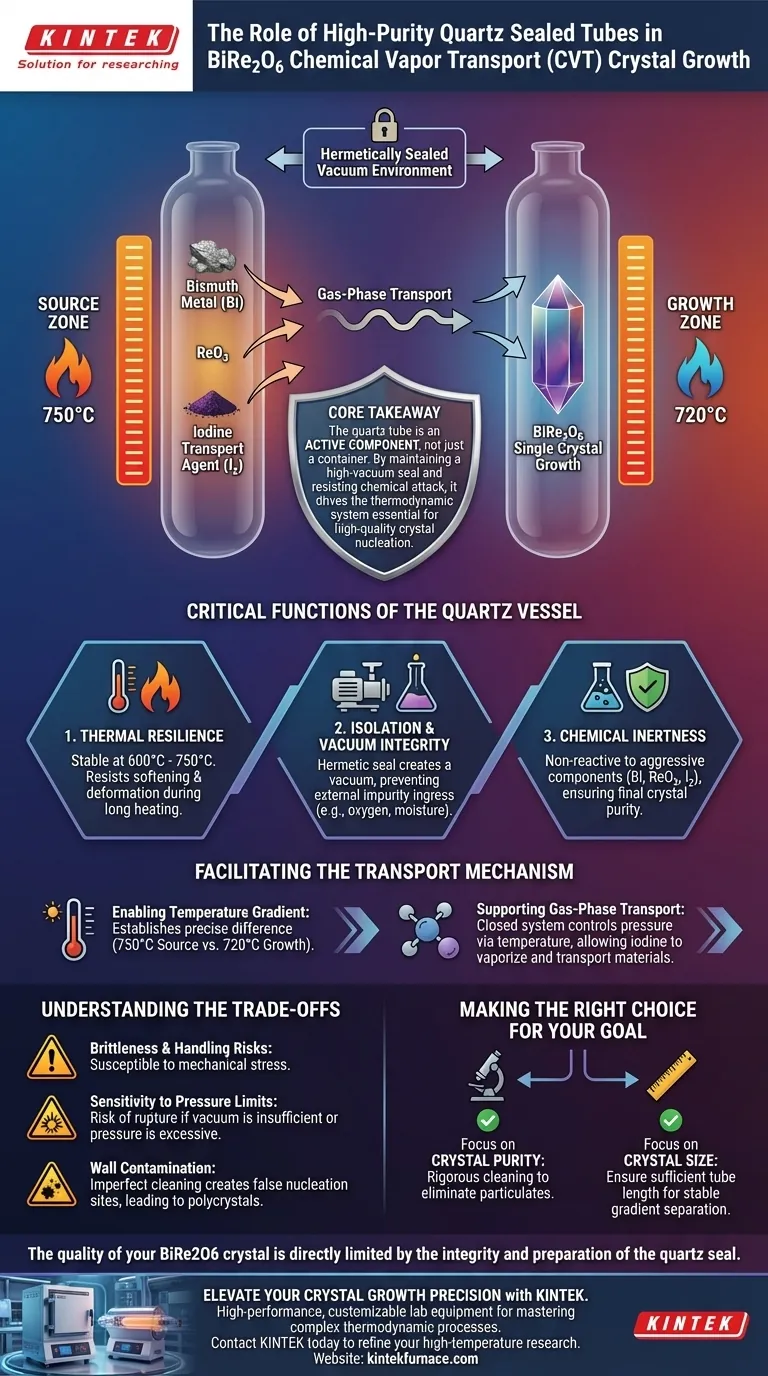
High-purity quartz sealed tubes serve as the primary containment vessel for the Chemical Vapor Transport (CVT) growth of BiRe2O6 crystals, creating the necessary isolated vacuum environment. These tubes are engineered to withstand operating temperatures between 600°C and 750°C while preventing the reactants—Bismuth metal, ReO3, and iodine—from interacting with atmospheric contaminants.
Core Takeaway The quartz tube is not merely a container; it is an active component of the thermodynamic system. By maintaining a high-vacuum seal and resisting chemical attack, it allows the iodine transport agent to facilitate gas-phase reactions across a specific temperature gradient, which is the mechanism that drives high-quality crystal nucleation.

The Critical Functions of the Quartz Vessel
The success of growing BiRe2O6 single crystals relies on the tube's ability to maintain three specific conditions simultaneously.
Thermal Resilience and Stability
The growth process for BiRe2O6 requires sustained high temperatures. The quartz material must remain structurally sound and chemically stable across a range of 600°C to 750°C.
This thermal resistance ensures the tube does not soften or deform during the extended heating periods required for the recrystallization process.
Isolation and Vacuum Integrity
The tube functions as a hermetically sealed barrier. It creates a vacuum environment that isolates the internal chemical reaction from the outside world.
This isolation is critical to prevent the ingress of external impurities, such as oxygen or moisture, which would contaminate the crystal lattice or oxidize the reactants.
Chemical Inertness
Inside the tube, aggressive chemical reactions occur involving Bismuth metal, ReO3, and iodine transport agents.
High-purity quartz is chemically inert, meaning it does not react with these volatile components. This ensures that the final crystals are composed solely of the intended precursors, maintaining high purity.
Facilitating the Transport Mechanism
Beyond simple containment, the geometry and material properties of the tube support the physics of the CVT process.
Enabling the Temperature Gradient
The tube allows for the establishment of a precise spatial temperature difference. For BiRe2O6, this typically involves a source zone at 750°C and a growth zone at 720°C.
Supporting Gas-Phase Transport
The sealed nature of the tube creates a closed system where pressure is controlled solely by temperature.
This allows the iodine transport agent to vaporize, react with the source material in the hot zone, travel to the cooler zone, and deposit the BiRe2O6 crystal, driving the "transport" mechanism essential for growth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While high-purity quartz is the standard for this process, it introduces specific constraints that must be managed to avoid failure.
Brittleness and Handling Risks
Quartz is inherently brittle. While it handles high heat well, it is susceptible to mechanical stress during the sealing process or when loading the precursor materials.
Sensitivity to Pressure Limits
The tube acts as a pressure vessel once the iodine vaporizes. If the initial vacuum is insufficient or if the reactant ratios create excessive internal pressure, the tube can rupture.
Wall Contamination
Although quartz is inert, if the tube walls are not perfectly clean before sealing, surface contaminants can become nucleation sites. This can lead to the growth of many small, low-quality polycrystals rather than the desired single large crystal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When preparing your CVT setup for BiRe2O6, focus your attention on these specific aspects of the quartz tube assembly.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Purity: Ensure the quartz tube undergoes a rigorous cleaning protocol before loading to eliminate microscopic particulates that act as false nucleation sites.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Size: Verify that the tube length is sufficient to maintain a distinct, stable separation between the 750°C source zone and the 720°C growth zone to control the transport rate.
The quality of your BiRe2O6 crystal is directly limited by the integrity and preparation of the quartz seal that protects it.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in CVT Process for BiRe2O6 |
|---|---|
| Material | High-purity Quartz (Chemically Inert) |
| Temperature Range | 600°C to 750°C Resilience |
| Atmosphere | Hermetically Sealed Vacuum Environment |
| Gradient Setup | 750°C (Source) to 720°C (Growth Zone) |
| Function | Contains iodine transport agents & prevents contamination |
Elevate Your Crystal Growth Precision
High-quality BiRe2O6 single crystals demand an environment free of contaminants and thermal instability. KINTEK provides the specialized lab equipment necessary to master these complex thermodynamic processes.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your unique research specifications. Whether you are optimizing CVT transport rates or scaling high-temp synthesis, our team delivers the reliability your lab requires.
Ready to refine your high-temperature research? Contact KINTEK today to discuss our custom furnace solutions and enhance your lab's efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Premakumar Yanda, Claudia Felser. Direct Evidence of Topological Dirac Fermions in a Low Carrier Density Correlated 5d Oxide. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202512899
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the post-deposition processing of Ge:ZnO thin films?
- Why are a split furnace and a PID temperature controller core in supercritical water gasification? Essential Guide
- What is the technical significance of using a dual-temperature zone tube furnace for CoTe2 tellurization?
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- Why is a high-vacuum tube furnace required for sintering aluminum composites? Achieve Superior Purity and Density
- Why is a tube reduction furnace necessary for sub-stoichiometric uranium dioxide? Precision Chemical Reduction Guide
- How do dual-zone tube furnaces facilitate the growth of BiRe2O6 single crystals? Precision Gradient Control Explained
- How does a tube furnace achieve high thermal efficiency? Optimize Energy Use for Cost Savings



















