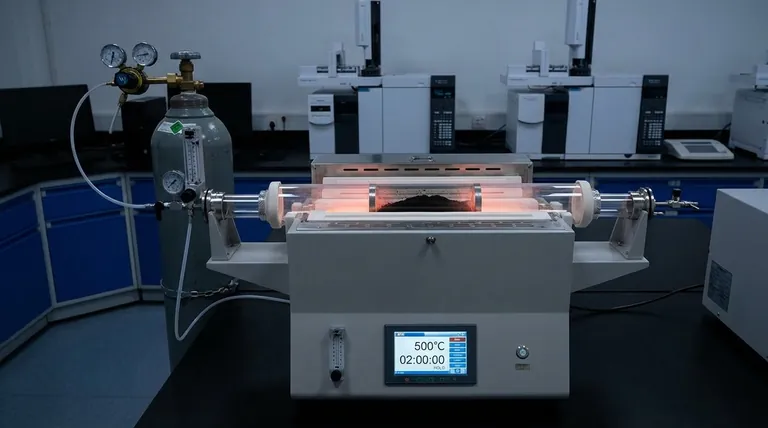
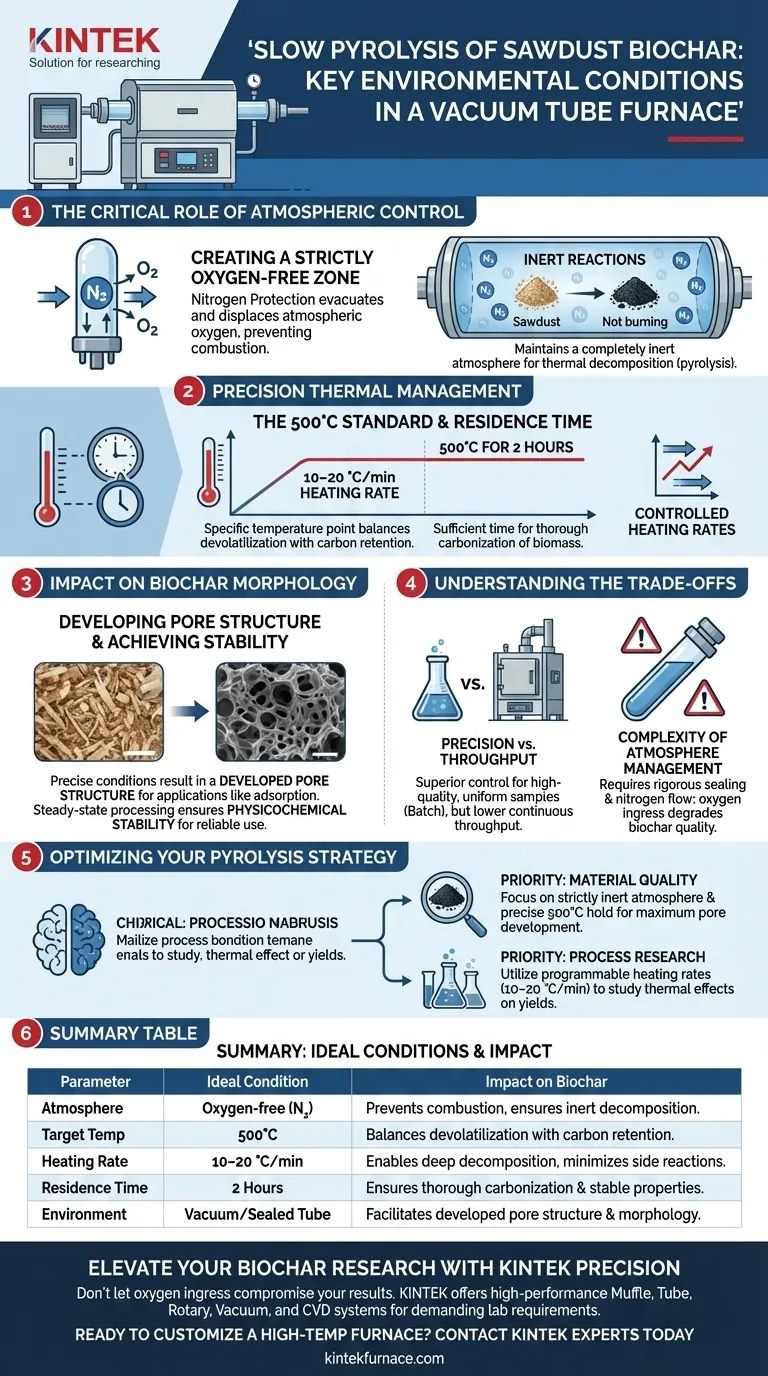
A vacuum tube furnace provides a strictly oxygen-free environment and a highly precise thermal profile. By utilizing nitrogen protection to displace air and adhering to specific temperature control curves—most notably maintaining 500°C for 2 hours—this equipment ensures the thorough carbonization of sawdust without the risk of combustion.
Core Takeaway The vacuum tube furnace is defined by its ability to isolate the biomass from oxidation while applying exacting thermal stress. This combination of a controlled inert atmosphere and regulated heating rates is the determining factor in producing biochar with a developed pore structure and stable physicochemical properties.

The Critical Role of Atmospheric Control
Creating a Strictly Oxygen-Free Zone
The primary function of the vacuum tube furnace in this context is to prevent combustion. Through the use of nitrogen protection, the furnace evacuates or displaces atmospheric oxygen from the reaction tube.
Ensuring Inert Reactions
By introducing high-purity nitrogen via a gas circuit control system, the furnace maintains a completely inert atmosphere. This ensures that the sawdust undergoes thermal decomposition (pyrolysis) rather than burning, which is essential for maximizing solid biochar yield.
Precision Thermal Management
The 500°C Standard
To achieve optimal sawdust pyrolysis, the furnace must maintain a specific target temperature. The primary standard for this process is 500°C, a temperature point that balances devolatilization with carbon retention.
Residence Time and Carbonization
Reaching the target temperature is not enough; the duration of heat exposure is equally critical. The furnace is programmed to hold this temperature for 2 hours, allowing sufficient time for the thorough carbonization of the biomass material.
Controlled Heating Rates
The quality of the final product relies on how the temperature rises, not just where it ends. The furnace allows for the flexible adjustment of heating rates (typically 10–20 °C/min), which enables deep thermal decomposition and minimizes undesirable side reactions.
Impact on Biochar Morphology
Developing Pore Structure
The specific environmental conditions provided by the vacuum tube furnace directly influence the microscopic architecture of the biochar. The precise combination of temperature and inert gas flow results in a developed pore structure, which is critical for applications like adsorption or soil amendment.
Achieving Physicochemical Stability
Because the heating environment is uniform and the atmosphere is stable, the resulting biochar exhibits consistent properties. This "steady-state" processing ensures the physicochemical stability of the final biochar base, making it reliable for further experimental or industrial use.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Precision vs. Throughput
While a vacuum tube furnace offers superior control over the reaction environment, it is generally a batch-processing tool. It excels at producing high-quality, uniform samples for research or small-scale production but may lack the continuous throughput capabilities of larger industrial rotary kilns.
Complexity of Atmosphere Management
Achieving a "strictly oxygen-free" environment requires rigorous sealing and gas management. If the nitrogen flow is interrupted or the tube seal is compromised, oxygen ingress will immediately degrade the biochar quality, turning the process from pyrolysis into partial combustion.
Optimizing Your Pyrolysis Strategy
To select the right approach for your sawdust biochar project, consider your end goals:
- If your primary focus is material quality: Prioritize the vacuum tube furnace's ability to maintain a strictly inert atmosphere and precise 500°C hold times to maximize pore development.
- If your primary focus is process research: Utilize the programmable heating rates (10–20 °C/min) to study how different thermal curves affect bio-oil vs. biochar yields.
By rigorously controlling the absence of oxygen and the precise delivery of heat, you transform raw sawdust from simple waste into a sophisticated, high-value carbon material.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Ideal Condition | Impact on Biochar |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Oxygen-free (Nitrogen protection) | Prevents combustion; ensures inert thermal decomposition. |
| Target Temp | 500°C | Balances devolatilization with maximum carbon retention. |
| Heating Rate | 10–20 °C/min | Enables deep decomposition and minimizes side reactions. |
| Residence Time | 2 Hours | Ensures thorough carbonization and stable chemical properties. |
| Environment | Vacuum/Sealed Tube | Facilitates developed pore structure and high-quality morphology. |
Elevate Your Biochar Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let oxygen ingress or uneven heating compromise your carbonization results. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed for the most demanding lab requirements. Whether you are optimizing sawdust pyrolysis or developing advanced carbon materials, our furnaces provide the strictly controlled inert atmospheres and precise thermal profiles you need.
Ready to customize a high-temp furnace for your unique lab needs?
Visual Guide
References
- Xin Pan, Sabry M. Shaheen. Functionalization of sawdust biochar using Mg-Fe-LDH and sodium dodecyl sulfonate enhanced its stability and immobilization capacity for Cd and Pb in contaminated water and soil. DOI: 10.1007/s42773-024-00401-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of high-purity quartz sealed tubes in CVT for BiRe2O6 growth? Achieve Pure Crystal Growth
- What are the key factors to consider when choosing a vertical tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance for Your Lab
- What are the primary applications of lab tubular furnaces in material science and engineering? Precision Heat for Advanced Materials
- What are the functions of a quartz tube fixed-bed reactor? Ensure Precision in Catalyst Evaluation
- How is a laboratory tube furnace applied in synthesis and processing? Unlock Precise Material Control
- What safety features are included in a High Temperature Tube Furnace? Ensure Safe Operation in Extreme Heat
- What are the applications of a laboratory tube furnace in physics research? Unlock Precise High-Temperature Experiments
- How does a drop tube work? A Key Tool for Microgravity Materials Research



















