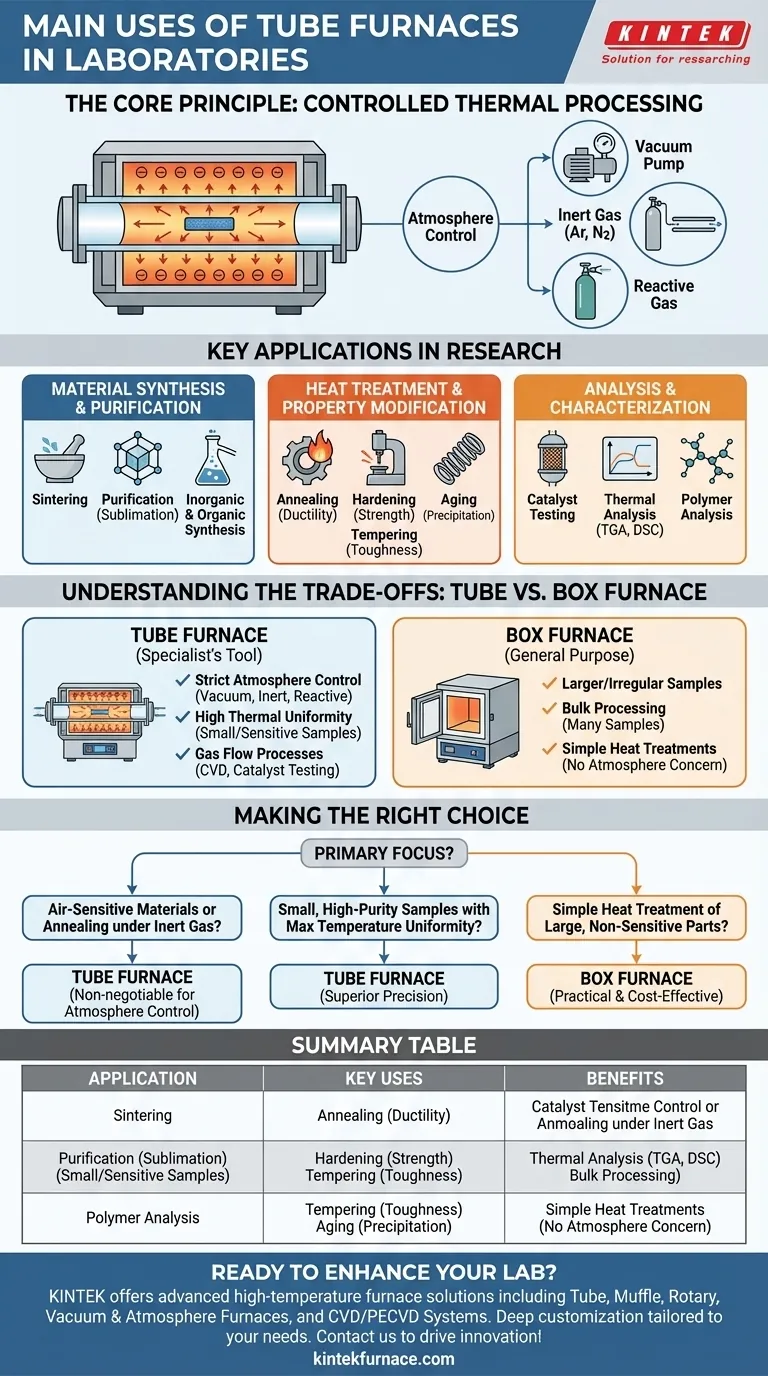
In a laboratory, a tube furnace is a high-temperature heating device used for a wide range of precise thermal processing applications. Its primary functions include synthesizing new materials, performing specific heat treatments like annealing and sintering, and conducting thermal analysis under tightly controlled conditions.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to create an isolated, uniform, and atmospherically controlled environment. This makes it an indispensable tool for experiments where precision and sample purity are paramount.

The Core Principle: Controlled Thermal Processing
A tube furnace's design is simple yet powerful. It uses heating elements to surround a ceramic or metallic tube, creating a highly uniform heated zone within the tube's central cavity.
Achieving Precise Temperature Uniformity
For repeatable scientific results, every part of a sample must experience the same temperature. A tube furnace excels at this, ensuring that heat is applied evenly across the entire sample, which is critical for processes like crystal growth and thermocouple calibration.
The Power of Atmosphere Control
This is the defining feature of a tube furnace. The tube can be sealed at both ends, allowing you to control the gaseous environment around your sample. You can create a vacuum, introduce an inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, or use a reactive gas to participate in a chemical synthesis.
This capability is impossible in an open-air or standard box furnace, making the tube furnace essential for air-sensitive materials.
Key Applications in Research
The combination of uniform heat and atmosphere control unlocks a vast number of applications, primarily in materials science, chemistry, and engineering.
Material Synthesis and Purification
Tube furnaces are workhorses for creating and refining compounds. This includes sintering, a process of forming a solid mass of material by heat without melting it, which is vital in ceramics and metallurgy.
They are also used for purifying compounds through processes like sublimation or for conducting inorganic and organic syntheses that require high temperatures.
Heat Treatment and Property Modification
Scientists use tube furnaces to intentionally alter the properties of a material. Key processes include:
- Annealing: Heating and then slowly cooling a material to reduce its hardness and increase its ductility.
- Hardening: Heating and then rapidly cooling a material to increase its hardness.
- Tempering: A secondary, lower-temperature heating process to reduce the brittleness created during hardening.
- Aging: A low-temperature heat treatment that causes precipitation of particles within a material to increase its strength.
Analysis and Characterization
Beyond making and changing materials, tube furnaces are used for analysis. They are critical for catalyst testing, where a gas is passed over a heated catalyst to measure its performance.
They are also used for thermal analysis and polymer analysis, where a material's reaction to heat provides crucial data about its properties and composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Tube vs. Box Furnace
Choosing the right furnace depends entirely on your experimental needs. The primary alternative to a tube furnace is a box furnace, and their differences are critical.
When to Choose a Tube Furnace
A tube furnace is the correct choice when your experiment requires one or more of the following:
- Strict atmosphere control (vacuum, inert, or reactive gas).
- High thermal uniformity for small or sensitive samples.
- Processes involving gas flow, such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or catalyst testing.
When a Box Furnace May Be Better
A box furnace is generally more suitable for:
- Heating larger or irregularly shaped samples that won't fit in a tube.
- Bulk processing where many samples are heated simultaneously.
- Simple heat treatments like drying or basic hardening where atmosphere control is not a concern.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heating instrument is the first step toward a successful experiment. Use these guidelines to inform your decision.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing air-sensitive materials or annealing under an inert gas: A tube furnace is non-negotiable due to its atmosphere control.
- If your primary focus is processing small, high-purity samples with maximum temperature uniformity: A tube furnace offers superior precision for reproducible results.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment of large, non-sensitive parts: A box furnace is likely the more practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, the tube furnace is the specialist's tool for achieving precision and control in advanced thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Uses | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Sintering, purification, inorganic/organic synthesis | Controlled atmosphere, uniform heating for high purity |
| Heat Treatment | Annealing, hardening, tempering, aging | Precise temperature control to modify material properties |
| Analysis | Catalyst testing, thermal analysis, polymer analysis | Accurate data collection in controlled environments |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a precision tube furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials science, chemistry, or engineering, our solutions ensure superior performance and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your research and drive innovation in your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















