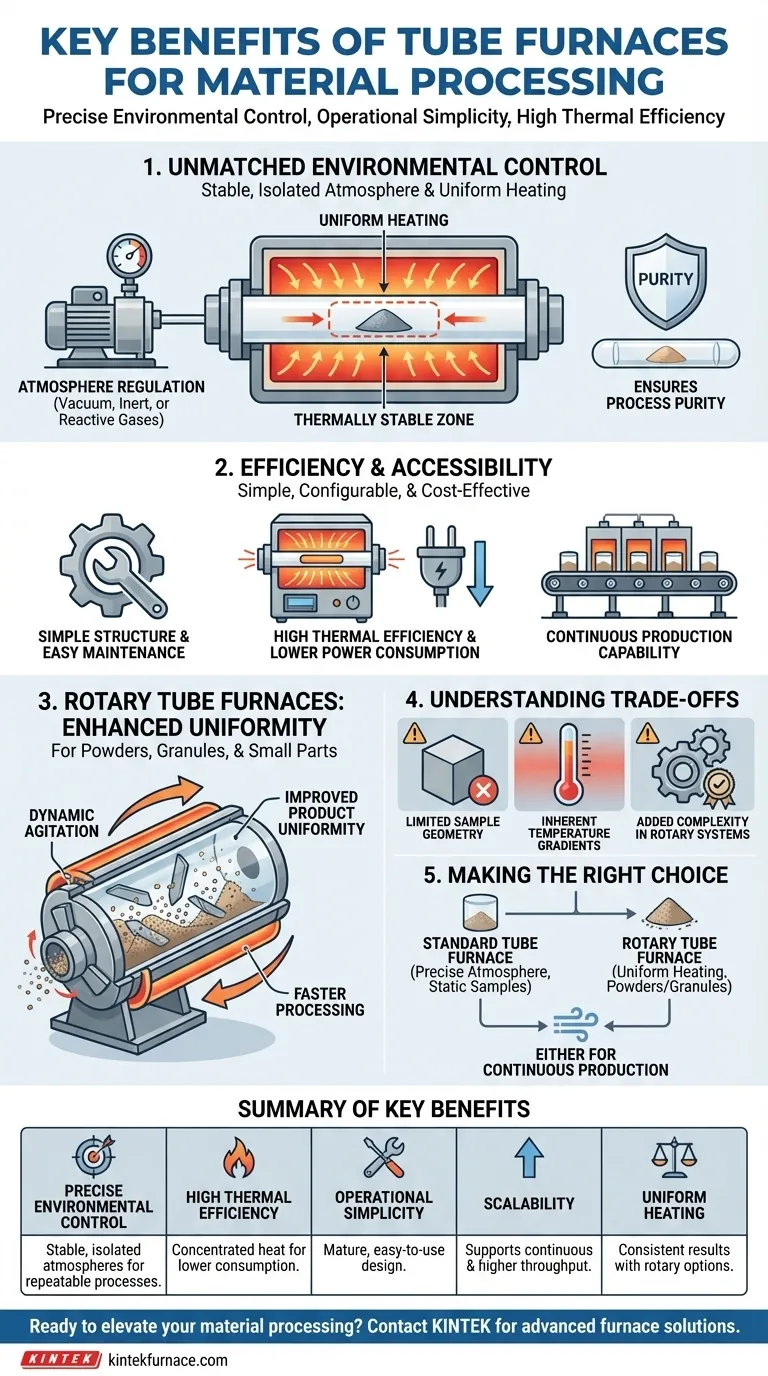
At their core, tube furnaces provide a powerful combination of precise environmental control, operational simplicity, and high thermal efficiency for material processing. They excel at creating a stable, isolated atmosphere around a sample, allowing for highly repeatable heat treatment under tightly regulated conditions, whether in a vacuum or with specific gases.
A tube furnace is more than just a heating device; it is a precisely controlled micro-environment. Its fundamental value comes from its ability to isolate a sample and subject it to a stable, uniform, and repeatable thermal process, which is critical for consistent, high-quality results.

The Foundation: Unmatched Environmental Control
The primary advantage of a tube furnace is its ability to create and maintain a highly specific processing environment, isolated from external factors.
Achieving Precise Temperature Uniformity
A tube furnace is designed with heating elements surrounding a central tube. This configuration naturally creates a thermally stable zone in the center of the tube, which provides exceptionally uniform heating.
While the ends of the tube are inherently cooler, this gradient allows for controlled heating and cooling as samples are inserted or removed.
Mastering Atmosphere Regulation
The sealed nature of the process tube makes it ideal for controlling the atmosphere. You can easily pull a vacuum to remove contaminants or introduce specific gases.
This allows for processes like annealing in an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation or using reactive gases for specific chemical reactions and surface treatments.
Ensuring Process Purity
By containing the sample within a ceramic or quartz tube, the furnace protects it from any potential contamination from the heating elements themselves. This separation is crucial for high-purity applications in electronics, research, and advanced materials.
Designed for Efficiency and Accessibility
Beyond control, tube furnaces are valued for their practical design, making them a staple in labs and industrial settings.
The Advantage of a Simple Structure
Most tube furnaces feature a mature, simple design. This results in equipment that is plentiful, relatively inexpensive, and easy to operate and maintain.
Their configurability allows for easy adaptation to different tube diameters and materials, making them a versatile tool for various applications.
High Thermal Efficiency
The enclosed, cylindrical design concentrates heat directly onto the process tube, leading to high thermal efficiency and lower power consumption compared to larger, open-chamber furnaces. This makes them cost-effective for both short experiments and long production runs.
Capability for Continuous Production
Many tube furnaces are designed for continuous operation, allowing for a steady flow of material to be processed. For larger-scale needs, multiple furnaces can be combined to increase throughput, providing a scalable production solution.
The Next Level: Understanding Rotary Tube Furnaces
For processing powders, granules, or small parts, the rotary tube furnace offers a significant enhancement over the standard static design.
What Makes a Rotary Furnace Different?
A rotary tube furnace adds the ability to rotate and tilt the process tube. This introduces dynamic movement to the material being processed inside.
These systems often feature multiple heating zones along the length of the tube to create a precise temperature profile for material as it moves through.
The Benefit of Dynamic Agitation
The rotation continuously tumbles the material, ensuring every particle is exposed to the same heat and atmospheric conditions. This eliminates inconsistencies and dramatically improves the uniformity of the final product.
This constant mixing enhances heat transfer, leading to faster and more efficient processing compared to static treatment of bulk materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, tube furnaces have inherent limitations that are important to recognize.
Limited Sample Size and Geometry
The most obvious limitation is the cylindrical geometry. Tube furnaces are not suitable for large, flat, or awkwardly shaped objects that cannot fit within the process tube's diameter.
Inherent Temperature Gradients
While the central zone is highly uniform, a temperature gradient always exists toward the cooler ends of the tube. This must be accounted for when processing very long samples or when absolute temperature uniformity is required across the entire sample length.
Added Complexity in Rotary Systems
The seals and rotation mechanism of a rotary tube furnace introduce mechanical complexity. These components require more maintenance than a simple static tube furnace to ensure the atmospheric seal remains intact.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the appropriate furnace depends entirely on your material and processing goals.
- If your primary focus is precise atmospheric treatment of static samples: A standard, single-zone tube furnace is your most reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating of powders, granules, or small parts: A rotary tube furnace is essential to ensure consistent, high-quality results through dynamic mixing.
- If your primary focus is scalability and continuous production: Both types support this, but rotary furnaces excel in continuous-feed applications where bulk material uniformity is critical.
By understanding these core principles and trade-offs, you can select the right furnace to transform your material processing from an art into a repeatable science.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Precise Environmental Control | Enables stable, isolated atmospheres with vacuum or specific gases for repeatable processes. |
| High Thermal Efficiency | Concentrates heat for lower power consumption and cost-effectiveness. |
| Operational Simplicity | Features a mature design that is easy to operate, maintain, and configure. |
| Scalability | Supports continuous production and can be combined for higher throughput. |
| Uniform Heating | Provides a thermally stable zone for consistent results, with rotary options for dynamic agitation. |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precision and efficiency? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in research, electronics, or advanced materials, we can help you achieve consistent, high-quality results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can transform your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















