To select the right vertical tube furnace, you must move beyond a simple feature list and analyze four primary factors: the maximum operating temperature, the required atmospheric conditions (vacuum or gas), the number of heating zones, and the compatibility of the process tube material with your work. These elements are not independent; they are deeply interconnected and define the furnace's true capabilities.
Choosing a vertical tube furnace is not about finding the one with the highest specifications. It is about precisely matching the furnace's thermal, atmospheric, and physical characteristics to the specific requirements of your scientific process or manufacturing goal.
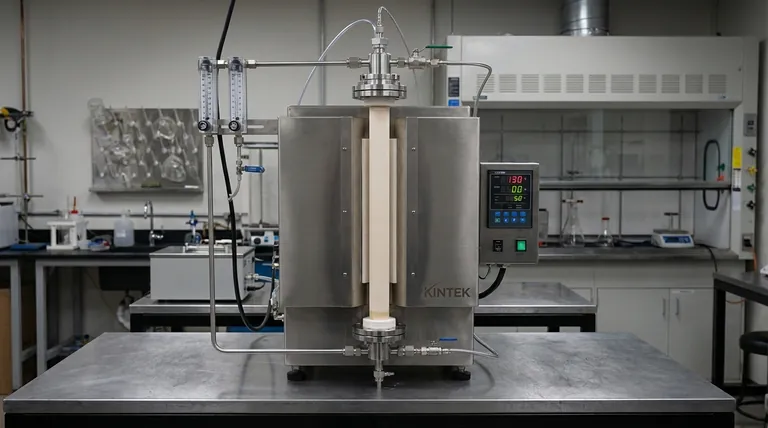

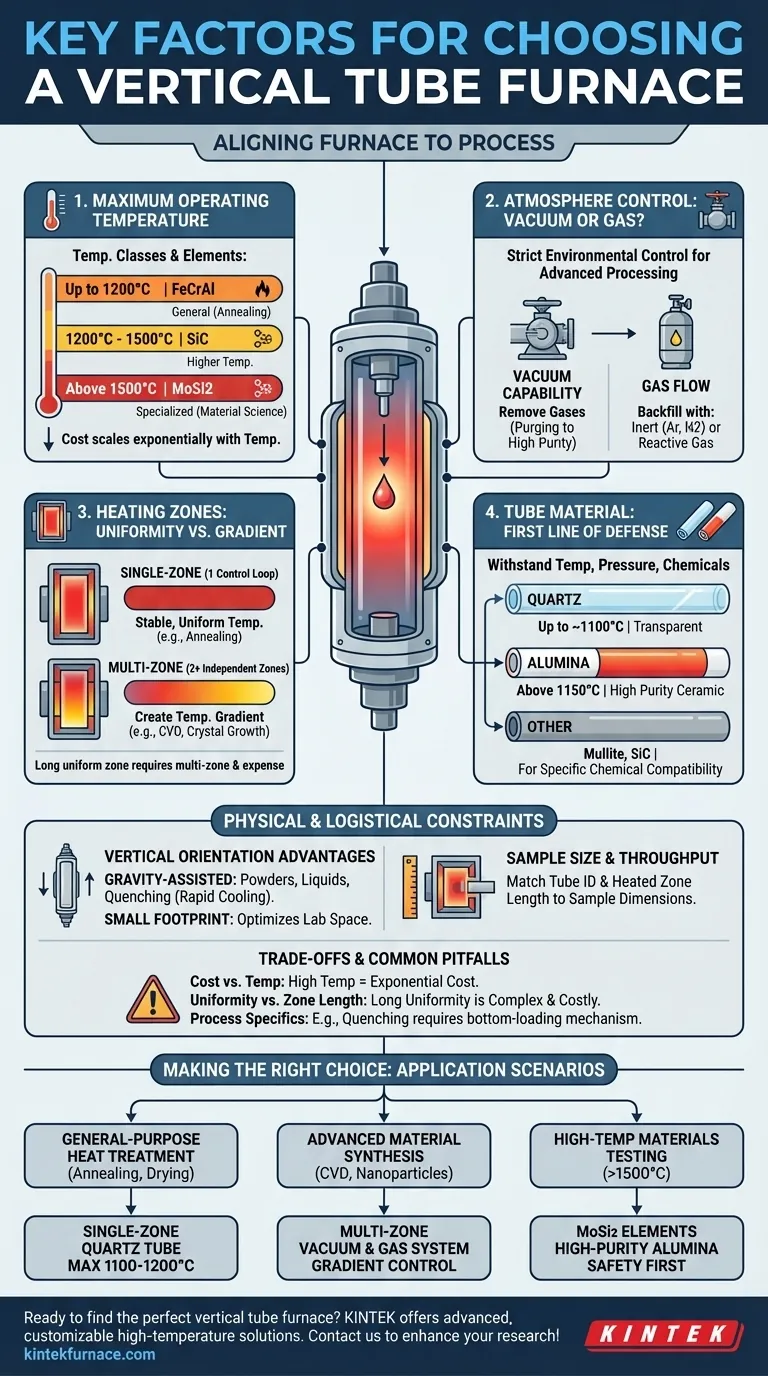
The Core Decision Framework: Aligning Furnace to Process
The ideal furnace is an extension of your experimental design. Before evaluating models, you must first define the non-negotiable parameters of the process you intend to run.
Defining Your Thermal Profile
The most fundamental characteristic of your process is its thermal requirement. This dictates the furnace's core construction.
Maximum Operating Temperature Your required temperature is the first and most critical filter. Furnaces are typically categorized into temperature classes based on their heating elements.
- Up to 1200°C: Often use iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) alloy elements. These are robust and cost-effective for general-purpose applications like annealing and calcination.
- 1200°C to 1500°C: Typically require silicon carbide (SiC) heating elements.
- Above 1500°C: Rely on molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) elements, which can reach 1700°C or even 1800°C for specialized high-temperature material science.
Heating Zones: Uniformity vs. Gradient The configuration of the heating elements determines the temperature profile along the tube's length.
- Single-Zone: A single control loop manages one heating element or a set of elements. This is ideal for processes requiring a stable, uniform temperature across the sample, such as annealing.
- Multi-Zone: Two or more independent heating zones are controlled separately. This is essential for creating a specific temperature gradient, a requirement for advanced processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) or certain types of crystal growth.
Controlling the Process Environment
What happens inside the furnace tube is just as important as the heat applied to the outside. The furnace must create and maintain the precise chemical environment your process demands.
Atmosphere Control: Vacuum or Gas?
Nearly all advanced material processing requires strict atmospheric control to prevent unwanted reactions, primarily oxidation.
- Vacuum Capability: A vacuum system removes atmospheric gases before a process begins. The required vacuum level can range from low vacuum (for simple purging) to high vacuum (for high-purity applications).
- Gas Flow: After evacuating the chamber, a process often requires backfilling with a specific gas. This can be an inert gas (like Argon or Nitrogen) to prevent reactions or a reactive gas that is part of the chemical process itself.
Tube Material: Your First Line of Defense
The process tube contains your sample and atmosphere. Its material must be able to withstand the temperature, pressure, and chemical environment of your work.
- Quartz: An excellent and common choice for temperatures up to approximately 1100°C. Its transparency is a major advantage for observing the process.
- Alumina: A high-purity ceramic required for temperatures above 1150°C. It is opaque but offers excellent thermal and chemical stability at extreme temperatures.
- Other Materials: For specific chemical compatibility, materials like Mullite or Silicon Carbide may be necessary.
Understanding the Physical & Logistical Constraints
The vertical furnace's design offers unique advantages and introduces specific physical considerations you must account for.
Why a Vertical Orientation?
The primary reason to choose a vertical setup is that it leverages gravity and optimizes space.
- Gravity-Assisted Processes: This orientation is ideal for processes involving powders, liquids, or dropping a sample, such as in quenching tests (rapid cooling). Gravity ensures uniform packing for powders and helps in certain crystal growth methods.
- Small Footprint: Vertical furnaces occupy significantly less floor space than their horizontal counterparts, a critical benefit in crowded labs.
Sample Size and Throughput
The physical dimensions of your sample dictate the required size of the furnace tube. Consider both the inner diameter of the tube and the length of the uniform heated zone to ensure your entire sample receives the correct thermal treatment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
An informed decision requires acknowledging the compromises inherent in any furnace design.
The Temperature vs. Cost Curve
Be aware that cost scales exponentially with temperature. A 1700°C furnace is significantly more expensive than a 1200°C model due to the higher cost of MoSi2 elements, high-purity alumina insulation, and more complex power controls.
Uniformity vs. Zone Length
Achieving a long, highly uniform heated zone is a significant engineering challenge. A longer uniform zone often requires a more expensive multi-zone configuration to compensate for natural heat loss at the ends of the tube.
Forgetting Process-Specific Needs
A standard vertical furnace may not be sufficient for specialized applications. For example, a quenching test requires a furnace with a bottom-loading mechanism that can rapidly drop the heated sample into a liquid bath below. Always map your entire workflow to the furnace's capabilities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your final selection.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treatment (annealing, drying, calcination): A single-zone furnace with a quartz tube and a maximum temperature of 1100-1200°C is often the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced material synthesis (CVD, nanoparticle growth): Prioritize a multi-zone furnace for gradient control and a high-quality vacuum and gas delivery system for precise atmosphere management.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature materials testing (>1500°C): Your decision will be dictated by furnaces built with MoSi2 elements and high-purity alumina tubes, with safety as a paramount concern.
Ultimately, a methodical evaluation of your process needs will ensure the vertical tube furnace you choose becomes a reliable tool for discovery and innovation.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | Determines heating element type (e.g., FeCrAl up to 1200°C, SiC up to 1500°C, MoSi2 above 1500°C) |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum levels and gas flow (inert or reactive) for process environment |
| Heating Zones | Single-zone for uniformity, multi-zone for gradients (e.g., CVD, crystal growth) |
| Tube Material | Quartz (up to 1100°C), alumina (above 1150°C), or others for chemical compatibility |
| Orientation & Size | Vertical for gravity-assisted processes and space savings; consider tube diameter and heated zone length |
Ready to find the perfect vertical tube furnace for your lab? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your research with tailored furnace solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















