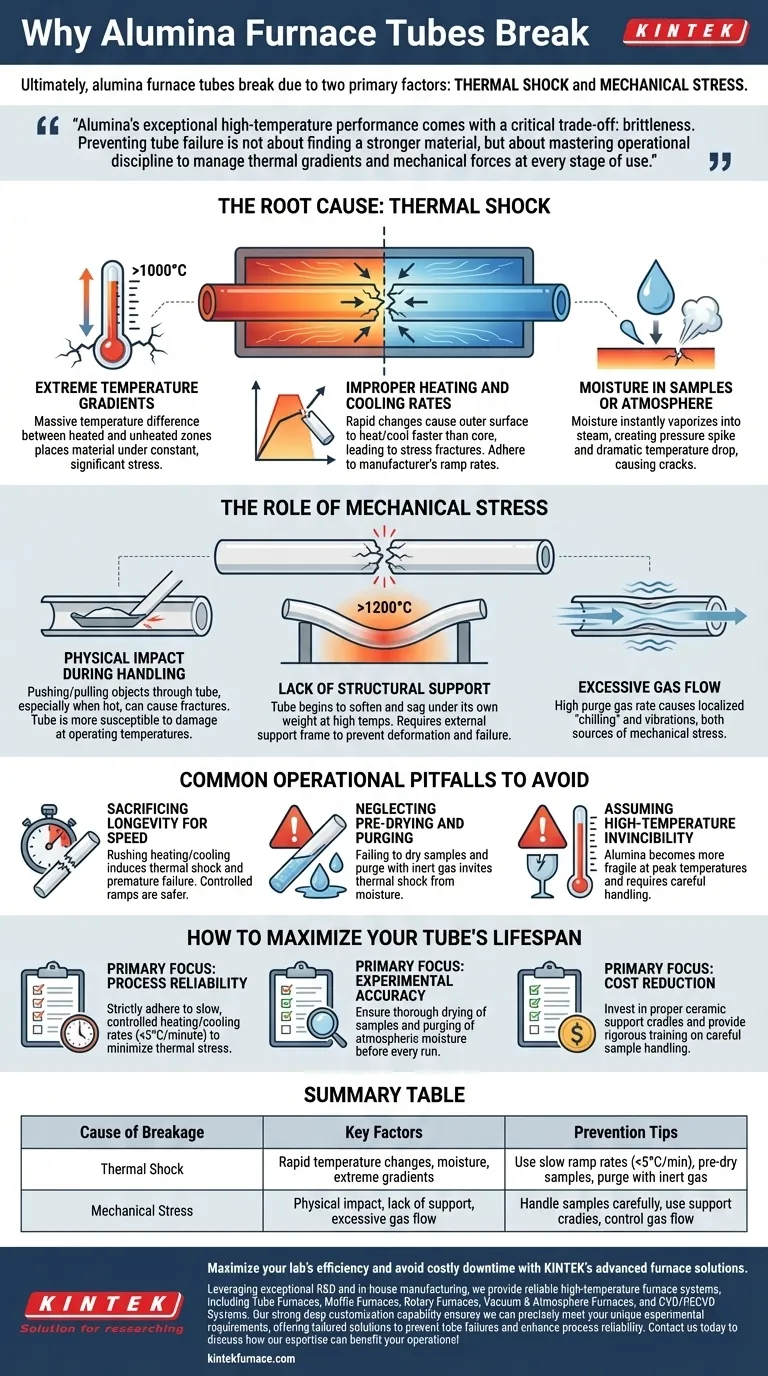
Ultimately, alumina furnace tubes break due to two primary factors: thermal shock and mechanical stress. The material is strong but brittle, and it fails when subjected to rapid temperature changes or physical force, especially when hot. The most common causes are excessive temperature differences between the heated and unheated zones, improper sample handling, and rapid heating or cooling cycles.
Alumina's exceptional high-temperature performance comes with a critical trade-off: brittleness. Preventing tube failure is not about finding a stronger material, but about mastering operational discipline to manage thermal gradients and mechanical forces at every stage of use.

The Root Cause: Thermal Shock
Thermal shock is the single greatest threat to an alumina tube. It occurs when one part of the tube expands or contracts at a different rate than another, creating immense internal stress that leads to cracking.
Extreme Temperature Gradients
A typical tube furnace creates a massive temperature difference—often exceeding 1000°C—between the central heating zone and the cooler ends of the tube. This differential expansion places the material under constant, significant stress.
Improper Heating and Cooling Rates
Rapidly changing the furnace setpoint is a direct cause of thermal shock. The outer surface of the tube heats or cools faster than the core, leading to stress fractures. Adhering to the manufacturer's recommended ramp rates is non-negotiable.
Moisture in Samples or Atmosphere
Introducing a sample with even a small amount of moisture into a hot furnace is catastrophic. The water instantly vaporizes into steam, creating a localized pressure spike and a sudden, dramatic temperature drop on the tube's inner surface, causing it to crack.
The Role of Mechanical Stress
While alumina is very hard, it cannot bend or flex. Any physical force, especially at high temperatures where its structural integrity is reduced, can lead to immediate failure.
Physical Impact During Handling
Pushing or pulling sample boats and other objects through the tube can easily cause fractures. This risk is highest at operating temperature, where the tube is more susceptible to damage from even minor impacts or scraping.
Lack of Structural Support
At high temperatures (typically above 1200°C), an alumina tube can begin to soften and sag under its own weight. Without a proper external support frame, this deformation will inevitably lead to stress cracks and catastrophic failure.
Excessive Gas Flow
A high rate of purge gas flowing through the tube can create two problems. It can cause localized "chilling" on the inner wall, inducing thermal stress, and it can create vibrations that act as a source of mechanical stress on the tube.
Common Operational Pitfalls to Avoid
Most tube failures are not accidents; they are the result of procedural errors that could have been prevented. Understanding these common mistakes is the key to improving equipment longevity.
Sacrificing Longevity for Speed
The most frequent mistake is rushing the heating or cooling process to save time. This directly induces thermal shock and is the primary driver of premature tube failure. A slow, controlled ramp is always the safer and more cost-effective approach.
Neglecting Pre-Drying and Purging
Placing a sample into the furnace without ensuring it is completely dry is a critical error. Likewise, failing to purge the tube with an inert gas to remove atmospheric moisture before heating invites thermal shock.
Assuming High-Temperature Invincibility
Operators sometimes forget that while alumina withstands heat, it becomes more fragile and susceptible to physical damage and sagging at peak temperatures. It must be handled with even greater care when hot.
How to Maximize Your Tube's Lifespan
Protecting your investment comes down to meticulous operational control. Your specific goal will determine your primary focus.
- If your primary focus is process reliability: Strictly adhere to slow, controlled heating and cooling rates (e.g., <5°C/minute) to minimize thermal stress above all else.
- If your primary focus is experimental accuracy: Ensure all samples are thoroughly dried and the tube is purged of atmospheric moisture before every run to prevent contamination and thermal shock.
- If your primary focus is cost reduction: Invest in proper ceramic support cradles for the furnace tube and provide rigorous training to operators on careful sample handling to prevent the most common forms of mechanical failure.
By treating the alumina tube as the precise but sensitive instrument it is, you can ensure its reliability and longevity for countless operations.
Summary Table:
| Cause of Breakage | Key Factors | Prevention Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock | Rapid temperature changes, moisture, extreme gradients | Use slow ramp rates (<5°C/min), pre-dry samples, purge with inert gas |
| Mechanical Stress | Physical impact, lack of support, excessive gas flow | Handle samples carefully, use support cradles, control gas flow |
Maximize your lab's efficiency and avoid costly downtime with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable high-temperature furnace systems, including Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, offering tailored solutions to prevent tube failures and enhance process reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- How does a vertical tube furnace facilitate the simulation of the industrial sintering process for iron ores?
- What core process conditions does a tube furnace provide? Mastering Catalyst Precursor Treatment
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















