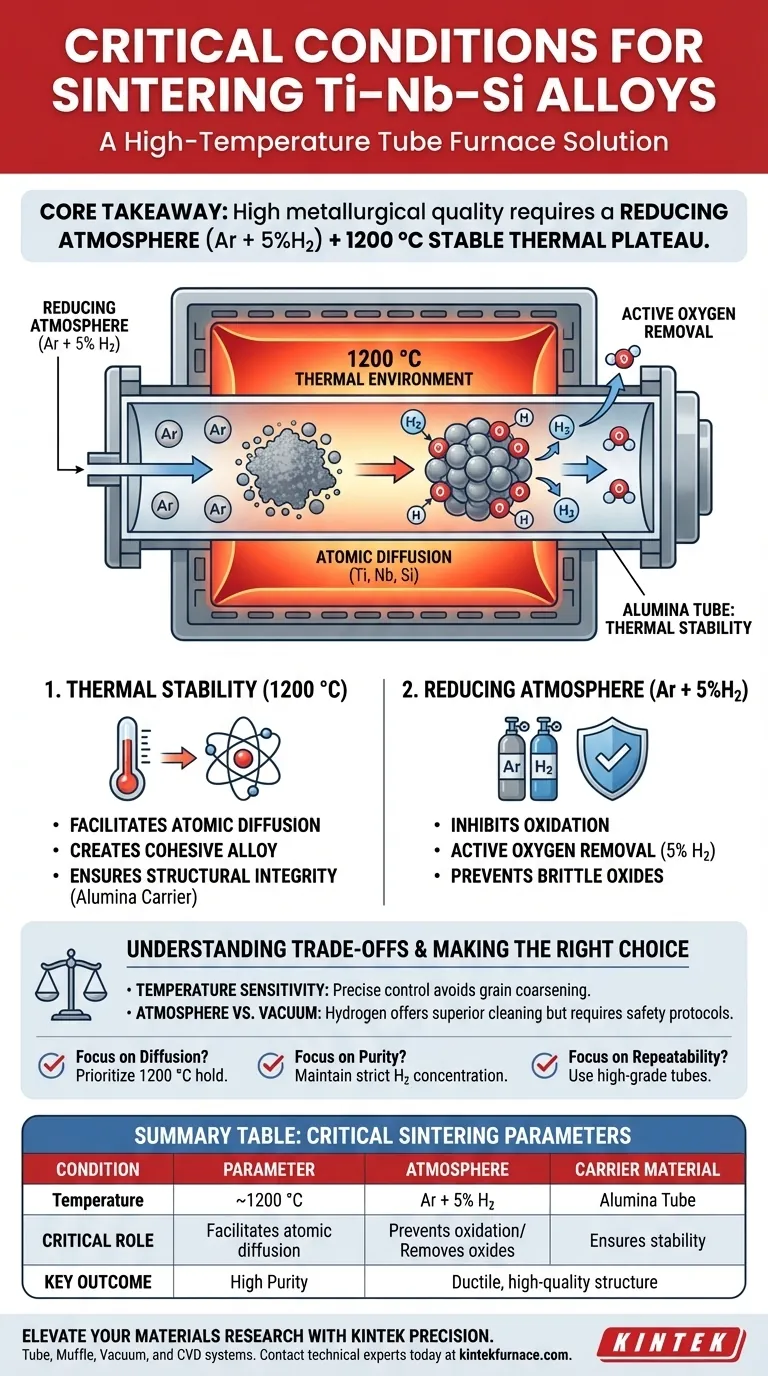
To successfully sinter Ti–Nb–Si alloys, a high-temperature tube furnace establishes two non-negotiable conditions: a stable thermal plateau of approximately 1200 °C and a specific reducing atmosphere.
This environment drives the necessary atomic diffusion for alloying while simultaneously preventing the oxidation that typically degrades titanium-based materials.
Core Takeaway Achieving high metallurgical quality in Ti–Nb–Si alloys requires more than just heat; it demands a reducing atmosphere (Ar + 5%H2). This specific gas mixture actively removes residual oxygen from powder surfaces while the 1200 °C thermal environment facilitates the diffusion bonding of the elemental components.
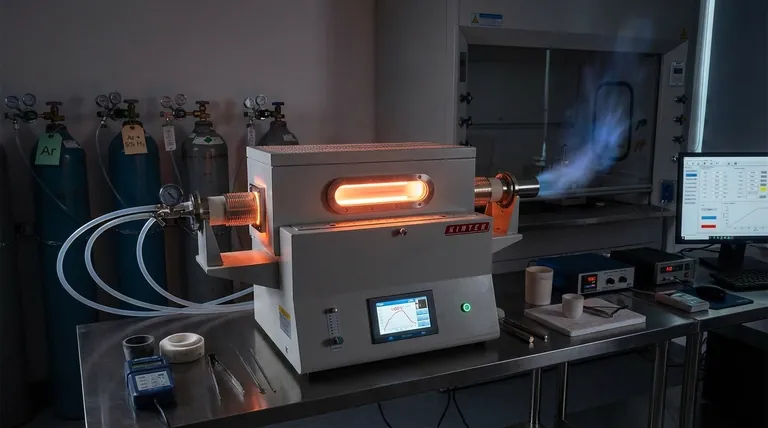

The Role of Thermal Stability
To transition from loose powder to a solid alloy, the furnace must provide a strictly controlled thermal environment.
Facilitating Atomic Diffusion
The primary function of the furnace is to maintain a temperature of typically 1200 °C.
At this specific thermal energy level, the atoms of titanium, niobium, and silicon gain sufficient mobility to migrate across particle boundaries.
This diffusion process is the mechanism that creates the actual alloy, turning distinct elemental powders into a cohesive, sintered material.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
The furnace utilizes ceramic alumina tubes to serve as the carrier for this reaction.
These tubes offer excellent thermal stability, withstanding the prolonged 1200 °C cycles without physical deformation.
This ensures the geometry of the heating zone remains constant, preventing hot spots or thermal gradients that could warp the sample.
The Necessity of a Reducing Atmosphere
Titanium and its alloys are highly sensitive to oxygen. Controlling the gas environment is as critical as controlling the temperature.
Inhibiting Oxidation
The furnace creates a protective barrier using a gas mixture of Argon (Ar) and Hydrogen (H2).
By flooding the chamber with this mixture, the furnace displaces atmospheric air.
This isolation prevents external oxygen from reacting with the titanium, which would otherwise form brittle oxides and ruin the mechanical properties of the alloy.
Active Oxygen Removal
The addition of 5% Hydrogen to the Argon carrier gas provides a "reducing" capability.
Unlike a pure vacuum or pure inert gas, this hydrogen component actively reacts with residual oxygen present on the powder surfaces.
This chemical scrubbing ensures the final sintered alloy possesses high metallurgical quality, free from the detrimental effects of oxide inclusions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tube furnace provides a robust environment, precise control is required to avoid common pitfalls.
Temperature Sensitivity
Maintaining the sample within the specific 1200 °C range is critical for controlling phase transformations.
Minor deviations in temperature can lead to excessive grain coarsening or unintended changes in phase content ratios.
If the furnace fails to hold the specific single-phase or two-phase region temperatures, the resulting microstructure may not meet design specifications.
Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
While some sintering processes (like hot pressing) rely on high vacuum to lower oxygen partial pressure, this specific tube furnace process relies on a flowing reducing gas.
The trade-off here is operational complexity: managing a flammable gas (hydrogen) requires stricter safety protocols than a static vacuum.
However, the chemical cleaning provided by the hydrogen often offers superior oxide removal for specific powder metallurgies compared to vacuum alone.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your sintering process, align your furnace parameters with your specific metallurgical objectives.
- If your primary focus is diffusion efficacy: Prioritize the stability of the 1200 °C hold time to ensure complete alloying of the Ti, Nb, and Si atoms.
- If your primary focus is purity and ductility: Ensure the 5% H2 concentration is strictly maintained to actively reduce surface oxides and prevent brittleness.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Use high-grade alumina tubes to prevent deformation and ensure a sealed, contaminant-free environment across multiple cycles.
Successful sintering of Ti–Nb–Si is less about reaching a high temperature and more about maintaining the precise chemical balance required to keep titanium metallic and ductile.
Summary Table:
| Condition | Parameter | Critical Role in Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | ~1200 °C | Facilitates atomic diffusion & bond formation |
| Atmosphere | Ar + 5% H2 | Prevents oxidation & actively removes surface oxides |
| Carrier Material | Alumina Tube | Ensures thermal stability & prevents contamination |
| Key Outcome | High Purity | Achieves ductile, high-quality metallurgical structure |
Elevate Your Materials Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect chemical balance and thermal stability for Ti–Nb–Si alloys requires equipment engineered for precision. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your specific lab requirements.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our furnaces ensure the exact reducing atmospheres and temperature uniformity needed for advanced powder metallurgy.
Ready to optimize your sintering results? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temp solution for your unique needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Douglas Daniel de Carvalho, Cristiano Binder. Effect of Nb and Si Content on Phase Stability, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Sintered Ti–Nb–Si Alloys. DOI: 10.3390/met15010034
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions does a vacuum tube furnace provide for sawdust biochar? Achieve Precise Pyrolysis Control
- Why are a tube furnace and nitrogen flow required? Master Carbon Microsphere Activation with Precision
- What are the benefits of a vertical tube furnace? Maximize Space and Purity in Your Lab
- How are tube furnaces used in the glass and ceramics industry? Unlock Precision Thermal Processing
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What reaction conditions does a vacuum/atmosphere tube furnace provide for Ti2AlN? Achieve Precise Synthesis Control
- What are the main uses of tube furnaces in laboratories? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis and Heat Treatment
- Why is a tube furnace with nitrogen flow necessary for BaFe2-xCoxFe16O27 ceramics? Master Iron Valence Engineering



















