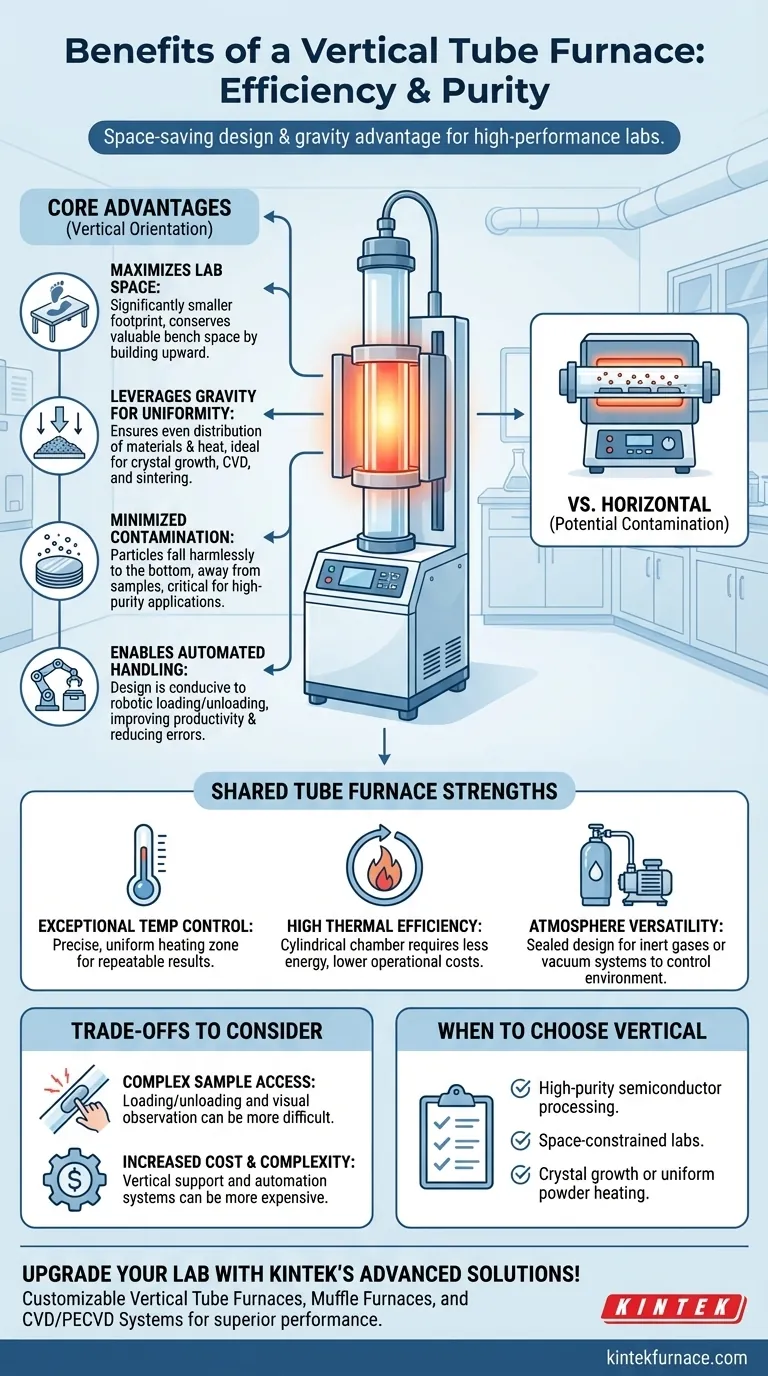
In essence, a vertical tube furnace offers two primary advantages over its horizontal counterpart: a significantly smaller footprint and the beneficial use of gravity. These attributes make it the ideal choice for space-constrained laboratories and for high-purity processes where uniform heating and minimal contamination are critical.
The decision between a vertical and horizontal tube furnace is not about which is "better," but which is correct for the specific task. Vertical furnaces excel in applications demanding high purity and spatial efficiency, leveraging gravity to improve results.

The Core Advantages of the Vertical Orientation
The defining feature of a vertical tube furnace is its orientation. This single design choice creates several distinct benefits that are not present in horizontal models.
Maximizing Laboratory Space
A vertical furnace has a much smaller physical footprint. By building upward instead of outward, it conserves valuable bench space, a critical factor in crowded labs or cleanroom environments.
Leveraging Gravity for Uniformity
Gravity becomes a useful tool in a vertical setup. For processes like crystal growth, chemical vapor deposition (CVD), or sintering powders, gravity ensures a more even distribution of materials and heat.
This pull helps prevent sample segregation and promotes a consistent thermal gradient along the length of the sample, which is difficult to achieve with materials resting horizontally.
Minimizing Particle Contamination
This is perhaps the most critical benefit for high-purity applications, such as semiconductor wafer processing. In a vertical furnace, any particles generated during the process fall harmlessly to the bottom, away from the sample wafers.
In a horizontal furnace, particles can settle directly on top of the samples, leading to defects and reduced yields.
Enabling Automated Handling
The vertical stack design is highly conducive to automation. Robotic systems can more easily load and unload "boats" or cassettes of wafers and other samples from the top or bottom of the furnace, improving productivity and reducing manual handling errors.
Shared Strengths of All Tube Furnaces
Vertical furnaces are a specialized type of tube furnace, and as such, they inherit the foundational benefits common to all tube furnace designs.
Exceptional Temperature Control
Tube furnaces are known for their ability to create a highly uniform and precisely controlled temperature zone in the center of the tube. The enclosed chamber design allows for stable, consistent heating that is essential for repeatable scientific experiments and manufacturing.
High Thermal Efficiency
The cylindrical heating chamber is inherently efficient. It requires less energy to achieve and maintain high temperatures compared to larger, box-style furnaces, leading to lower operational costs.
Atmosphere Versatility
The sealed nature of the tube makes it simple to control the internal atmosphere. These furnaces can easily be configured for use with inert gases like argon or nitrogen, or they can be attached to a vacuum system to remove atmospheric contaminants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No design is perfect for every situation. A vertical furnace introduces certain considerations that may make a horizontal model a better choice for some applications.
Sample Handling and Access
Loading and unloading a vertical furnace can be more complex than a simple horizontal tube. It often requires specialized sample holders or elevators, and visual observation of the sample during the process is more difficult. A horizontal furnace offers straightforward access and visibility.
Increased Cost and Complexity
The systems required for vertical support, and especially for automated loading, can make vertical furnaces more expensive and mechanically complex than their horizontal counterparts.
Suitability for the Task
For simple, general-purpose heating, annealing, or drying where particle contamination is not a concern and gravity offers no benefit, the simplicity and lower cost of a horizontal furnace often make it the more practical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace requires matching its core strengths to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is high-purity semiconductor processing: A vertical furnace is the superior choice due to its ability to minimize particle contamination.
- If your primary focus is working in a space-constrained lab: The smaller footprint of a vertical furnace makes it the most practical solution.
- If your primary focus is crystal growth or uniform powder heating: The gravity-assisted uniformity of a vertical furnace will yield more consistent and reliable results.
- If your primary focus is simple sample heating with easy access: A less complex and more accessible horizontal furnace is often the most efficient option.
By understanding how the furnace's orientation directly impacts your process, you can confidently select the right tool for your work.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Small Footprint | Saves bench space by building upward, ideal for crowded labs. |
| Gravity-Assisted Uniformity | Ensures even material distribution and consistent heating for processes like CVD. |
| Minimized Contamination | Particles fall away from samples, crucial for semiconductor and high-purity work. |
| Automated Handling | Vertical design supports easy robotic loading/unloading, boosting productivity. |
| Exceptional Temperature Control | Provides uniform, precise heating in a sealed tube for repeatable results. |
| Atmosphere Versatility | Compatible with inert gases or vacuum systems to control internal environment. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Vertical Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're in semiconductor processing, materials research, or any high-purity application, our furnaces deliver superior performance, space efficiency, and contamination control. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















