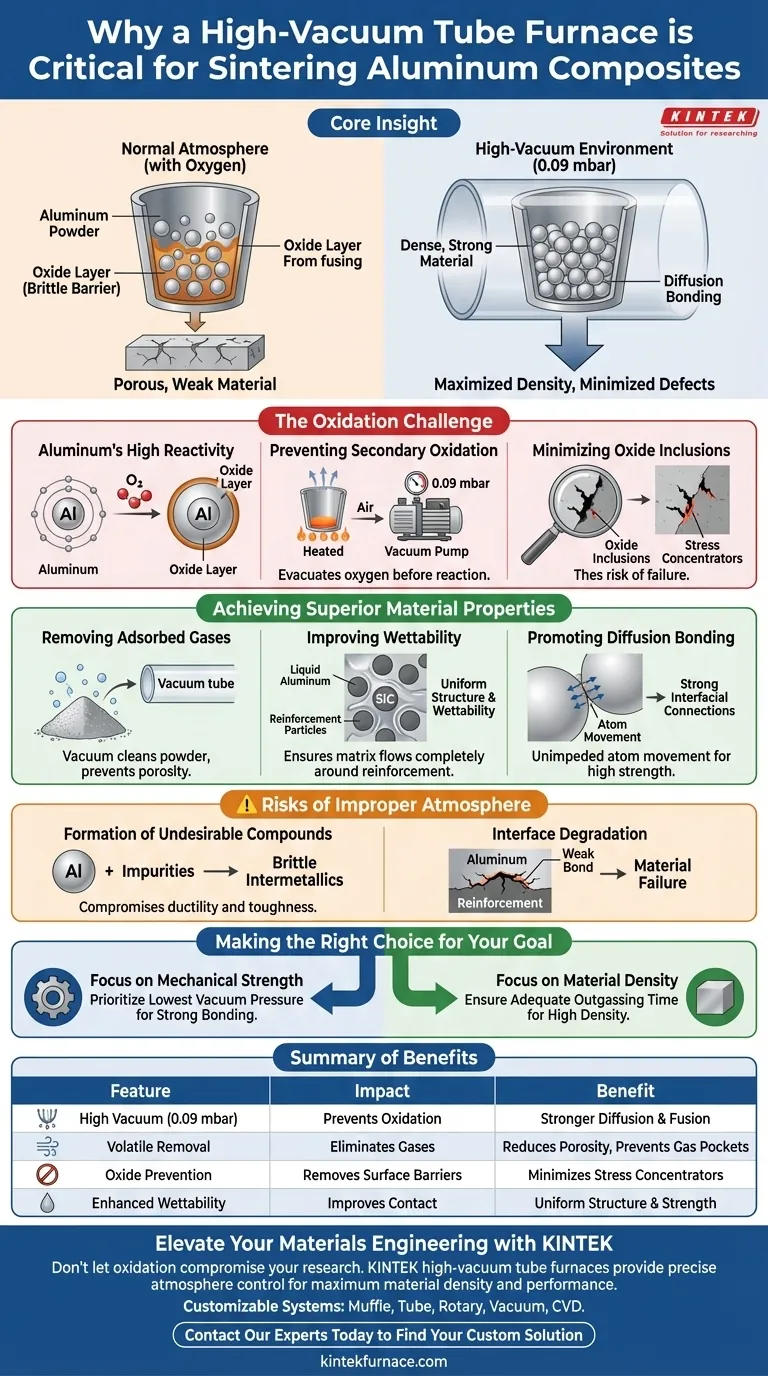
A high-vacuum tube furnace is essential for sintering aluminum-based composites because aluminum is extremely reactive to oxygen. By maintaining a pressure environment typically around 0.09 mbar, the furnace prevents the aluminum powder surfaces from undergoing secondary oxidation during high-temperature processing. This allows for effective diffusion bonding between particles, resulting in a denser and mechanically stronger material.
Core Insight: The primary role of the vacuum is to create a pristine chemical environment that removes volatile contaminants and prevents the formation of brittle oxide barriers. This ensures the aluminum matrix can physically bond with reinforcement materials, maximizing density and minimizing structural defects.

The Critical Challenge of Oxidation
Aluminum's High Reactivity
Aluminum has a natural affinity for oxygen. When exposed to heat in a standard atmosphere, aluminum powder instantly reacts to form a tough, stable oxide layer on its surface.
Preventing Secondary Oxidation
A high-vacuum environment is required to stop this "secondary oxidation." Even trace amounts of oxygen can create barrier layers that prevent the metal particles from fusing together.
By operating at extremely low pressures (e.g., 0.09 mbar), the furnace ensures that oxygen is evacuated before it can react with the heated aluminum surfaces.
Minimizing Oxide Inclusions
If oxidation occurs, oxide inclusions become trapped within the material. These inclusions act as stress concentrators, significantly degrading the final mechanical properties of the composite.
Achieving Superior Material Properties
Removing Adsorbed Gases
Beyond oxygen, raw powder materials often contain adsorbed gases and other volatile impurities on their surfaces.
The vacuum system effectively "cleans" the powder by drawing out these volatiles as the temperature rises. This prevents gas pockets from forming inside the sintered part, which would otherwise lead to porosity and weakness.
Improving Wettability
For composite materials, the aluminum matrix must bond with a reinforcement phase, such as Silicon Carbide (SiC).
A clean, vacuum-processed atmosphere improves the wettability between the liquid or semi-solid aluminum and the reinforcement particles. This ensures the matrix flows completely around the reinforcement, creating a uniform structure.
Promoting Diffusion Bonding
Sintering relies on diffusion—the movement of atoms across particle boundaries to fuse them together.
Oxide layers act as a wall that stops this movement. By preventing oxidation, the vacuum environment facilitates unimpeded diffusion bonding, leading to strong interfacial connections and high material density.
Understanding the Risks of Improper Atmosphere
Formation of Undesirable Compounds
Without a controlled vacuum, the chemical balance of the sintering process changes. This can lead to the formation of undesirable intermetallic compounds.
These brittle compounds can compromise the ductility and toughness of the composite. A high-vacuum furnace minimizes their formation, preserving the intended characteristics of the alloy.
Interface Degradation
If the interface between the aluminum and the reinforcement is contaminated by oxides or gases, the bond will be weak. Under stress, the material is likely to fail at these interfaces rather than utilizing the strength of the reinforcement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the success of your sintering process, align your equipment settings with your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Strength: Prioritize achieving the lowest possible vacuum pressure to eliminate oxide layers that inhibit strong interfacial bonding.
- If your primary focus is Material Density: Ensure the heating profile includes adequate time under vacuum to fully outgas adsorbed volatiles before the sintering temperature is reached.
The high-vacuum tube furnace is not merely a heating device; it is a critical process control tool that ensures the chemical purity required to engineer high-performance aluminum composites.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on Aluminum Sintering | Benefit to Composite Material |
|---|---|---|
| High Vacuum (0.09 mbar) | Prevents secondary oxidation | Stronger diffusion bonding and particle fusion |
| Volatile Removal | Eliminates adsorbed gases | Reduces porosity and prevents internal gas pockets |
| Oxide Prevention | Removes brittle surface barriers | Minimizes stress concentrators and inclusions |
| Enhanced Wettability | Improves matrix-reinforcement contact | Uniform structure with superior interfacial strength |
Elevate Your Materials Engineering with KINTEK
Don’t let oxidation compromise your research or production quality. KINTEK’s high-vacuum tube furnaces are engineered specifically for the rigorous demands of aluminum-based composite sintering, providing the precise atmosphere control needed to achieve maximum material density and mechanical performance.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we offer a full range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique laboratory or industrial needs. Partner with KINTEK to ensure every sintering cycle delivers pristine results.
Contact Our Experts Today to Find Your Custom Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Palak H. Desai, Bharati Rehani. Aluminium-Nano Ceria-Fly Ash Hybrid Composite Prepared by High Energy Milling. DOI: 10.21608/jesaun.2025.394241.1558
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What critical conditions does a high-temperature tube furnace provide for Ti–Nb–Si alloys? Master Sintering Success
- How does a tubular furnace work? Achieve Precise, Uniform Heat for Your Lab
- What process conditions are provided by a horizontal tube furnace for AuNPs@MOF catalysts? Precise Thermal Control
- What should be considered when purchasing a vacuum tube furnace? Key Factors for Precision and Performance
- What are the key benefits of using a tube furnace for material processing? Achieve Precise Heat Control for Superior Results
- How does a horizontal tube furnace facilitate the single-step annealing of BZSM nanophosphors? Expert Thermal Control
- How can the uniform length of a tube furnace be improved? Boost Temperature Uniformity with Proven Methods
- What technical requirements affect the external thermal strength of furnace tubes? Optimize for High-Temp Performance



















